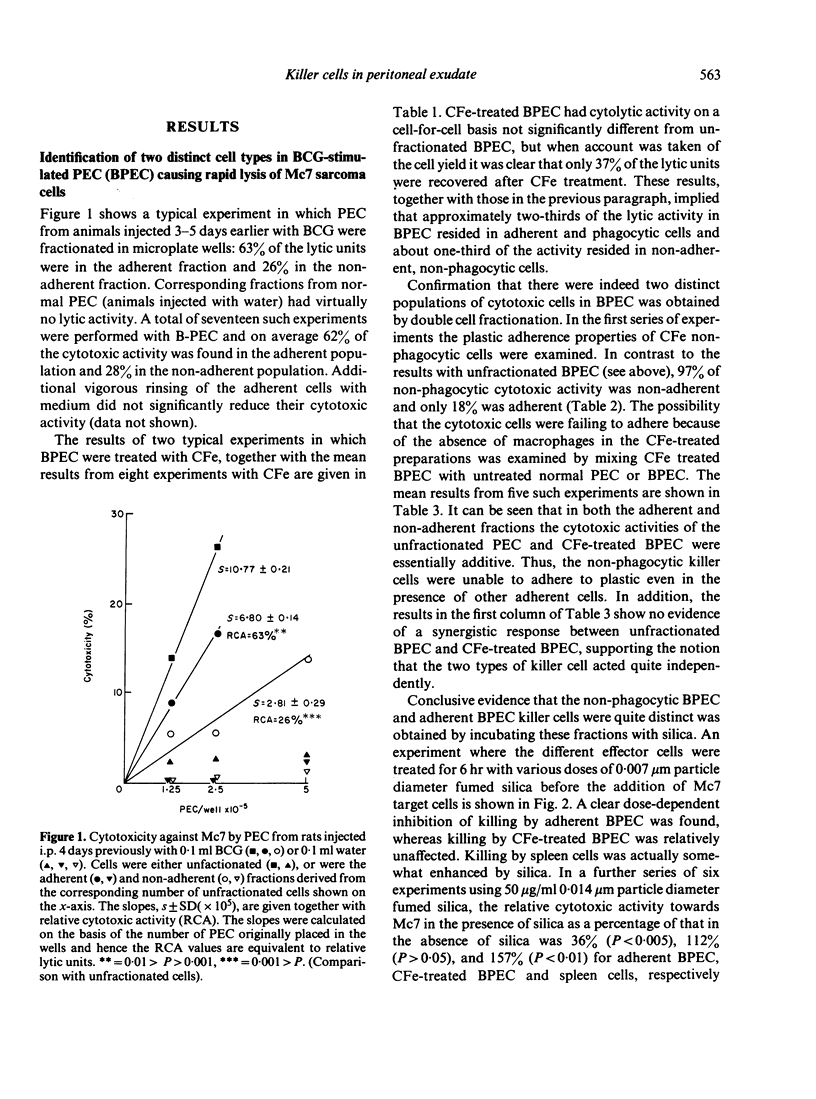
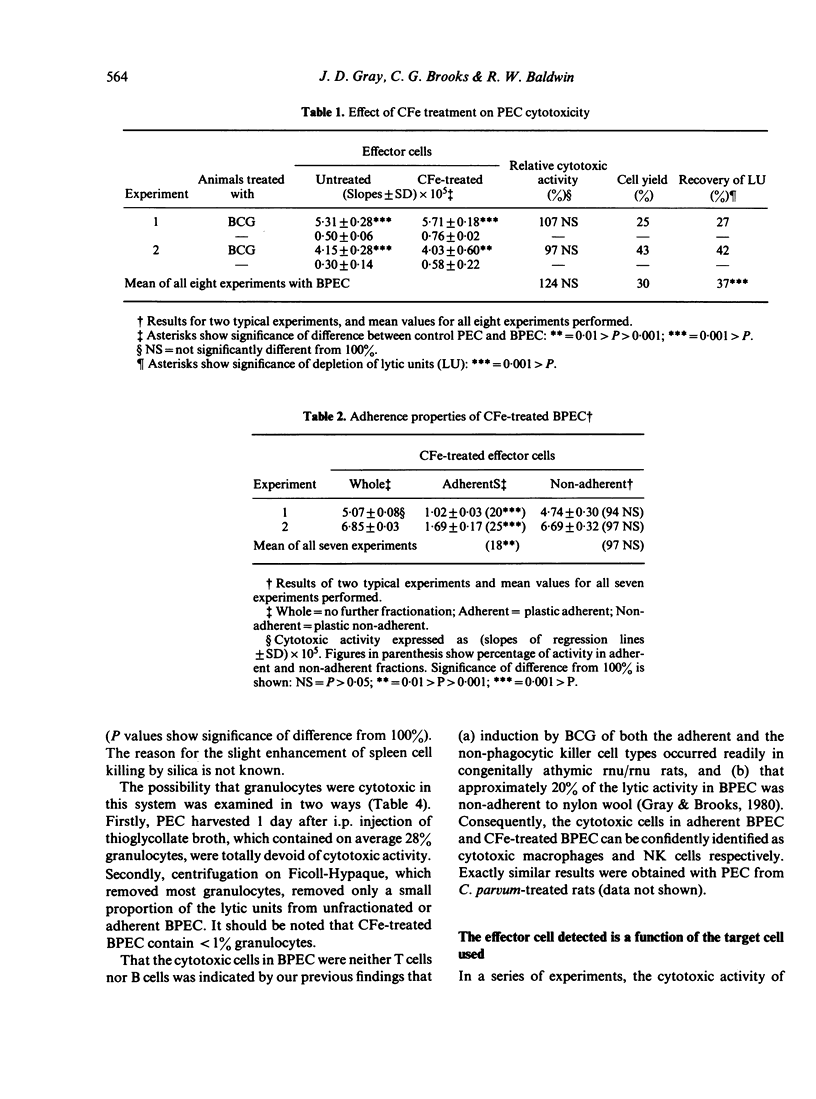
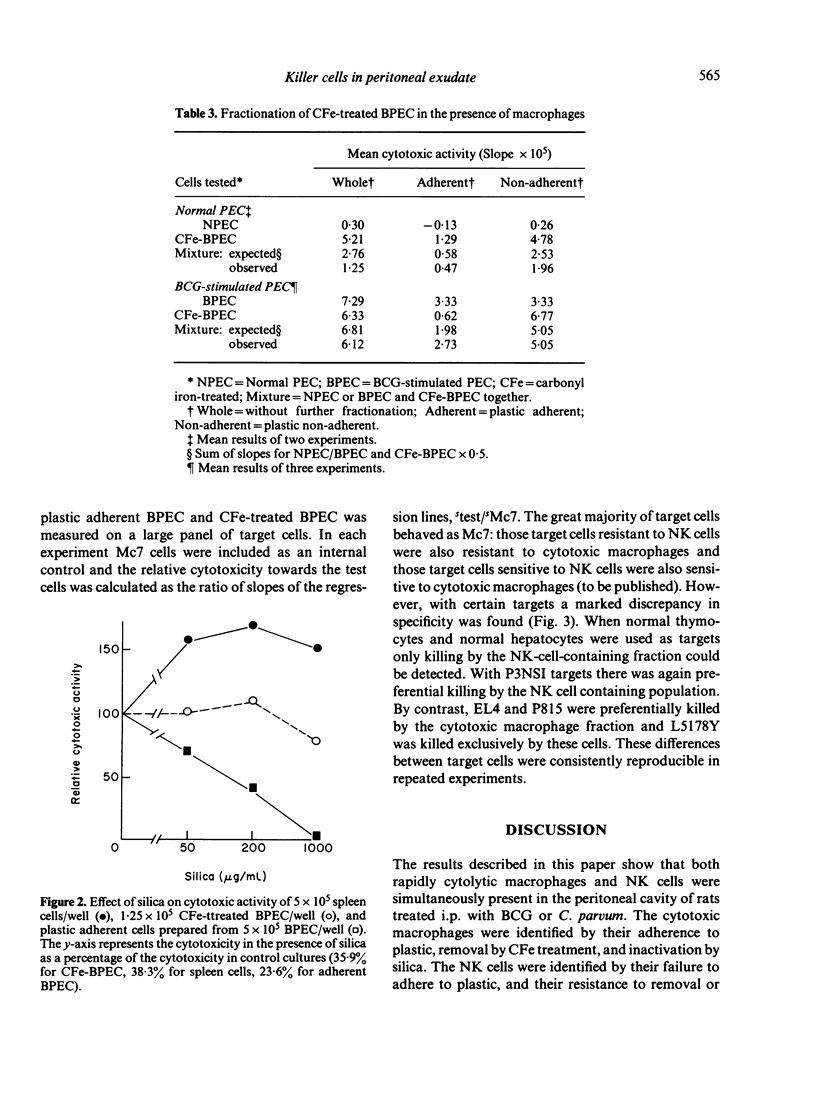
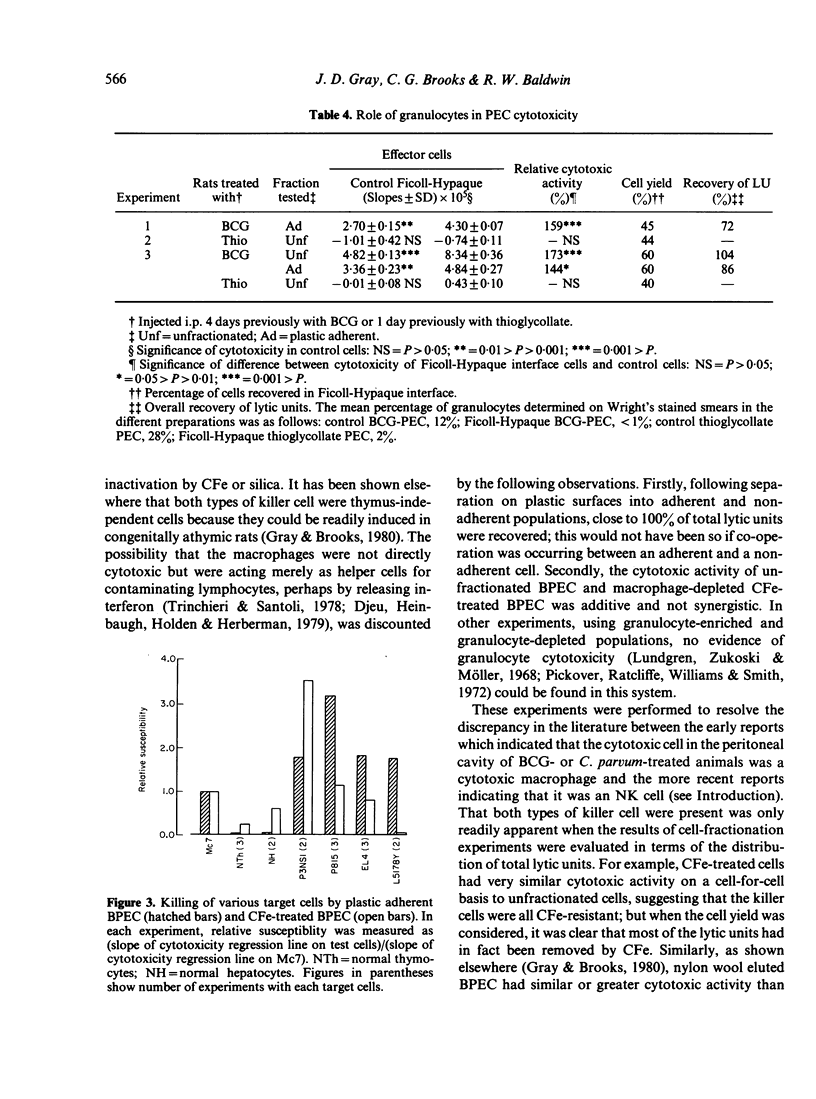
Abstract
The nature of the cytotoxic cells present in the peritoneal cavity of rats treated with Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) or Corynebacterium parvum was investigated using a 6 hr chromium release assay and a quantitative method of analysis based on consideration of target-cell killing as an enzyme-substrate reaction. When the results of cell-fractionation experiments were evaluated in terms of recovery of total lytic units and when appropriate target cells (such as sarcoma Mc7) were used, the simultaneous presence of both cytotoxic macrophages and NK cells in peritoneal exudates could be readily demonstrated. With certain other target cells different results were obtained. Thus, with normal thymocytes, normal hepatocytes, or myeloma P3NSI as targets, NK cells were preferentially detected, whereas with leukaemias L5178Y, P815, and EL4 as targets, cytotoxic macrophages were preferentially detected. These findings resolve the previously conflicting reports concerning the nature of cytotoxic cells in activated peritoneal exudates.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Flannery G. R. Quantitative studies of natural immunity to solid tumours in rats. Persistence of natural immunity throughout reproductive life, and absence of suppressor cells in infant rats. Immunology. 1980 Feb;39(2):187–194. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Flannery G. R., Webb P. J., Baldwin R. W. Quantitative studies of natural immunity to solid tumours in rats. The nature of the killer cell depends on the type of assay. Immunology. 