Abstract
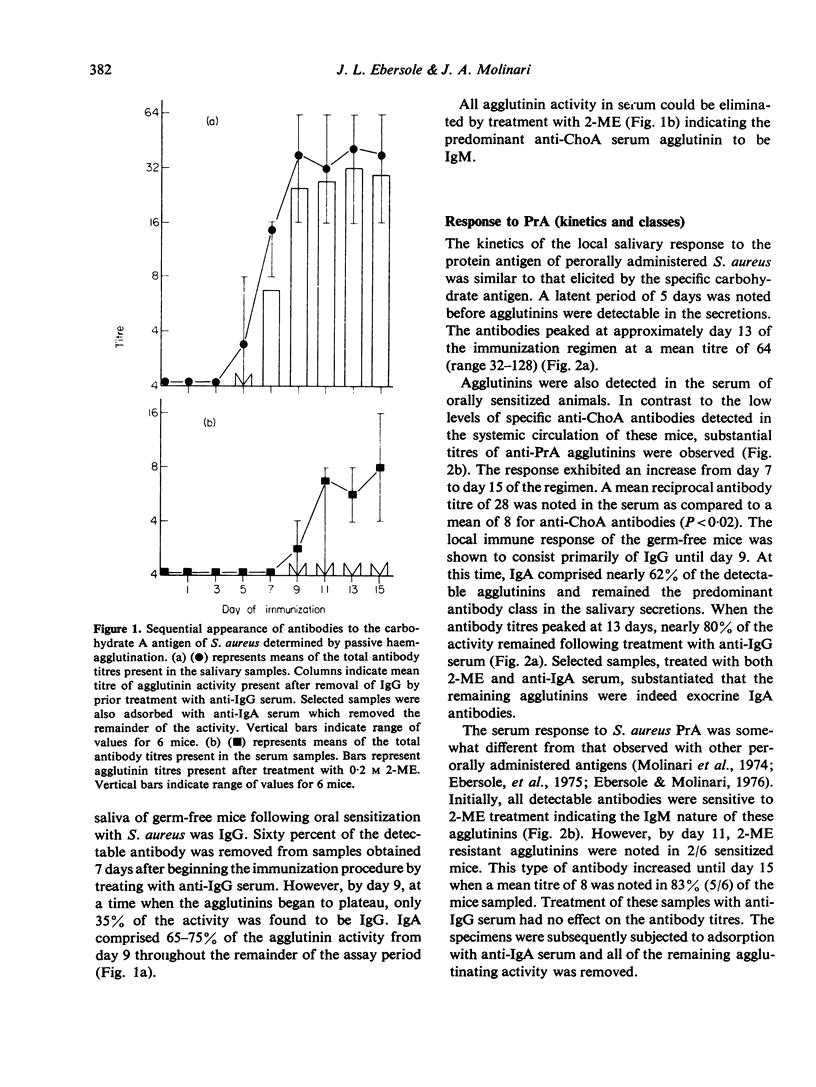
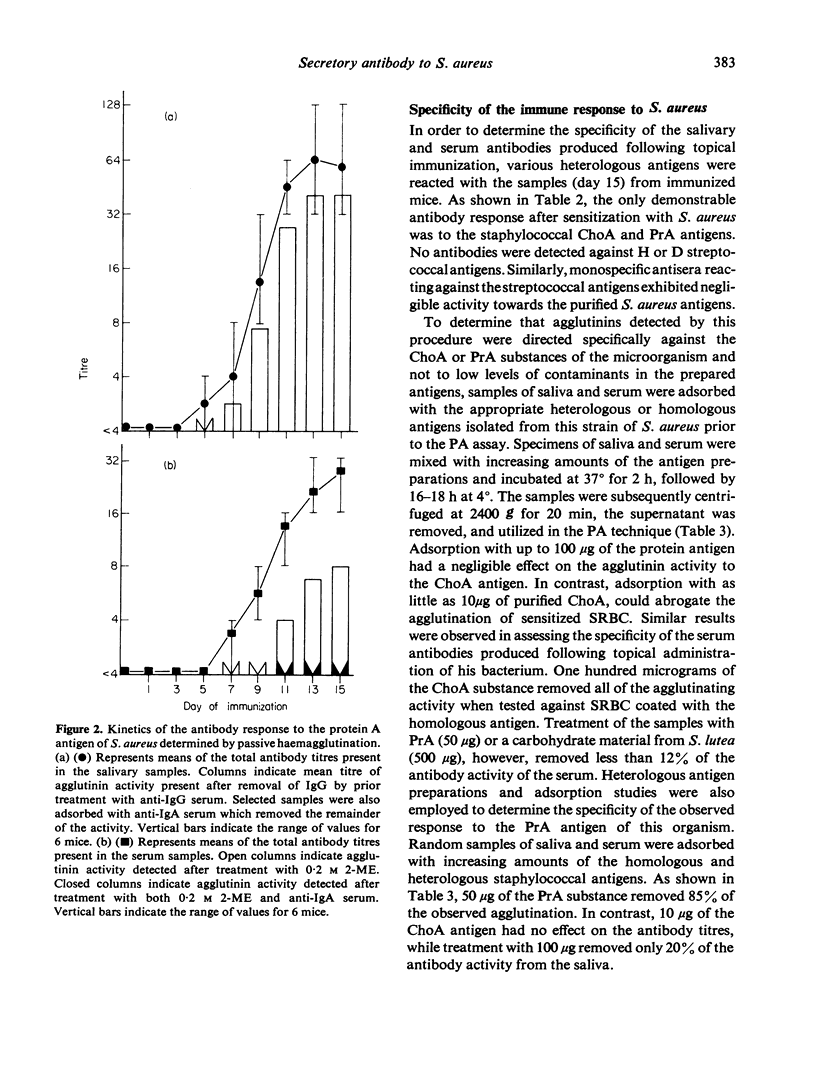
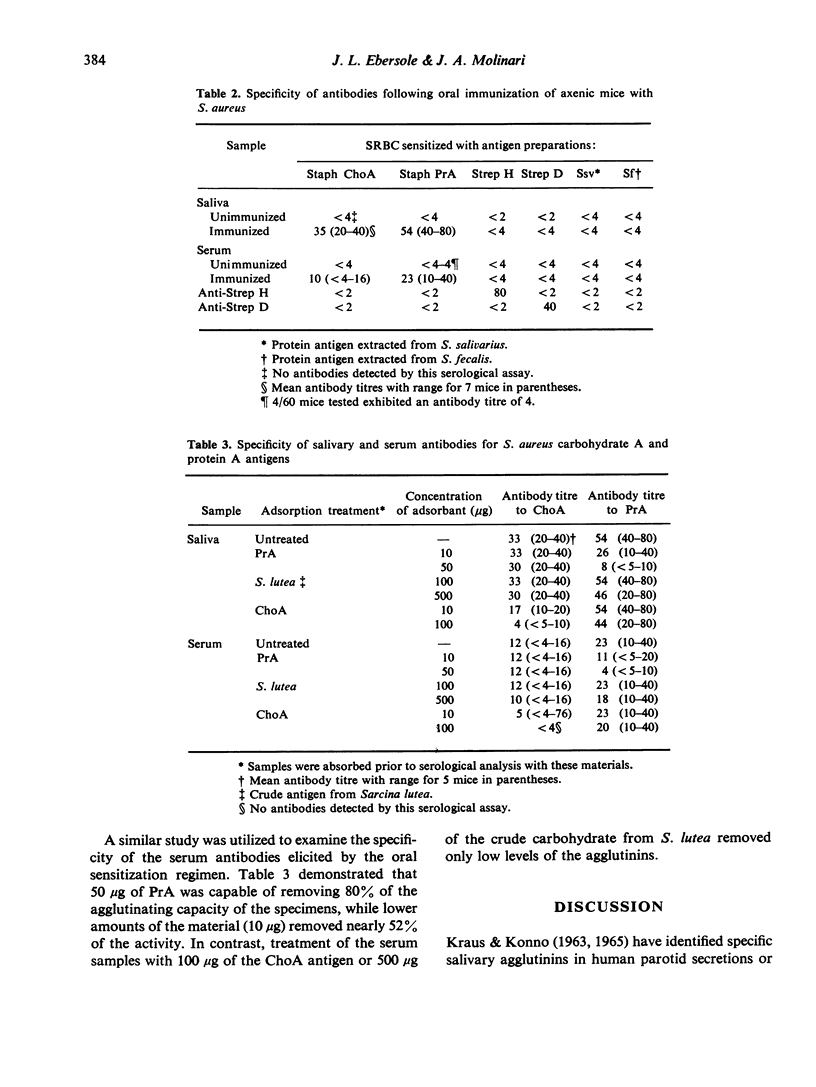
Topical oral immunization of axenic mice with non-replicating Staphylococcus aureus resulted in the production of both serum and salivary agglutinins. A latent period of approximately 5 days was noted before salivary antibodies were detected against both a carbohydrate (ChoA) and a protein (PrA) antigen isolated from this micro-organism. The local response to ChoA exhibited a linear increase until day 9 when the reciprocal titres reached a plateau [32 (16--64)]. Salivary antibodies to PrA peaked by day 13 at a mean reciprocal titre of 60 (32--128). The agglutinin response in saliva was found to be initially IgG; however, by day 9 of a 14-day-immunization regimen, IgA became the predominant class of exocrine anti-S. aureus antibodies. The serum agglutinin response followed that found in saliva by approximately 2--4 days. By day 14, all sera (6/6) contained PrA agglutinins, while 4/6 sera agglutinated sheep erythrocytes coated with ChoA. Serum antibodies to ChoA were exclusively IgM, in contrast to IgM and IgA agglutinins elicited by PrA. Absorption studies provided evidence of a specific local and systemic immune response to both ChoA and PrA antigens of perorally administered S. aureus.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste J., Lespinats G., Salomon J. Serum and secretory IgA in axenic and holoxenic mice. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1656–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN J. O., NEWTON W. L., CHERRY W. B., UPDYKE E. L. NORMALLY OCCURRING STAPHYLOCOCCAL ANTIBODIES IN GERMFREE MICE. J Immunol. 1963 Mar;90:358–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. Minor salivary glands as a major source of secretory immunoglobin A in the human oral cavity. Science. 