Abstract
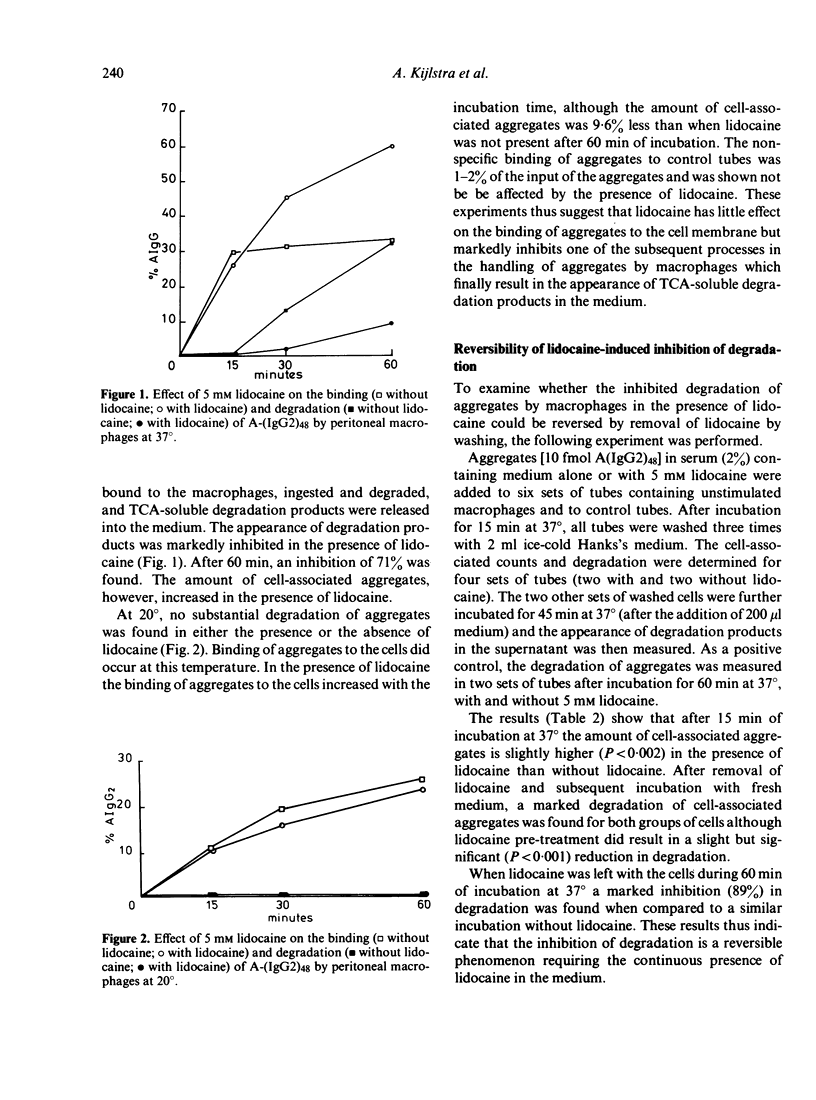
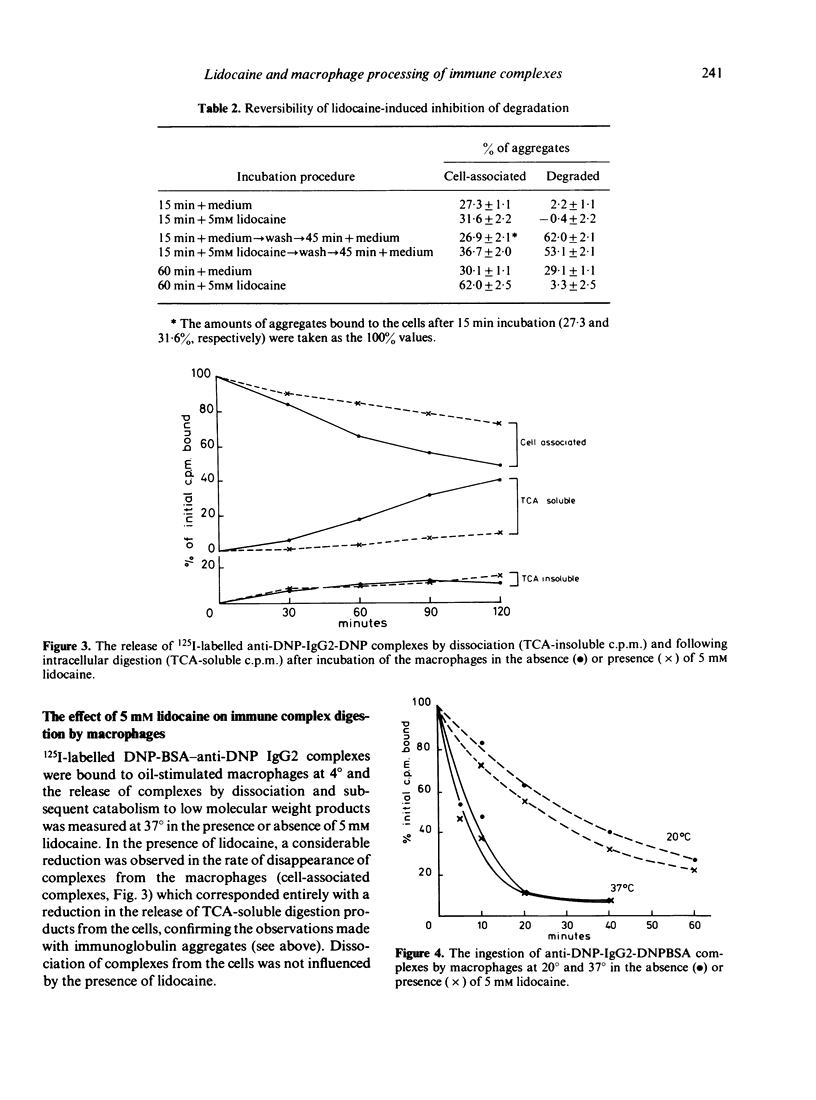
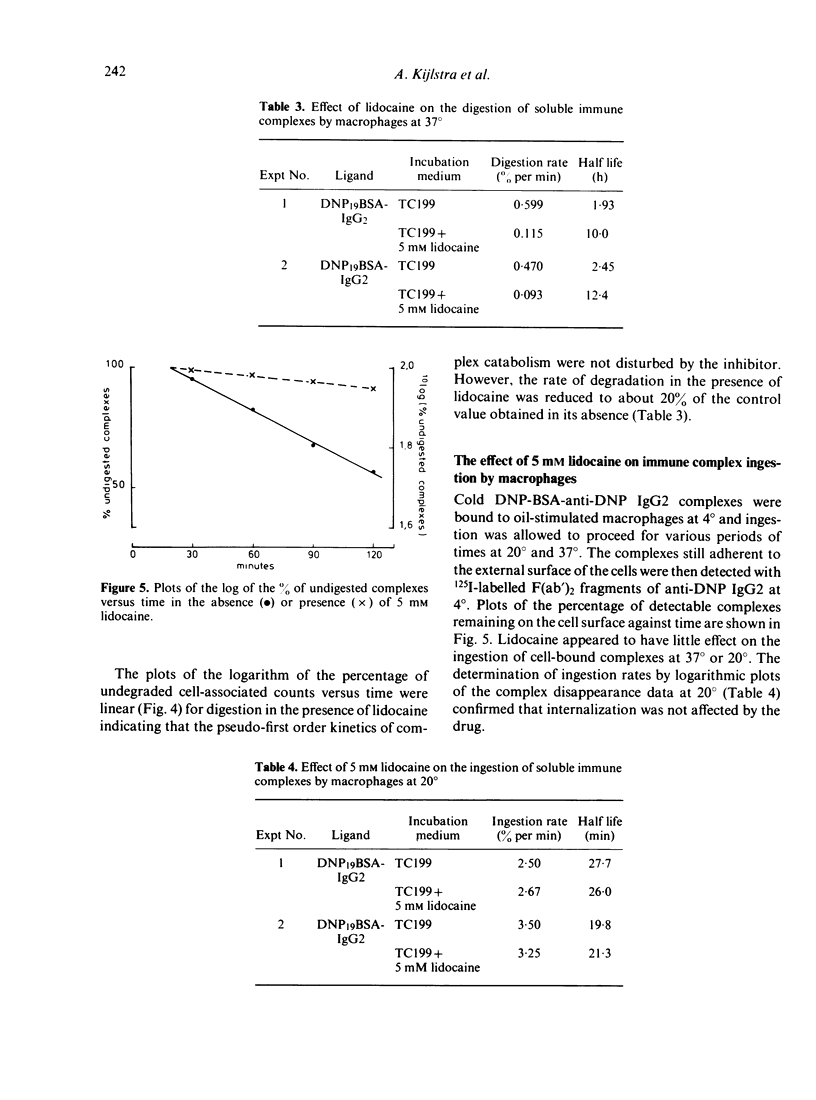
In a search for new techniques which would specifically identify the various steps of the handling of immune complexes by macrophages the local anaesthetic, lidocaine, was investigated. Lidocaine was shown to inhibit selectively the digestion of immune complexes and immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages whereas it had little effect on the binding or ingestion steps. Due to the reversible inhibitory effect of lidocaine, this drug may be used in future studies to assess the role of extracellular stimuli on the fate of intracellular immune complexes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cullen B. F., Haschke R. H. Local anesthetic inhibition of phagocytosis and metabolism of human leukocytes. Anesthesiology. 1974 Feb;40(2):142–146. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197402000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Lind S., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Influence of local anesthetics upon human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function in vitro. Reduction of lysosomal enzyme release and superoxide anion production. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):483–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Enhanced degradation of soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages in the presence of complement. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):673–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A. Association and dissociation of aggregated IgG from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1368–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G., Alexander M. D. Cytophilic antibodies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;88:25–104. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67331-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G., Cohen S. Cytophilic activity of IgG2 from sera of unimmunized guinea-pigs. Immunology. 1974 Oct;27(4):577–587. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G., Melamed M. D., Cohen S. The products from papain and pepsin hydrolyses of guinea-pig immunoglobulins gamma 1G and gamma 2 G. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):829–837. doi: 10.1042/bj1210829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Levine B. B., Quagliata F., Uhr J. W. Mechanisms underlying binding of immune complexes to macrophages. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):589–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Papahadjopoulos D., Nicolson G. L. Local anesthetics affect transmembrane cytoskeletal control of mobility and distribution of cell surface receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., DeStefano M. Cell to substrate adhesion and spreading: inhibition by cationic anesthetics. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Apr;85(2 Pt 1):189–193. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


