Abstract
Studies were carried out with mice to explore in vitro the effector function(s) of macrophages from two different anatomical compartments (peritoneal cavity and lungs). The cytotoxic capacity of macrophages was measured by determining their cytostatic and cytocidal effects on EL-4 tumour target cells, and the microbicidal capacity of macrophages was measured by determining their ability to kill or inhibit the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Neither peritoneal macrophages (PM) nor bronchoalveolar macrophages (BAM) from normal mice were ever microbicidal or cytotoxic. Intravenous treatment with Corynebacterium parvum greatly enhanced (activated) both effector functions of PM but did not activate BAM. Chronic infection with Toxoplasma activated PM throughout the period of observation (greater than 140 days), but the presence of activated BAM was transient and appeared to coincide with the occurrence of an inflammatory response in the lungs.
Full text
PDF


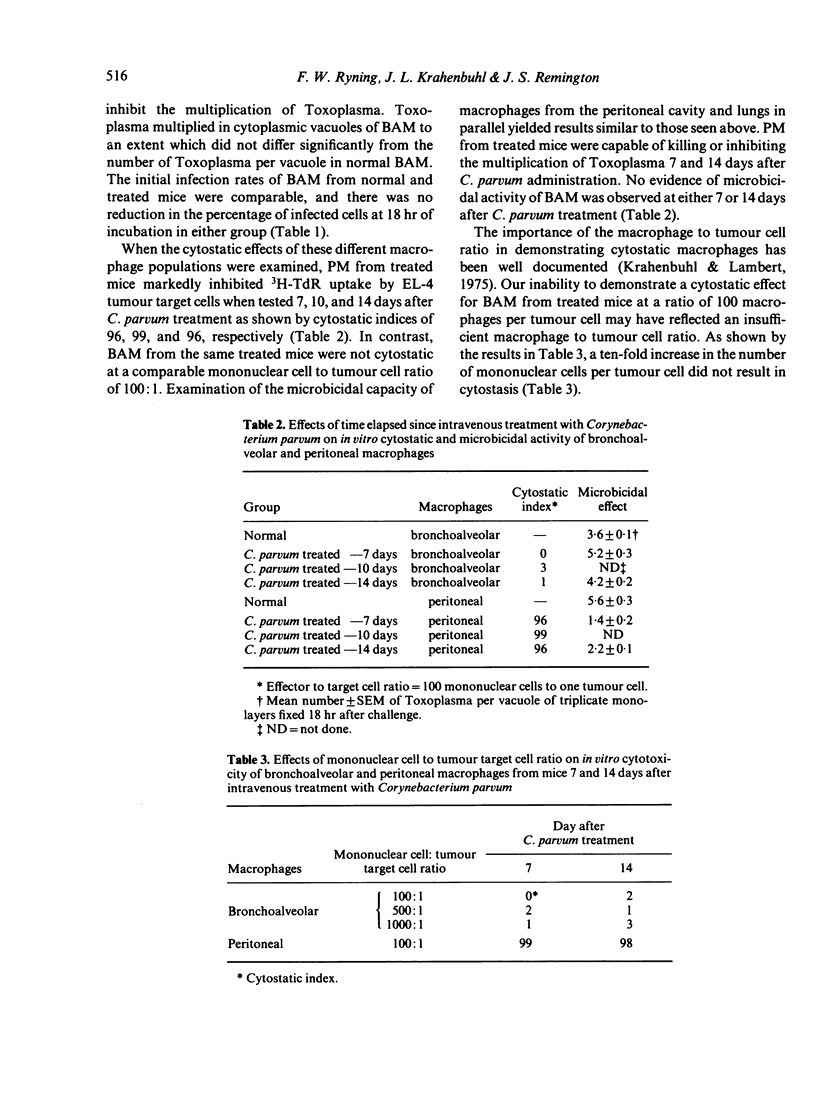
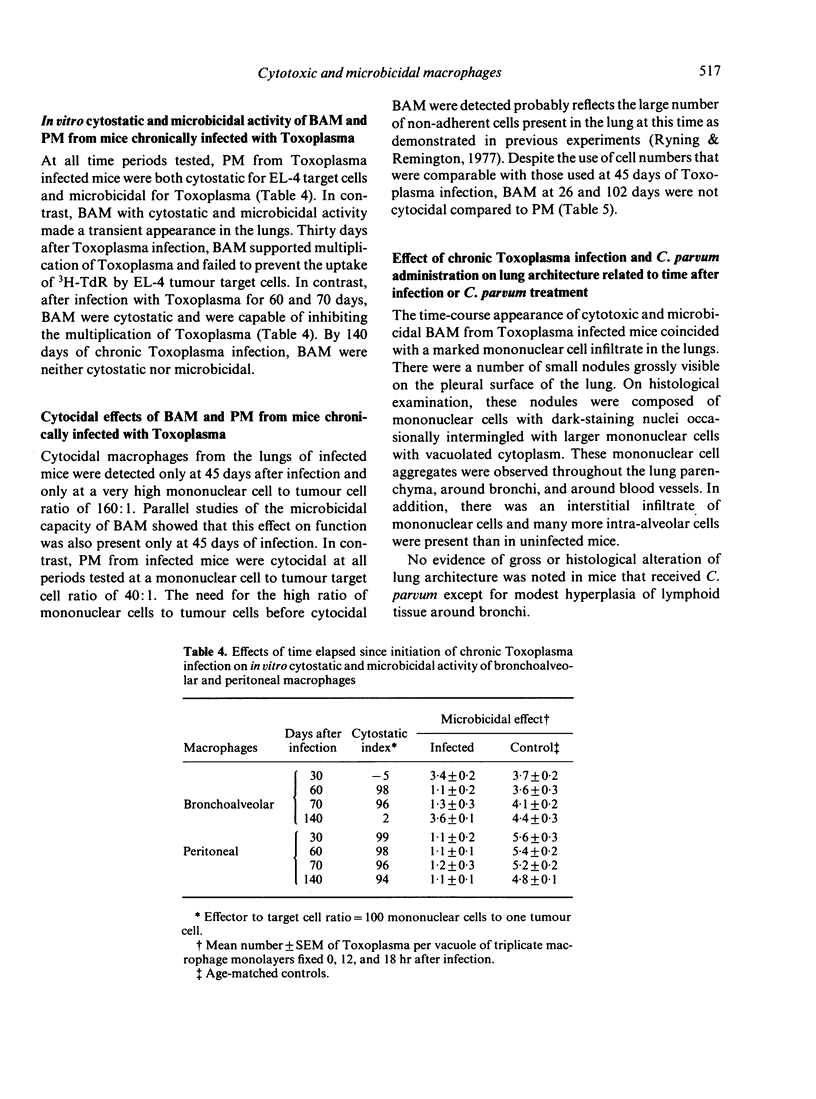


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Cooperation of immune lymphoid cells with macrophages in tumour immunity. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):620–622. doi: 10.1038/228620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner I. D., Remington J. S. Aging and the immune response. II. Lymphocyte responsiveness and macrophage activation in Toxoplasma gondii-infected mice. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):944–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Remington J. S. Resistance against Cryptococcus conferred by intracellular bacteria and protozoa. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):22–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Fauci A. S. Immunological reactivity of the lung. I. A guinea pig model for the study of pulmonary mononuclear cell subpopulations. Cell Immunol. 1976 Sep;26(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Tsunoda K., Suzuki K. Distribution of Toxoplasma gondii, RH strain, in infected mice as determined by the fluorescent antibody technique and the histopathology of toxoplasmosis. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1967 Winter;7(4):208–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Lambert L. H., Jr Cytokinetic studies of the effects of activated macrophages on tumor target cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1433–1437. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivotto M., Bomford R. In vitro inhibition of tumour cell growth and DNA synthesis by peritoneal and lung macrophages from mice injected with Corynebacterium parvum. Int J Cancer. 1974 Apr 15;13(4):478–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Krahenbuhl J. L., Mendenhall J. W. A role for activated macrophages in resistance to infection with Toxoplasma. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):829–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.829-834.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin J., Rengton J. S. Role for the macrophage in acquired immunity to phylogenetically unrelated intracellular organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:474–477. doi: 10.1128/AAC.8.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryning F. W., Remington J. S. Effect of alveolar macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):746–753. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.746-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzberg J. E., Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. Dichotomy between macrophage activation and degree of protection against Listeria monocytogenes and Toxoplasma gondii in mice stimulated with Corynebacterium parvum. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1037–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1037-1043.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Gardner I. D., Ryning F. W., Remington J. S. Dissociation of effector functions in populations of activated macrophages. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):642–644. doi: 10.1038/268642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