1975 Dec 19;190(4220):1206–1209. doi: 10.1126/science.1198107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H. D., Martin R. R., White A. Reactions of sera and nasal secretions with staphylococcal antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jun;73(6):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Molinari J. A., Platt D. Sequential appearance of salivary antibodies after oral immunization of axenic mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):353–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.353-359.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Molinari J. A. Specificity of secretory antibodies to bacterial immunogens. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):53–62. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.53-62.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenkranz N. J. Nasal rejection of experimentally inoculated Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for an immune reaction in man. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):509–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmings F. G., Evans R. T., Genco R. J. Antibody response in the parotid fluid and serum of Irus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) after local immunization with Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):281–292. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.281-292.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Nordström K. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus: the biological significance of its reaction with IgG. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):252–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from Staphylococcus aureus. 3. Reaction with rabbit gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUKENES G., ELLWOOD D. C., BADDILEY J., OEDING P. Serological cross-reactivity between polysaccharide A and teichoic acid of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 28;53:425–426. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90461-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUS F. W., KONNO J. Antibodies in saliva. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:311–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUS F. W., KONNO J. THE SALIVARY SECRETION OF ANTIBODY. Ala J Med Sci. 1965 Jan;2:15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenblat P. E., Rothberg R. M., Minden P., Farr R. S. Immune responses of human adults after oral and parenteral exposure to bovine serum albumin. J Allergy. 1968 Apr;41(4):226–235. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfkvist T. Further studies of a preparation of protein A (Jensen's antigen A) from Staphylococcus aureus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(3):240–253. doi: 10.1159/000229705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Arnold R. R., Bozzo L. Ingestion of Streptococcus mutans induces secretory immunoglobulin A and caries immunity. Science. 1976 Jun 18;192(4245):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.1273589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinari J. A., Ebersole J. L., Platt D. Investigation of secretory immunoglobulins in saliva from germfree mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1207–1212. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1207-1212.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton R. P., Stoop J. W., Ballieux R. E., Mul N. A. Pneumococcal antibodies in IgA of serum and external secretions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):201–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg R. M., Kraft S. C., Farr R. S. Similarities between rabbit antibodies produced following ingestion of bovine serum albumin and following parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):386–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirisinha S., Charupatana C. Antibodies to indigenous bacteria in human serum, secretions, and urine. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1471–1473. doi: 10.1139/m71-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Yurchision A. Formation of agglutinating and reaginic antibodies in rabbits following oral administration of soluble and particulate antigens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;35(6):579–590. doi: 10.1159/000230211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


