Abstract
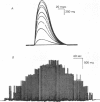
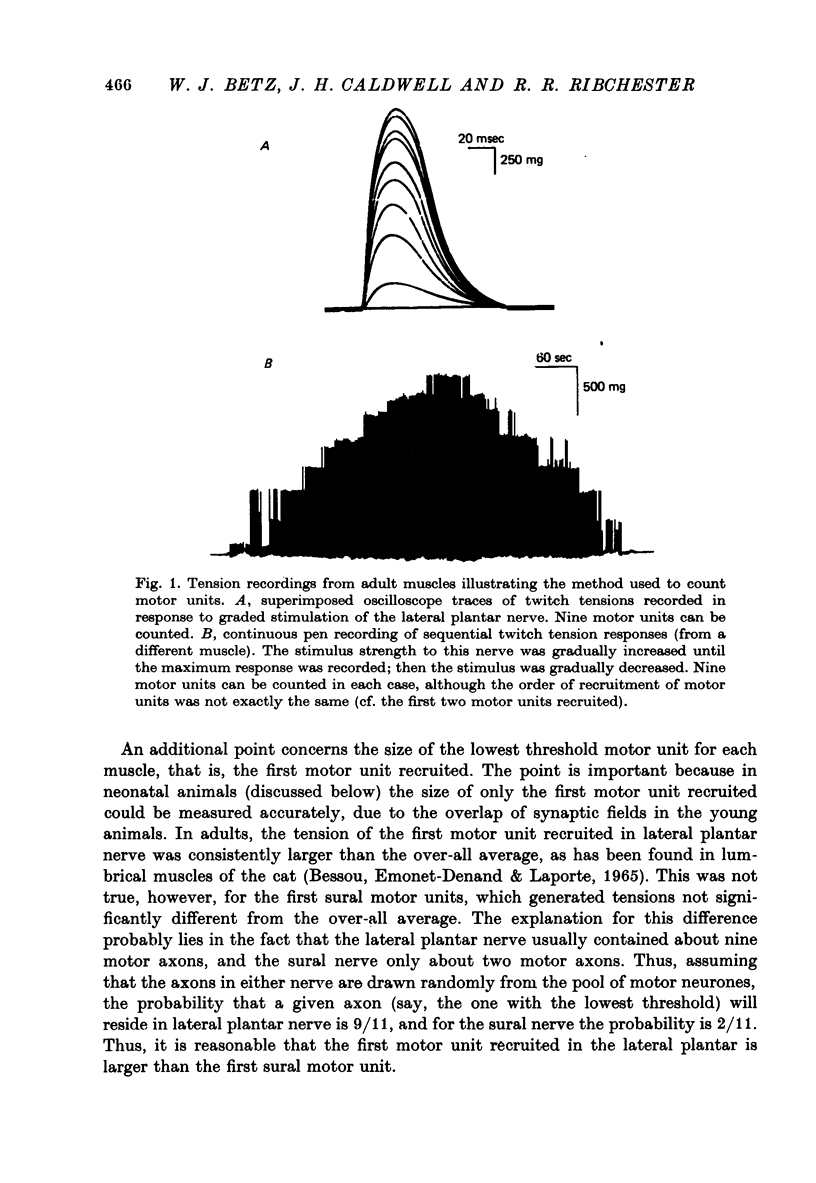
1. The number of muscle fibres innervated by individual motor neurones (motor unit size) was measured in lumbrical muscles of rats aged 0--28 days, during the period of elimination of polyneuronal innervation. Motor unit sizes were determined from twitch tension measurements combined with muscle fibre counts made from histological sections of the muscles. 2. The relative tensions contributed by individual motor units declined from about 25% of the total tension at birth, to about 9% at 28 days of age. Intracellular recordings showed that part of this decrease reflected the elimination of synapses from polyneuronally innervated muscle fibres. 3. During the same period, however, new muscle fibres were produced. The total number of muscle fibres present increased from about 500 at birth to about 950 fibres in mature muscles. 4. These two processes were offsetting: some synapses were eliminated (from polyneuronally innervated fibres) while simultaneously others were formed de novo (on newly produced muscle fibres). Quantitative measurements showed that for the first 10 days after birth, there was little change in motor unit size. Thereafter production of new muscle fibres ceased, and motor unit size decreased to the adult level. 5. It is concluded that during early post-natal development, a lumbrical motor neurone maintains a nearly constant number of synapses, but extensively reorganizes its synaptic field, retracting synapses from some muscle fibres, while forming new synapses with other fibres.
