Abstract
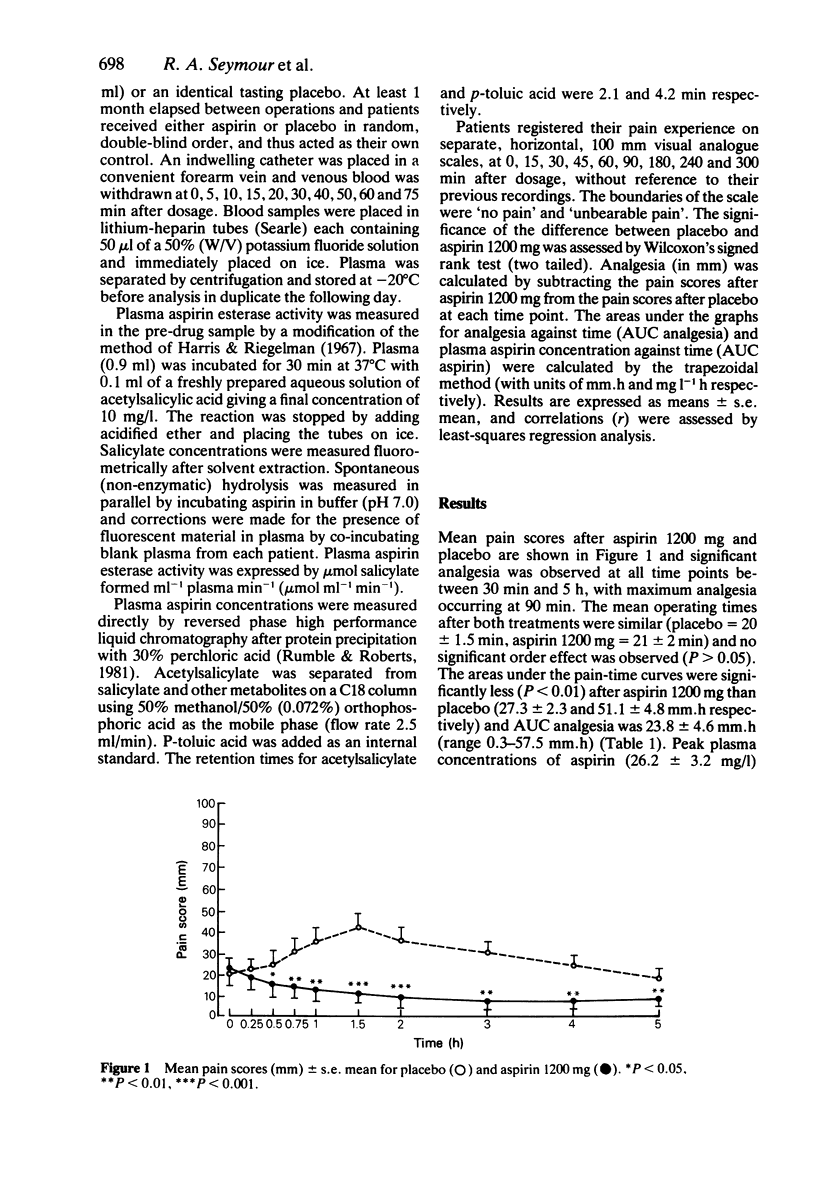
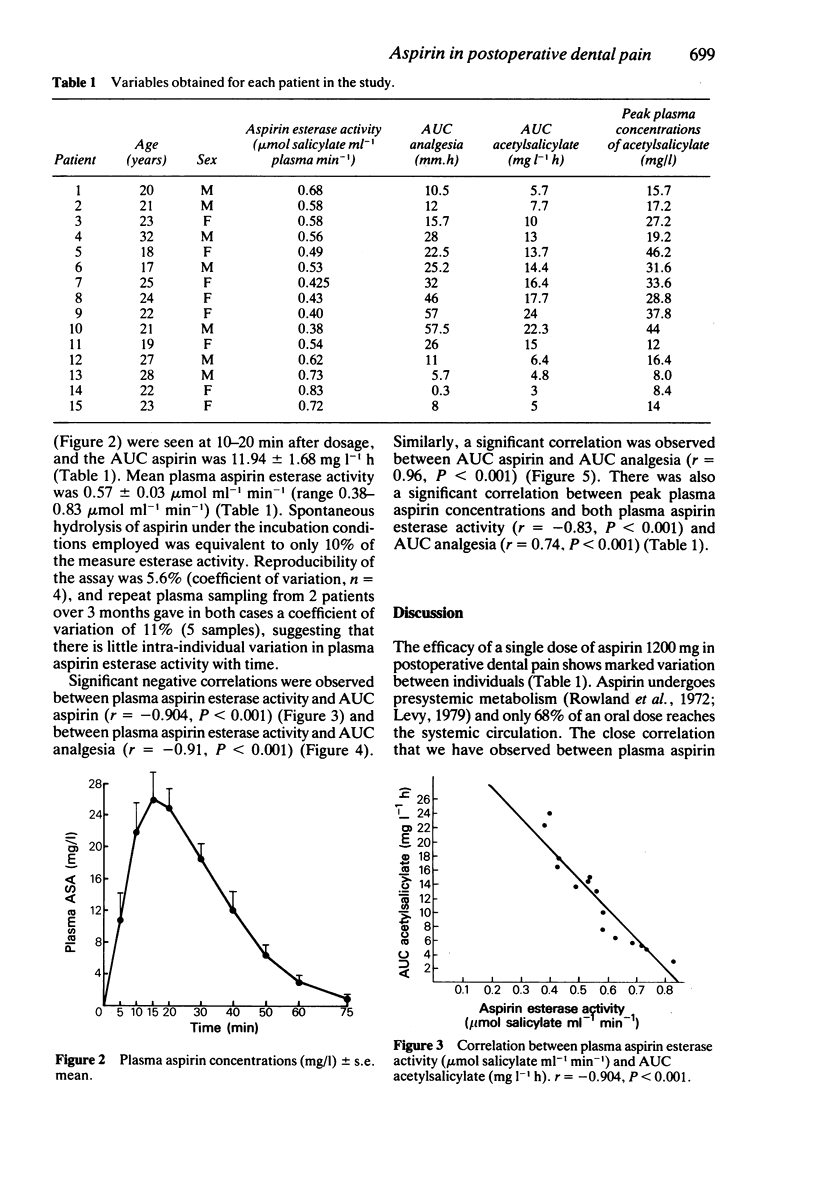
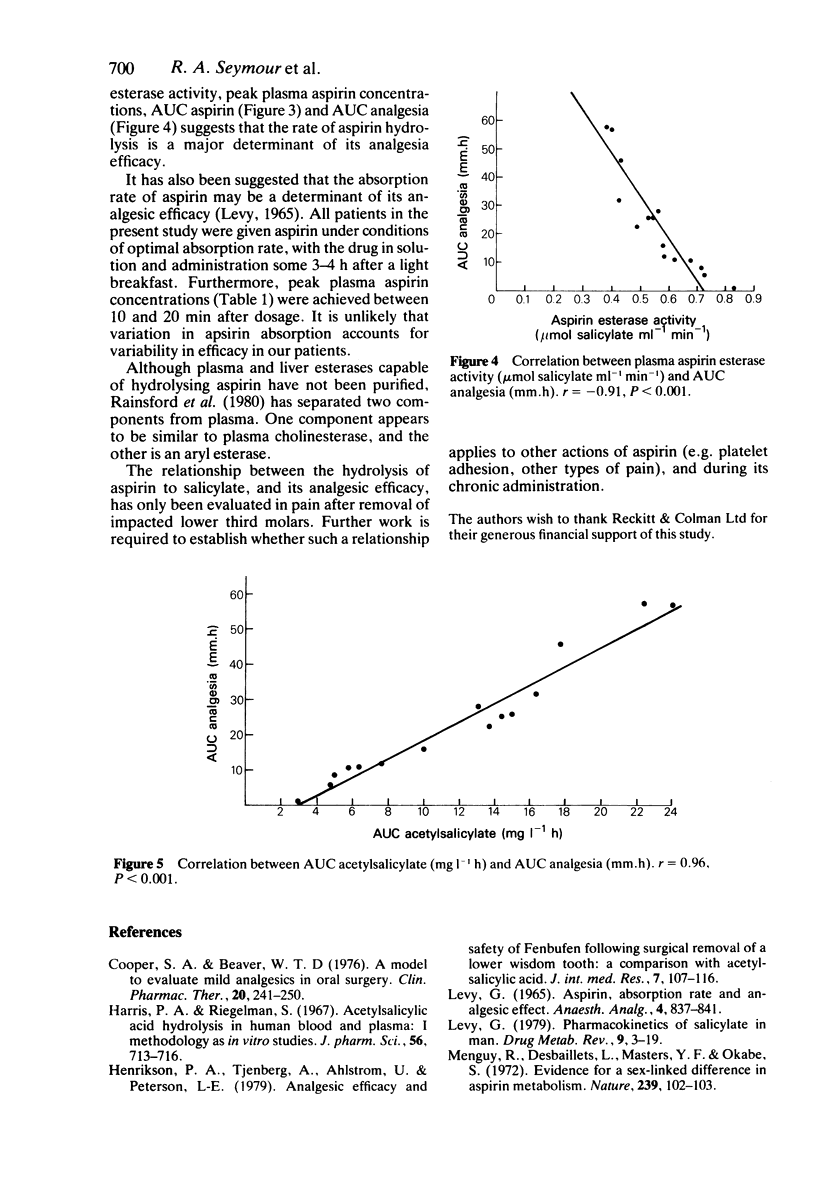
Aspirin 1200 mg was compared with placebo in a randomised, double-blind, crossover study in 15 patients with postoperative pain after removal of impacted lower third molars. Over a 5 h investigation period, patients reported significantly less pain (P less than 0.01) after treatment with aspirin, than after treatment with placebo. Peak concentrations of aspirin occurred at 15 min after dosage. Significant negative correlations were observed between plasma aspirin esterase activity and both AUC aspirin (r = -0.904, P less than 0.001) and AUC analgesia (r = -0.91, P less than 0.001). Similarly, a significant correlation was observed between AUC aspirin and AUC analgesia (r = 0.96, P less than 0.001). Evidence from this study would suggest that an individual's pain relief in postoperative dental pain is determined by the rate of aspirin hydrolysis to salicylate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper S. A., Beaver W. T. A model to evaluate mild analgesics in oral surgery outpatients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Aug;20(2):241–250. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976202241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. A., Riegelman S. Acetylsalicylic acid hydrolysis in human blood and plasma. I. Methodology and in vitro studies. J Pharm Sci. 1967 Jun;56(6):713–716. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600560610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. Aspirin, absorption rate and analgesic effect. Anesth Analg. 1965 Nov-Dec;44(6):837–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. Pharmacokinetics of salicylate in man. Drug Metab Rev. 1979;9(1):3–19. doi: 10.3109/03602537909046431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menguy R., Desbaillets L., Masters Y. F., Okabe S. Evidence for a sex-linked difference in aspirin metabolism. Nature. 1972 Sep 8;239(5367):102–103. doi: 10.1038/239102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainsford K. D., Ford N. L., Brooks P. M., Watson H. M. Plasma aspirin esterases in normal individuals, patients with alcoholic liver disease and rheumatoid arthritis: characterization and the importance of the enzymic components. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;10(5):413–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M., Riegelman S., Harris P. A., Sholkoff S. D. Absorption kinetics of aspirin in man following oral administration of an aqueous solution. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Mar;61(3):379–385. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumble R. H., Roberts M. S., Wanwimolruk S. Determination of aspirin and its major metabolites in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography without solvent extraction. J Chromatogr. 1981 Sep 11;225(1):252–260. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour R. A., Rawlins M. D., Clothier A. The efficacy and pharmacokinetics of sodium salicylate in post-operative dental pain. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;17(2):161–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour R. A., Rawlins M. D. Efficacy and pharmacokinetics of aspirin in post-operative dental pain. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;13(6):807–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graffenried B., Nüesch E., Maeglin B., Hägler W., Kuhn M. Assessment of analgesics in dental surgery outpatients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(6):479–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00874659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


