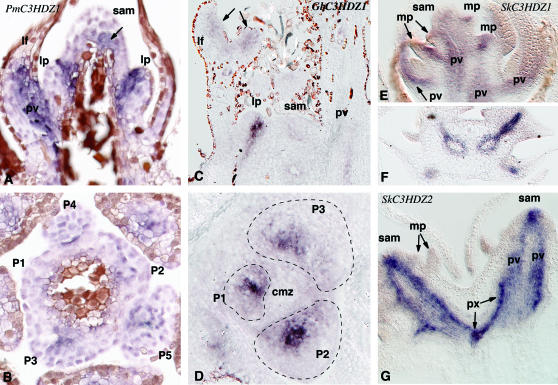
Figure 6.
In situ hybridization of class III HD–Zip genes in Pseudotsuga, Ginkgo, and Selaginella. (A) Nearly median longitudinal section through shoot apex of Pseudotsuga hybridized to PmC3HDZ1. The brown coloration is due to the presence of tannins. (B) Transverse section through shoot apex of Pseudotsuga at the level of emergence of leaf primordia, hybridized to PmC3HDZ1. Primordia are labeled P1–P5 from youngest to oldest. (C) Nearly median longitudinal section through shoot apex of Ginkgo hybridized to GbC3HDZ1. (D) Transverse section through shoot apex of Ginkgo at the level of emergence of leaf primordia, hybridized to GbC3HDZ1. Primordia are labeled P1–P3 from youngest to oldest. (E) Median longitudinal section through shoot apex of Selaginella hybridized to SkC3HDZ1. (F) Transverse section through shoot of Selaginella several nodes below the SAM hybridized to SkC3HDZ1. (G) Median longitudinal section through shoot apex of Selaginella hybridized to SkC3HDZ2. cmz, central mother cell zone; lf, leaf; lp, leaf primordium; mi, microphyll; mp, microphyll primordium; pv, provascular tissue; px, protoxylem; SAM, shoot apical meristem; x, xylem.