Full text
PDF
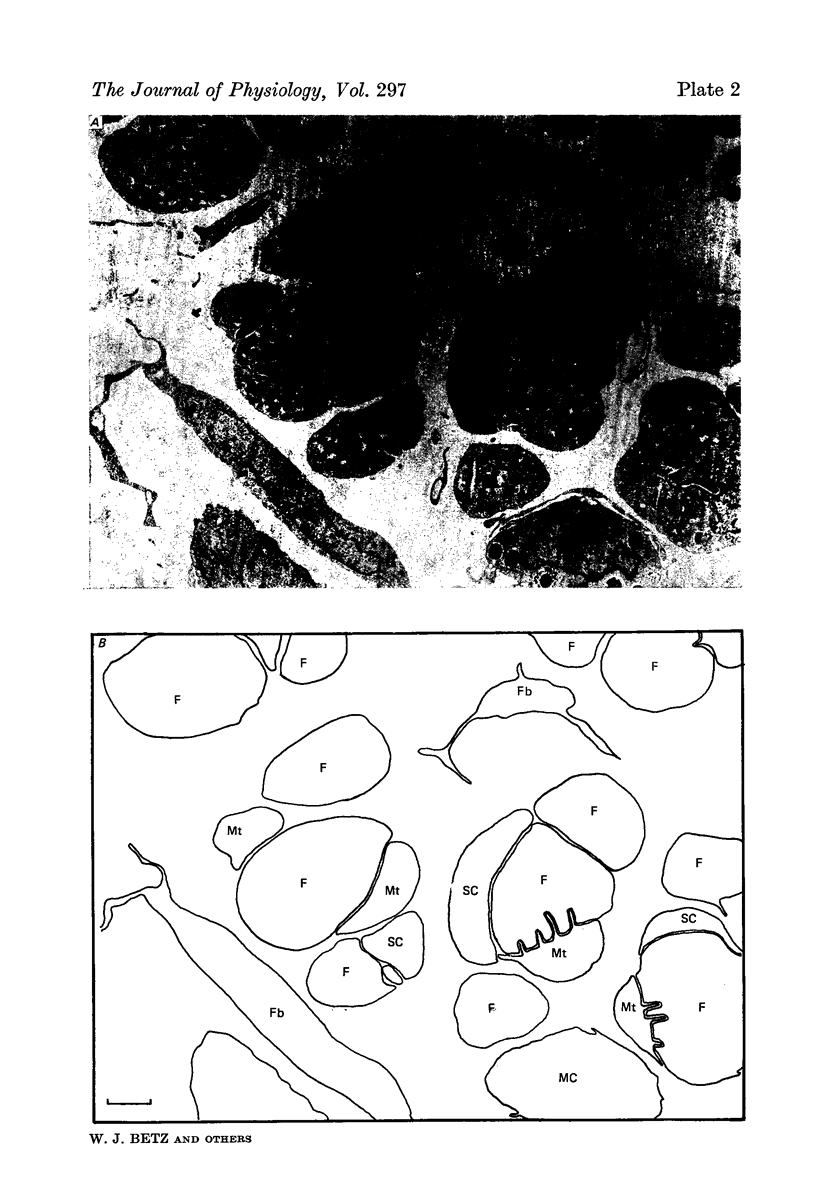



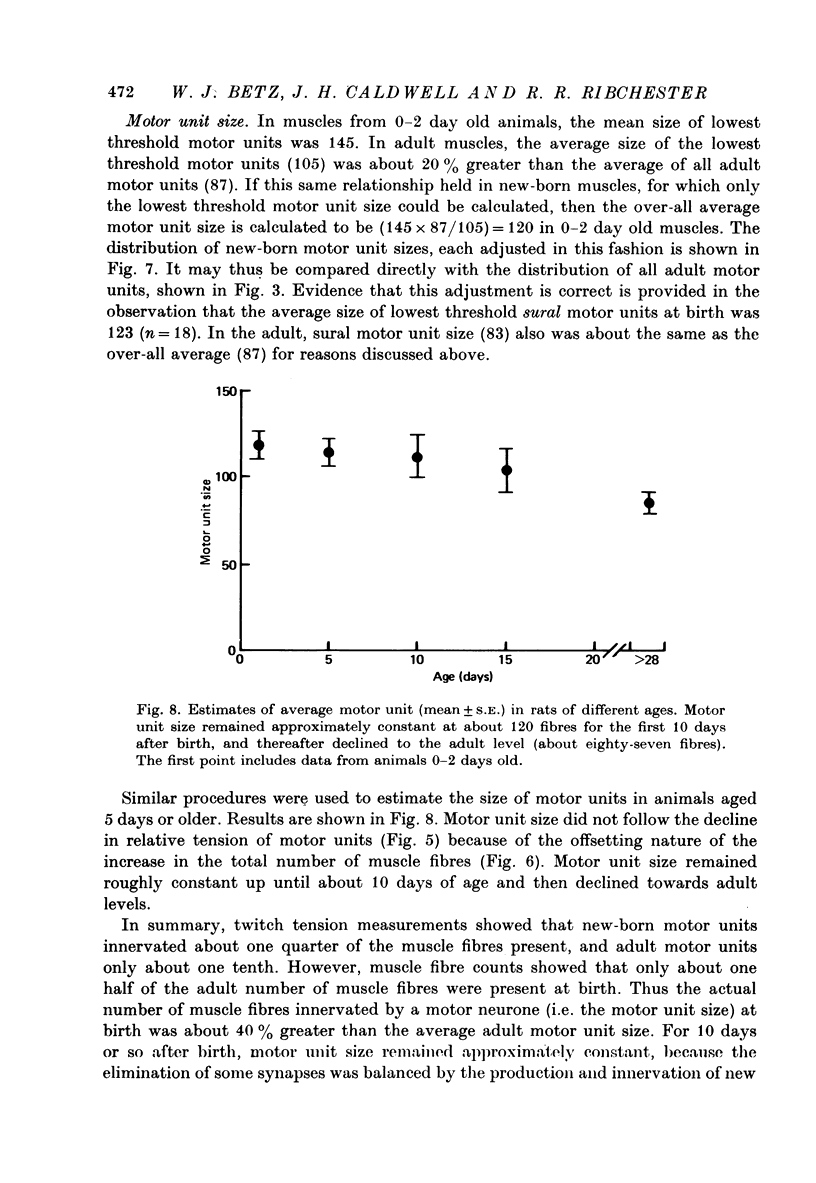
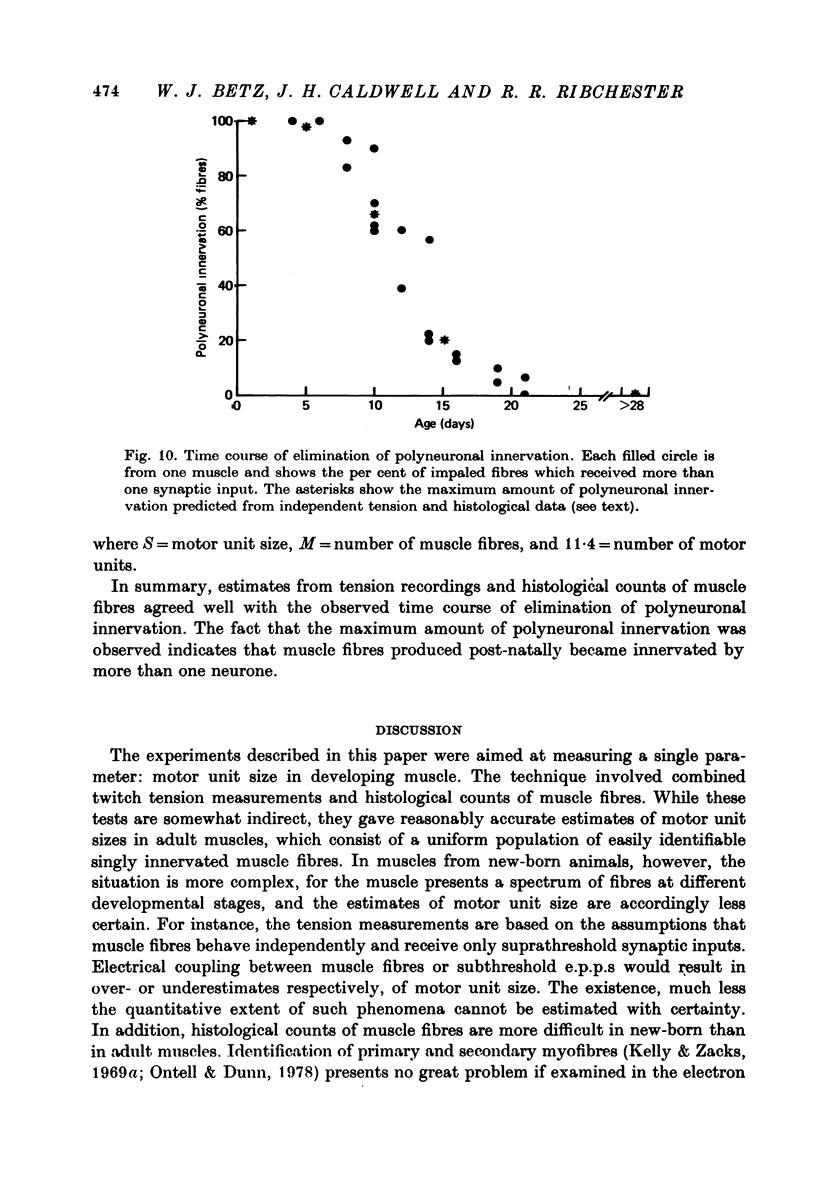
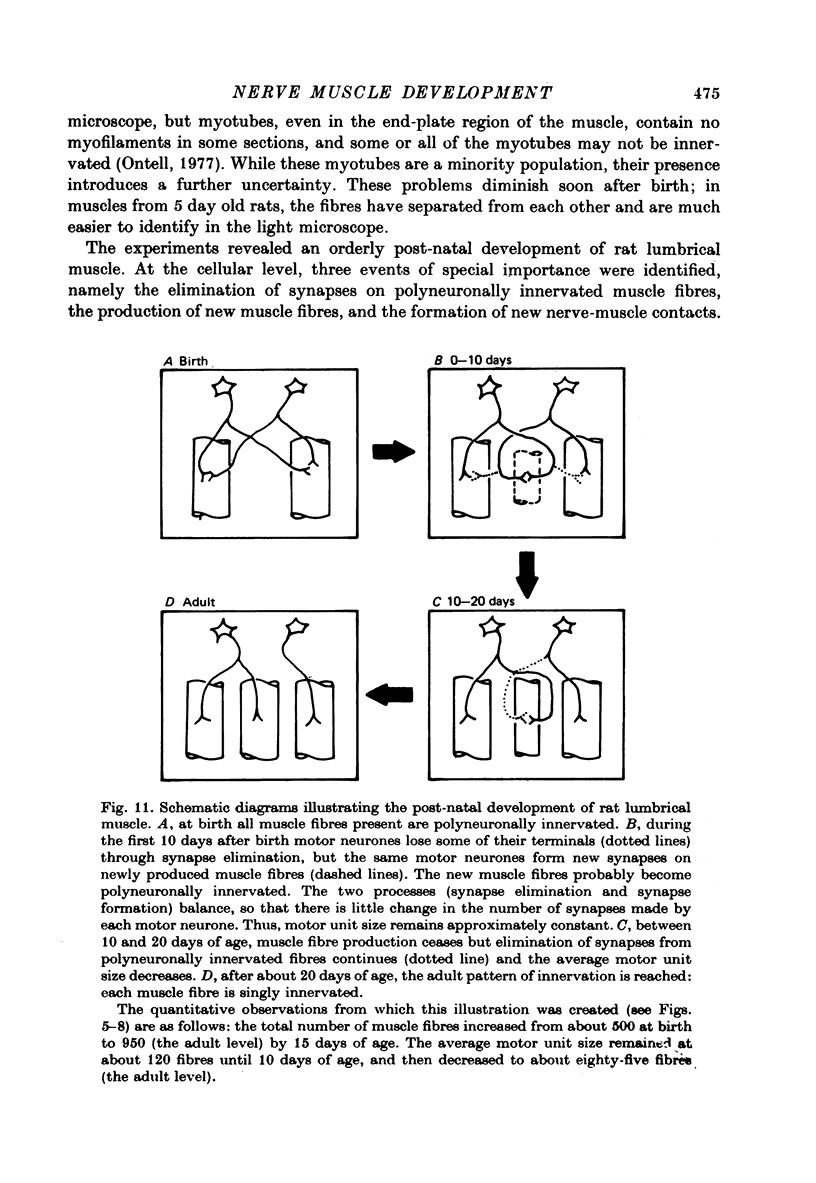





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARSTAD J. A. Presynaptic effect of the neuro-muscular transmitter. Experientia. 1962 Dec 15;18:579–580. doi: 10.1007/BF02172193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN M. C., MATTHEWS P. B. An investigation into the possible existence of polyneuronal innervation of individual skeletal muscle fibres in certain hind-limb muscles of the cat. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:436–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Westerman R. A. Polyneuronal innervation of kitten skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;229(1):241–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Pettigrew A. G. The formation of synapses in striated muscle during development. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):515–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Motor fibres innervating extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):649–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Caldwell J. H., Ribchester R. R. Post-natal development of motor units and muscle fibers in rat lumbrical muscles [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:52P–53P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Ironton R. Sprouting and regression of neuromuscular synapses in partially denervated mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:325–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Jansen J. K., Van Essen D. Polyneuronal innervation of skeletal muscle in new-born rats and its elimination during maturation. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):387–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A. M., Zacks S. I. The fine structure of motor endplate morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):154–169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A. M., Zacks S. I. The histogenesis of rat intercostal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):135–153. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ontell M., Dunn R. F. Neonatal muscle growth: a quantitative study. Am J Anat. 1978 Aug;152(4):539–555. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001520408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ontell M. Neonatal muscle: an electron microscopic study. Anat Rec. 1977 Dec;189(4):669–690. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091890410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P. A. Neuromuscular transmission in new-born rats. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):701–709. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Jansen J. K. The extent of sprouting of remaining motor units in partly denervated immature and adult rat soleus muscle. Neuroscience. 1977;2(4):523–535. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. Reinnervation of partially denervated rat soleus muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 May;103(1):81–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]