1980 Nov;41(3):673–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Rees R. C., Leach R. H. High nonspecific reactivity of normal lymphocytes against mycoplasma-infected target cells in cytotoxicity assays. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Feb;9(2):159–165. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Role of macrophages in the augementation of mouse natural killer cell activity by poly I:C and interferon. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffar A., Cullen R. T., Dunbar N., Woodruff M. F. Anti-tumour effect in vitro of lymphocytes and macrophages from mice treated with Corynebacterium parvum. Br J Cancer. 1974 Mar;29(3):199–205. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. D., Brooks C. G. The induction of cytotoxic macrophages and natural killer cells in congenitally athymic rnu/rnu rats. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 1;53(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Bartram S., Haskill J. S., Nunn M., Holden H. T., West W. H. Fc receptors on mouse effector cells mediating natural cytotoxicity against tumor cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):322–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. II. Characterization of effector cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):230–239. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T. Low density of Thy 1 antigen on mouse effector cells mediating natural cytotoxicity against tumor cells. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Chapman H. A., Jr, Weinberg J. B. Macrophage tumor killing: influence of the local environment. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.327547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. T., McBride W. H., Weir D. M. The in vitro killing of syngeneic cells by peritoneal cells from adjuvant-stimulated mice. Cell Immunol. 1975 Aug;18(2):375–383. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Ruco L. P., Boraschi D., Nacy C. A. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: analysis of intermediary reactions. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Oct;26(4):403–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Tucker R. W., Sanford K. K., Leonard E. J. Interaction of BCG-activated macrophages with neoplastic and nonneoplastic cell lines in vitro : quantitation of the cytotoxic reaction by release of tritiated thymidine from prelabeled target cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 May;54(5):1177–1184. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.5.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke E. J., Halstead S. B., Allison A. C., Platts-Mills T. A. Specific lethality of silica for human peripheral blood mononuclear phagocytes, in vitro. J Immunol Methods. 1978;19(2-3):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler J. R., Lindsay L. R., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity in rats. II. In vivo augmentation of NK-cell activity. Int J Cancer. 1978 Feb 15;21(2):210–220. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo E., Haller O., Kimura A., Wigzell H. An analysis of conditions allowing Corynebacterium parvum to cause either augmentation or inhibition of natural killer cell activity against tumor cells in mice. Int J Cancer. 1978 Apr 15;21(4):444–452. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo E., Haller O., Wigzell H. Corynebacterium parvum-induced peritoneal exudate cells with rapid cytolytic activity against tumour cells are non-phagocytic cells with characteristics of natural killer cells. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(3):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivotto M., Bomford R. In vitro inhibition of tumour cell growth and DNA synthesis by peritoneal and lung macrophages from mice injected with Corynebacterium parvum. Int J Cancer. 1974 Apr 15;13(4):478–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickaver A. H., Ratcliffe N. A., Williams A. E., Smith H. Cytotoxic effects of peritoneal neutrophils on a syngeneic rat tumour. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):186–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio235186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. R., Moore M. The effect of BCG stimulation on natural cytotoxicity in the rat. Immunology. 1980 Mar;39(3):427–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Domzig W., Kiessling R., Haller O. A functional comparison of tumor cell killing by activated macrophages and natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):283–288. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb P. J., Brooks C. G. Macrophage-like suppressor cells in rats. I. Inhibition of natural macrophage-like suppressor cells by red blood cells. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jul 1;52(2):370–380. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Tracey D. E., Henney C. S. BCG-induced murine effector cells. II. Characterization of natural killer cells in peritoneal exudates. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1152–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


