Abstract
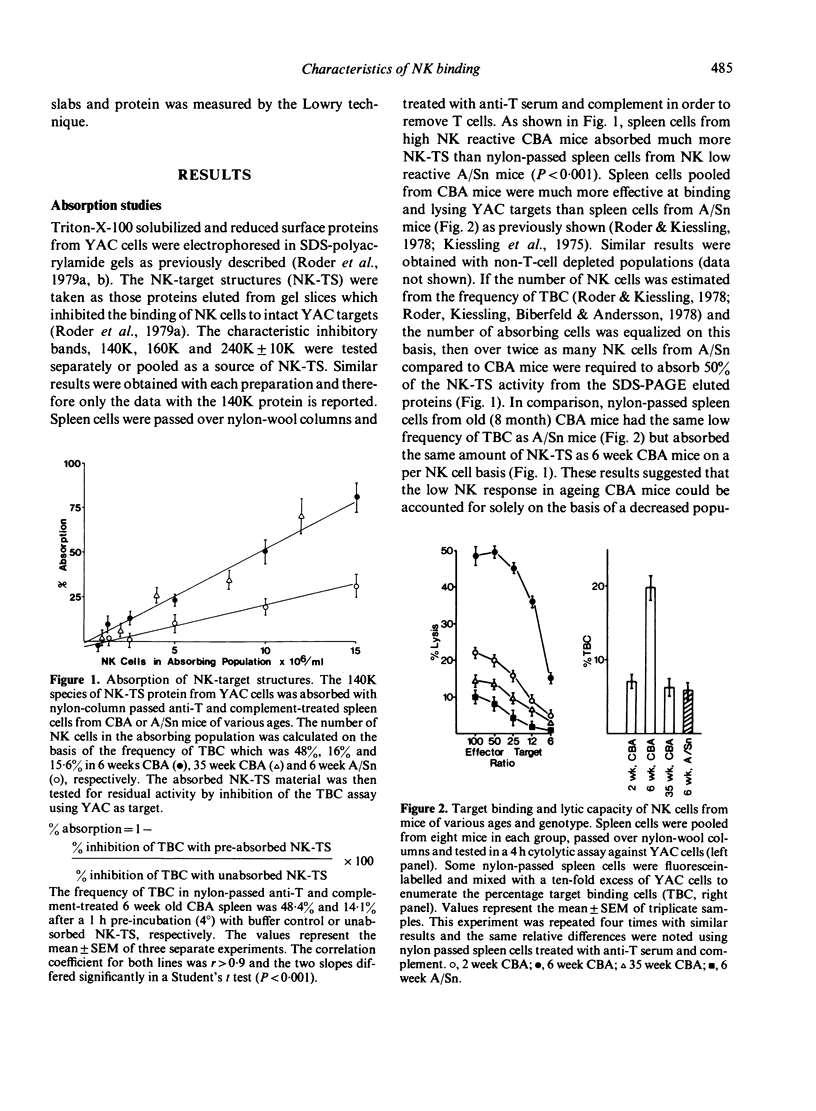
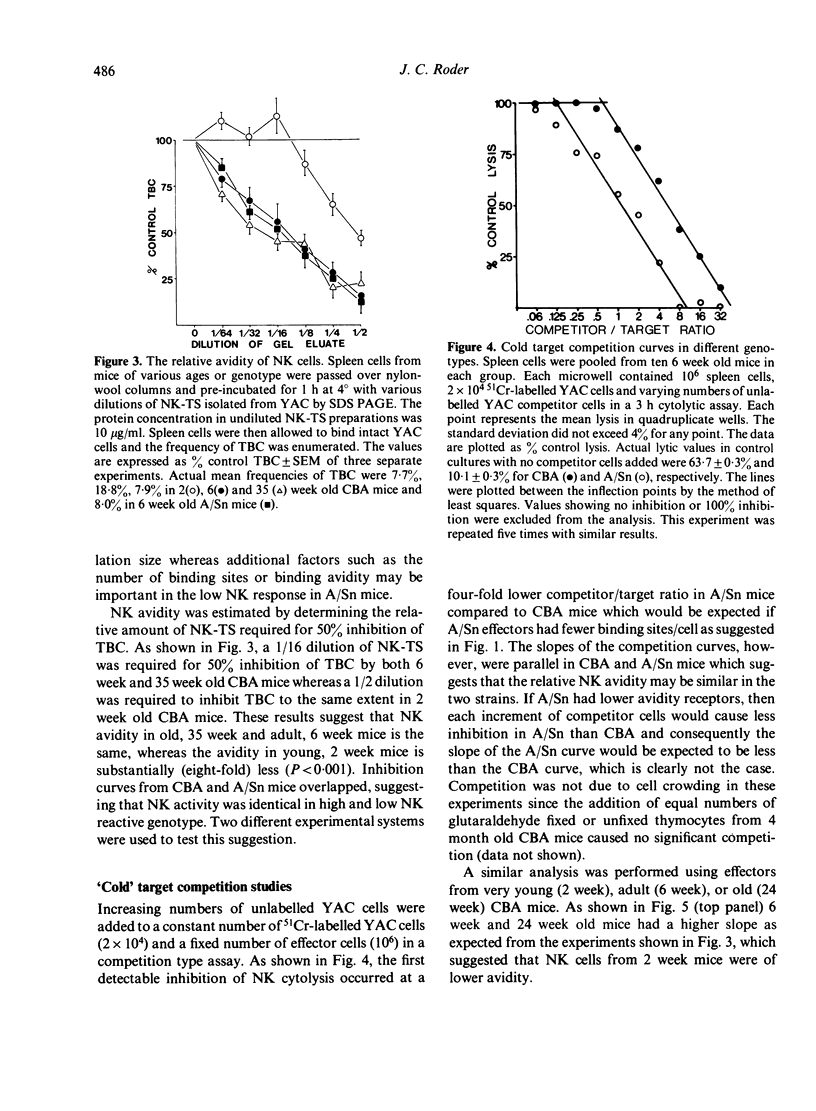
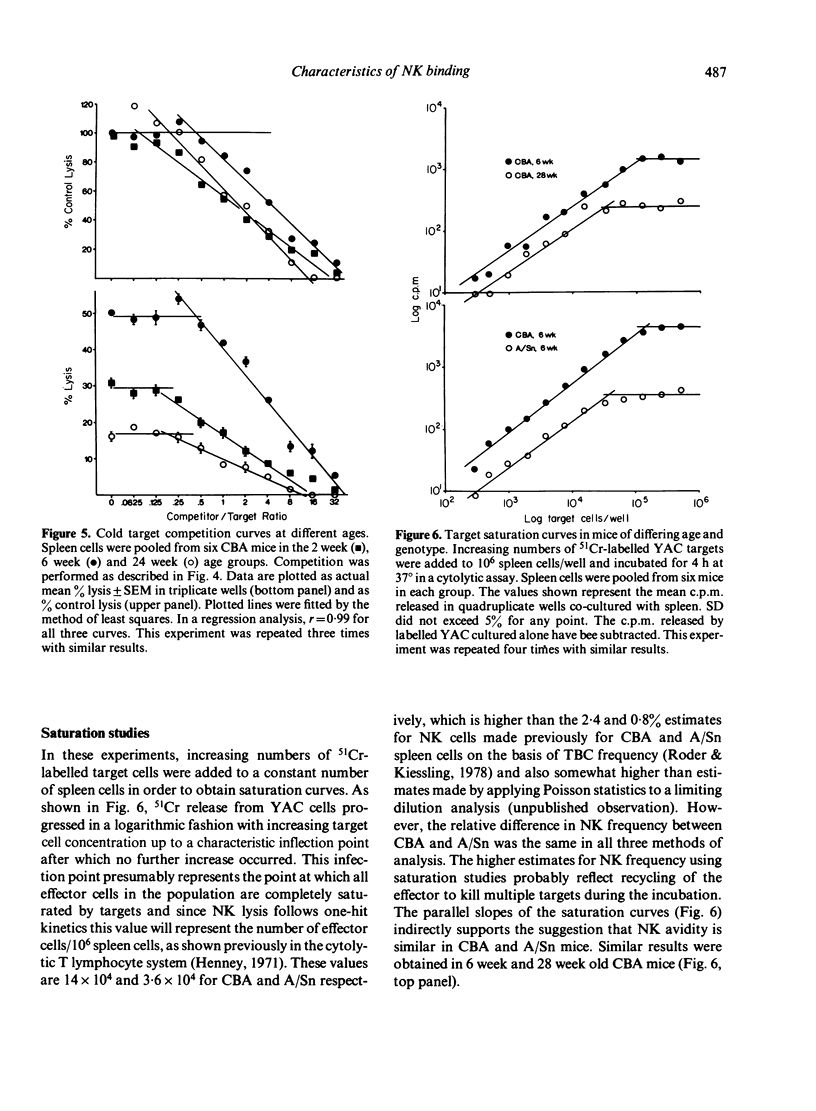
Four independent assays were used to compare target-cell binding by NK cells in different populations. First, detergent solubilized and reduced proteins from the surface of Moloney lymphoma cells (YAC) were electrophoresed in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. The glycoproteins recognized by NK cells (NK-TS) were eluted from the gels and used in semi-quantitative absorption studies or were used to inhibit the formation of target-effector conjugates as an estimate of relative avidity. These findings were supported by a comparative analysis of cold target competition curves and saturation studies in which 51Cr-labelled target cells were carefully titrated. The results suggest that NK cells 'mature' during ontogeny to higher avidity binding whereas the decline in NK function during senescence can solely be attributed to a decrease in population size. A comparison of high (CBA) and low (A/Sn) NK reactive strains revealed that in low responder (i) absolute NK frequency was decreased, (ii) relative NK-TS absorption per NK cells was low, and (iii) relative avidity of NK cells was identical to that in the high responder strain. These results suggest that the putative NK receptor to YAC may be of restricted heterogeneity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gidlund M., Orn A., Wigzell H., Senik A., Gresser I. Enhanced NK cell activity in mice injected with interferon and interferon inducers. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):759–761. doi: 10.1038/273759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Hansson M., Kiessling R., Wigzell H. Role of non-conventional natural killer cells in resistance against syngeneic tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):609–611. doi: 10.1038/270609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. Quantitation of the cell-mediated immune response. I. The number of cytolytically active mouse lymphoid cells induced by immunization with allogeneic mastocytoma cells. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1558–1566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Wigzell H. An analysis of the murine NK cell as to structure, function and biological relevance. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:165–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Ahrlund-Richter L., Jondal M. Target-effector interaction in the human and murine natural killer system: specificity and xenogeneic reactivity of the solubilized natural killer-target structure complex and its loss in a somatic cell hybrid. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):471–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R., Biberfeld P., Andersson B. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK) cell system. II. The isolation of NK cells and studies on the mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2509–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R. Target--effector interaction in the natural killer cell system. I. Covariance and genetic control of cytolytic and target-cell-binding subpopulations in the mouse. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(2):135–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Rosén A., Fenyö E. M., Troy F. A. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer cell system: isolation of target structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1405–1409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


