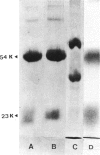
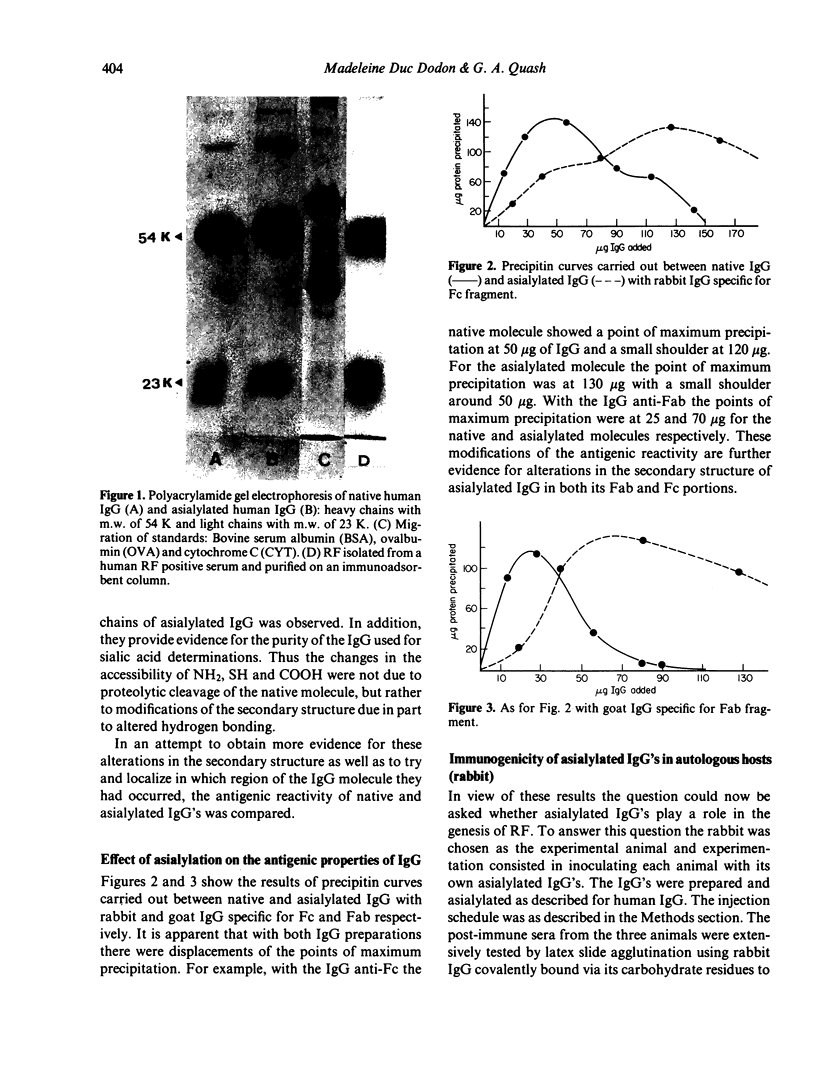
Abstract
Native IgG of human or rabbit origin, from which terminal sialic acid is removed by immobilized neuraminidase, undergoes changes in structure and antigenicity. Such asialylated rabbit IgG's tend to agglutinate, and are immunogenic in autologous hosts. The sialic acid content of rheumatoid factor (RF) isolated from the serum of a rheumatoid patient and identified as IgG and IgM, was also found to be lower than that of normal IgG and IgM. These findings indicate that carbohydrate residues influence the secondary structure of IgG and suggest an enzymic mechanism for the genesis of RF.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHO K., SIMONS K. STUDIES OF THE ANTIBODY NATURE OF THE RHEUMATOID FACTOR. REACTION OF THE RHEUMATOID FACTOR WITH HUMAN SPECIFIC PRECIPITATES AND WITH NATIVE HUMAN GAMMA GLOBULIN. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Dec;6:676–688. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAMP J. R., PUTNAM F. W. THE CARBOHYDRATE PROSTHETIC GROUP OF HUMAN GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3233–3240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake S., Hay F. C., Roitt I. M. The binding constants of IgM rheumatoid factors and their univalent fragments for native and aggregated human IgG;. Immunology. 1977 Mar;32(3):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODFRIEND T. L., LEVINE L., FASMAN G. D. ANTIBODIES TO BRADYKININ AND ANGIOTENSIN: A USE OF CARBODIIMIDES IN IMMUNOLOGY. Science. 1964 Jun 12;144(3624):1344–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3624.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn L. G. Recent concepts on the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Ric Clin Lab. 1977 Oct-Dec;7(4):299–311. doi: 10.1007/BF02886644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMBURGER N., HEIDE K., HAUPT H., SCHULTZE H. E. BAUSTEINANALYSEN VON HUMANSERUMPROTEINEN. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Oct;10:293–307. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIROSE S. I., OSLER A. G. INTERACTION OF RHEUMATOID FACTORS WITH AGGREGATED SUBUNITS OF HUMAN GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:927–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond K. S., Papermaster D. S. Fluorometric assay of sialic acid in the picomole range: a modification of the thiobarbituric acid assay. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):292–297. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson U. B. Effect of straight chain aliphatic amino acids, amines and carboxylic acids on the aggregation of IgG on freezing. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;24(5):1585–1589. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-1585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for detection of IgG and IgM antiglobulins in seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 26;3(5977):203–204. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5977.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunneyball I. M., Stanworth D. R. The effects of chemical modification on the antigenicity of human and rabbit immunoglobulin G. Immunology. 1976 Jun;30(6):881–894. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E., Cooke T. D. The inflammatory role of immune complexes trapped in joint collagenous tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Sep;33(3):416–424. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Carbohydrate structure of glycopeptides isolated from an hepatic membrane-binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5292–5299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochwa S., Brownell M., Rosenfield R. E., Wasserman L. R. Adsorption of proteins by polystyrene particles. I. Molecular unfolding and acquired immunogenicity of IgG. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):981–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Roitt I. M., Hay F. C. Analysis of immune complexes in synovial effusions of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):297–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nineham L. J., Hay F. C., Roitt I. M. Laboratory diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: a solid phase radioassay for IgG and IgM antiglobulins. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Dec;29(12):1121–1126. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.12.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti- -globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. II. The reactivity of anti- -globulin rheumatoid factors with altered G-globulin. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jul;8(7):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quash G., Roch A. M., Niveleau A., Grange J., Keolouangkhot T., Huppert J. The preparation of latex particles with covalently bound polyamines, IgG and measles agglutinins and their use in visual agglutination tests. J Immunol Methods. 1978;22(1-2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEVEAR J. W., SMITH E. L. Glycopeptides. I. Isolation and properties of glycopeptides from a fraction of human gamma-globulin. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER J. M., ORESKES I., ALTMANN G. The mechanism of particulate carrier reactions. IV. Adsorption of human gamma-globulin to tanned sheep erythrocytes and their sensitization for agglutination with rheumatoid arthritis serum. J Immunol. 1962 Aug;89:227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver H. K., Karim K. A., Archibald E. L., Salinas F. A. Serum sialic acid and sialyltransferase as monitors of tumor burden in malignant melanoma patients. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):5036–5042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H. Dunlop-Dottridge lecture. Rehumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid factor and the Epstein-Barr virus. J Rheumatol. 1979 Jul-Aug;6(4):381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelhake J. L., Nicolson G. L. Aglycosylantibody. Effects of exoglycosidase treatments on autochthonous antibody survival time in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1074–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]