Abstract
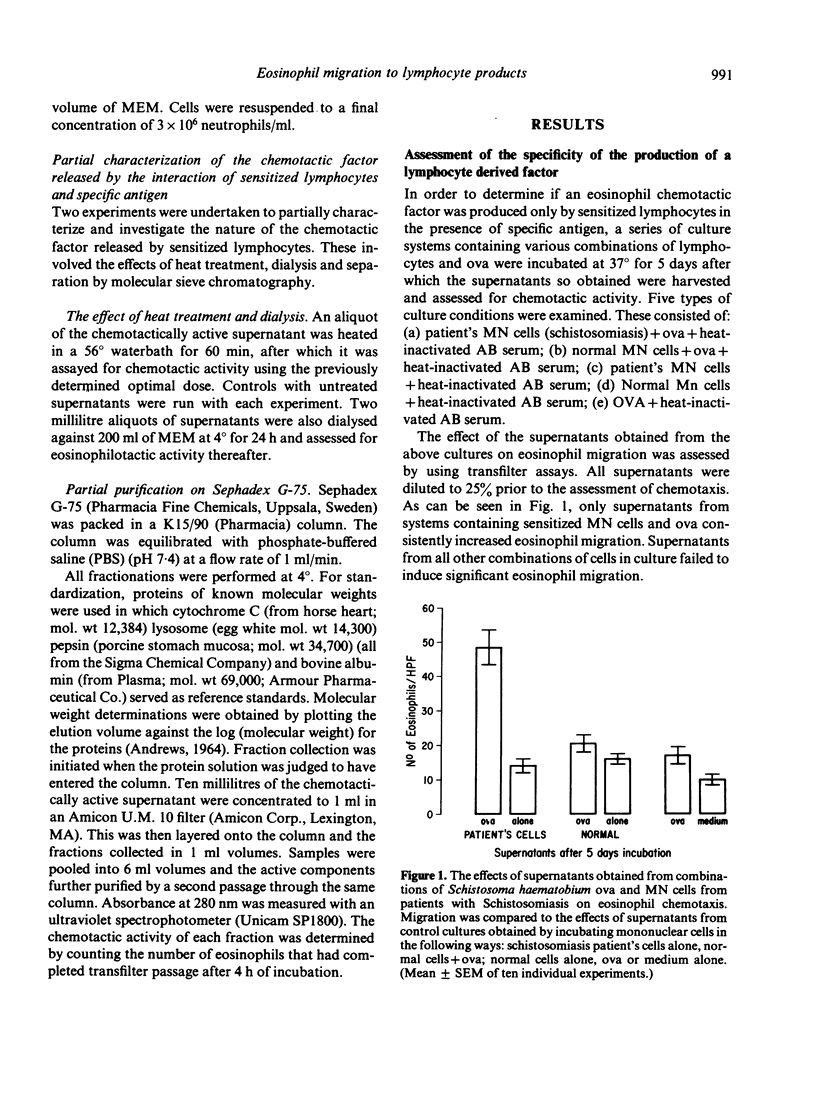
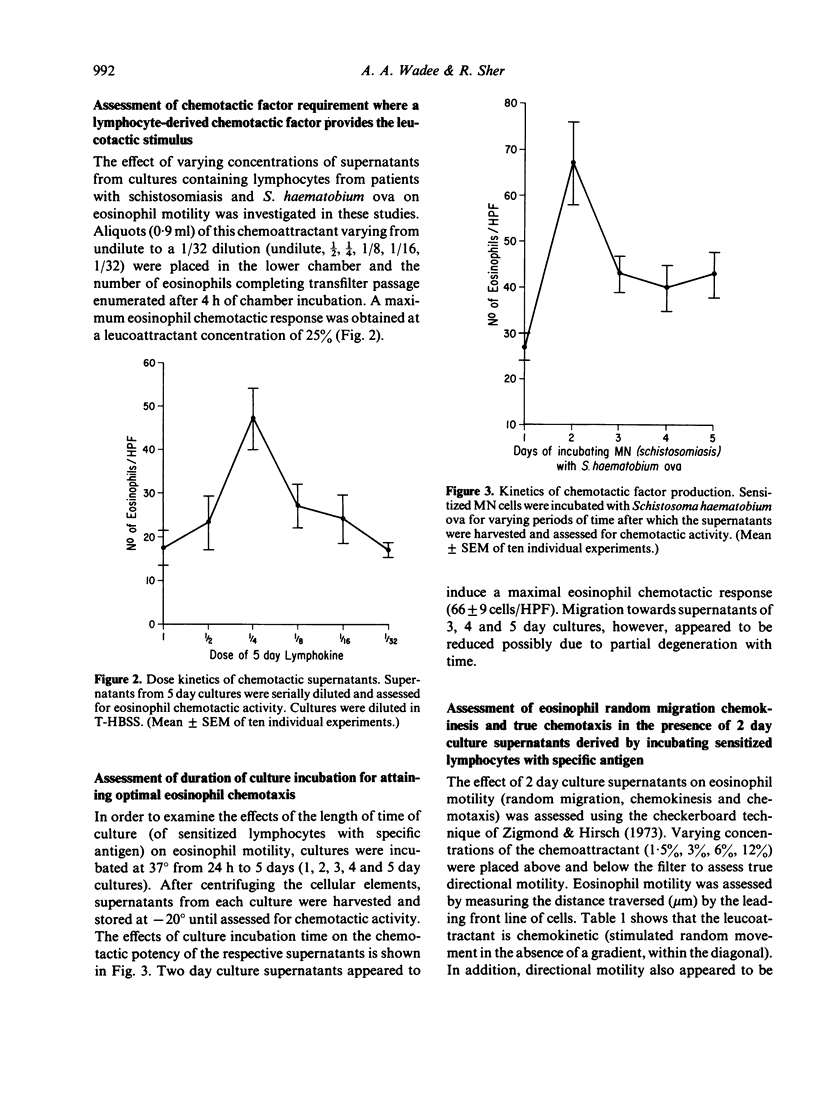
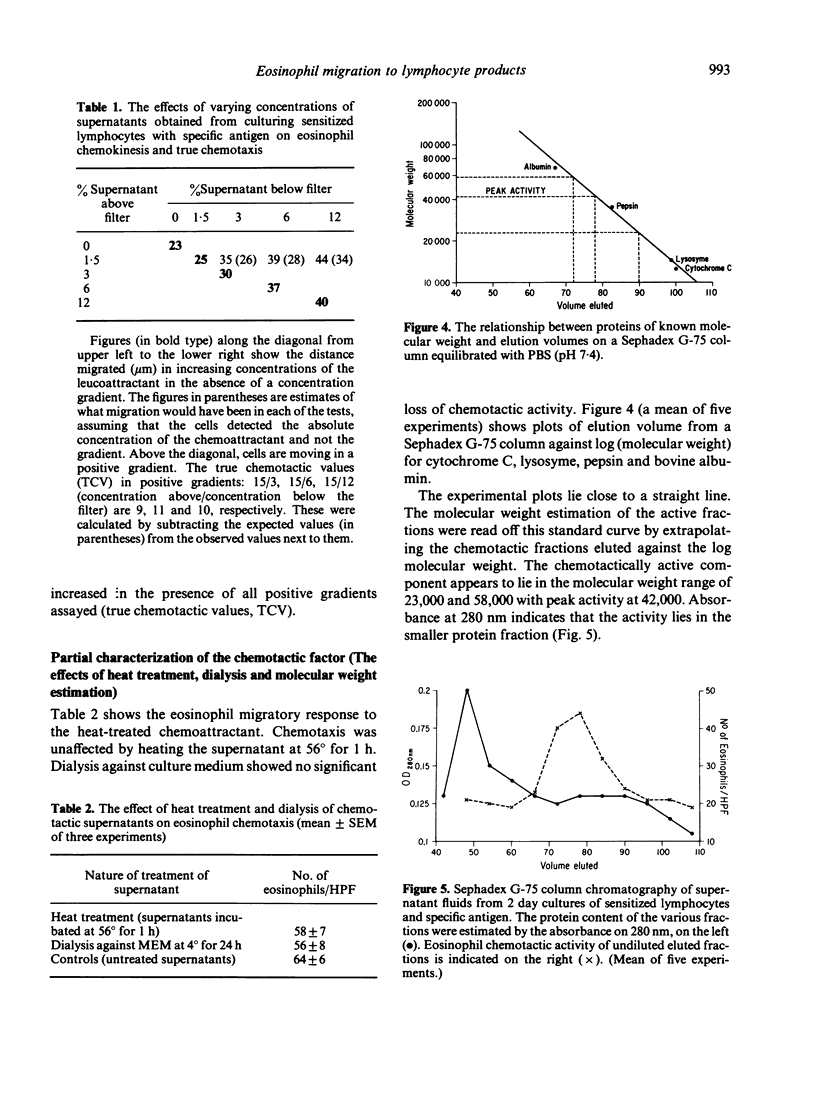
Incubation of sensitized mononuclear cells from patients with schistosomiasis with specific antigen containing a suspension of viable Schistosoma haematobium ova resulted in the release of a soluble factor which was chemotactic for eosinophils. Production of this substance was detectable at 24 h and demonstrated peak chemotactic activity after 2 days in culture. The chemotactic potential was dose-dependent and attracted eosinophils obtained from patients with schistosomiasis or allergic diathesis. Human neutrophil motility was unaffected by this chemoattractant. Preliminary studies demonstrated that the chemotactic factor is a heat-stable substance with peak activity associated with a molecular weight of approximately 42,000. These findings may reflect an in vitro correlate of cell-mediated immunity and may indicate a role played by the lymphocyte in the control of eosinophil function in human biology.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ward P. A. In vitro and in vivo activity of a lymphocyte and immune complex-dependent chemotactic factor for eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):133–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Eosinophils and immune mechanisms. Eosinophil stimulation promoter (ESP): a lymphokine induced by specific antigen or phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1419–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene B. M., Colley D. G. Eosinophils and immune mechanisms. II. Partial characterization of the lymphokine eosinophil stimulation promoter. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):910–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene B. M., Colley D. G. Eosinophils and immune mechanisms. III. Production of the lymphokine eosinophil stimulation promoter by mouse T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1078–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., McVie J. M., Stuart A. E., Krajewski A., Turnbull L. W. Eosinophil chemotaxis of supernatants from cultured Hodgkin's lymph node cells. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jun;28(6):502–505. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.6.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazura J. W., Mahmoud A. A., Karb K. S., Warren K. S. The lymphokine eosinophil stimulation promoter and human schistosomiasis mansoni. J Infect Dis. 1975 Dec;132(6):702–706. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.6.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Turk J. L. The biological activities of soluble lymphocyte products. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jan;10(1):1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Mediators of cellular immunity, their nature and assay. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Sep;67(3):372–380. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher R., Glover A. Isolation of human eosinophils and their lymphocyte-like rosetting properties. Immunology. 1976 Sep;31(3):337–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdimarsson H., Gross N. J. Human skin responses to products of concanavalin A-activated lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):485–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadee A. A., Sher R. Staining of eosinophil granulocytes in chemotactic studies. J Immunol Methods. 1978;22(3-4):383–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


