Abstract
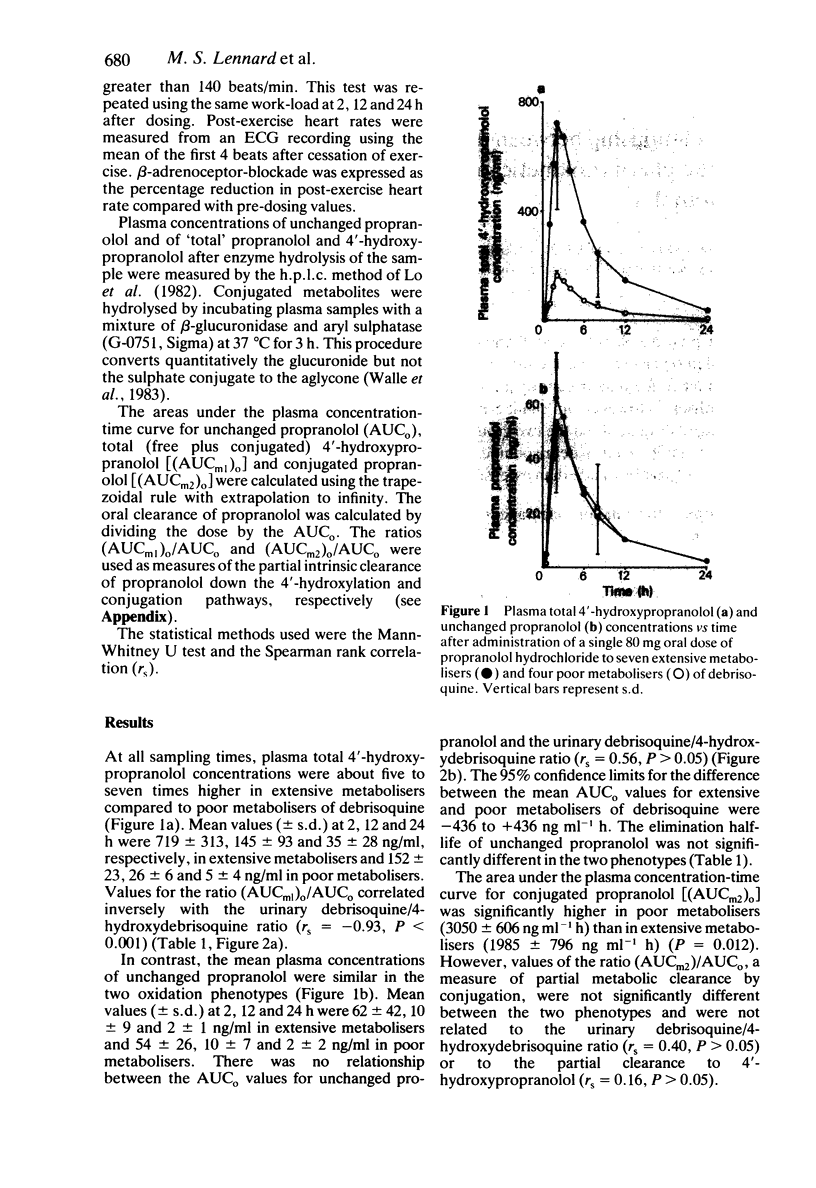
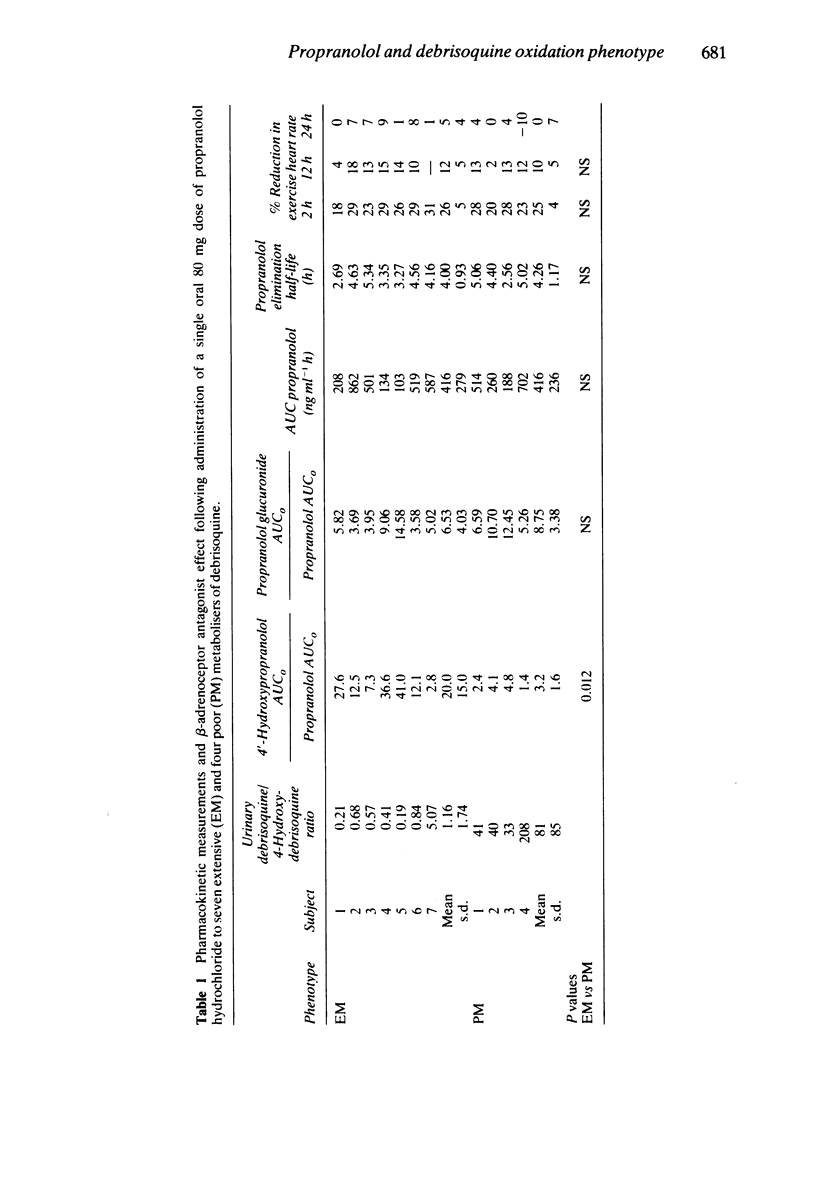
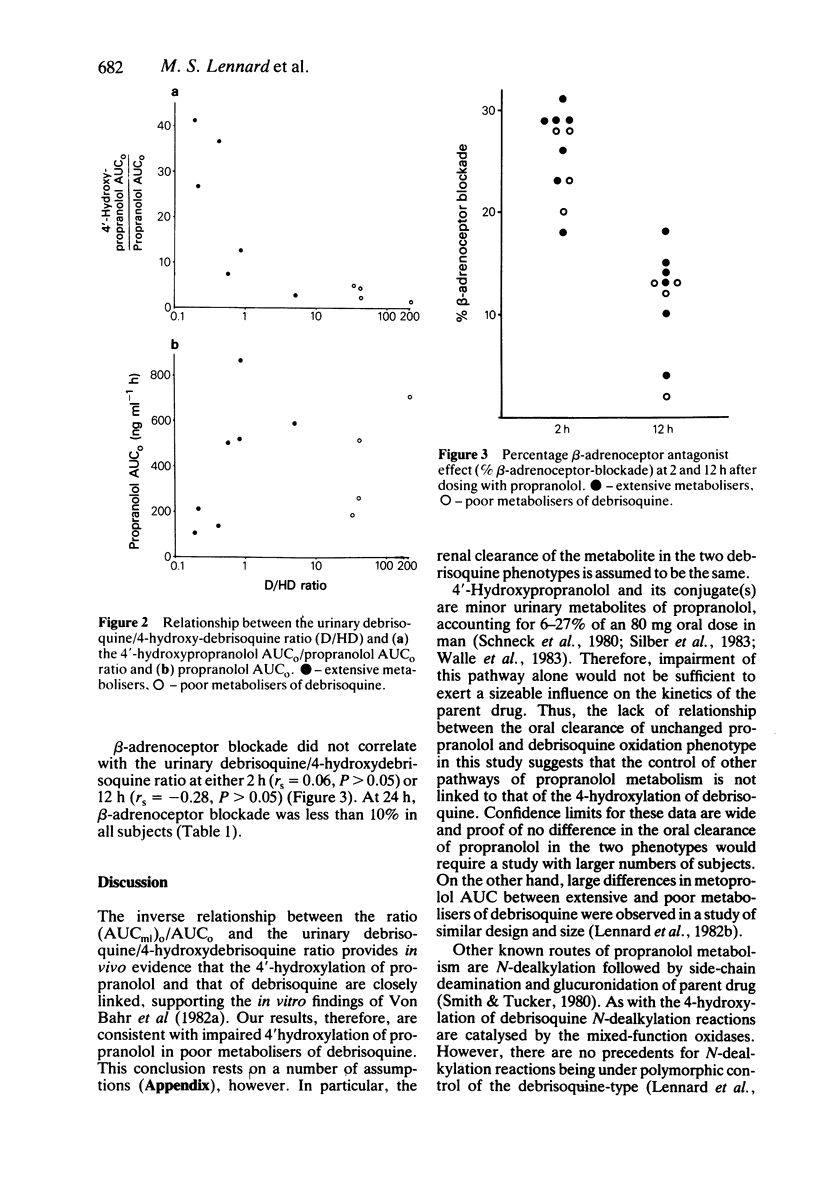
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of propranolol (80 mg by mouth) were studied in seven extensive and four poor metabolisers of debrisoquine. Evidence for impairment of the 4'-hydroxylation of propranolol was found in poor metabolisers. However, no significant difference was detected in the oral clearance of unchanged drug between the two groups of debrisoquine oxidation phenotypes. Poor metabolisers of debrisoquine did not experience more intense or more prolonged beta-adrenoceptor blockade than extensive metabolisers of debrisoquine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bai S. A., Abramson F. P. Interaction of phenobarbital with propranolol in the dog. 3. Beta blockade. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaveland C. R., Shand D. G. Effect of route of administration on the relationship between -adrenergic blockade and plasma propranolol level. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Mar-Apr;13(2):181–185. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972132181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer P., Courvoisier F., Kupfer A., Balant-Gorgia A., Balant L., Fabre J. Conséquences pharmacocinétiques et cliniques du polymorphisme génétique de l'oxydation. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1983 Feb 26;113(8):295–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer P., Kubli A., Kupfer A., Courvoisier F., Balant L., Fabre J. Defective hydroxylation of bufuralol associated with side-effects of the drug in poor metabolisers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 May;13(5):750–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. D., O'Donnell S. R. Pharmacology of 4-hydroxypropranolol, a metabolite of propranolol. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;43(1):222–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard M. S., Silas J. H., Freestone S., Ramsay L. E., Tucker G. T., Woods H. F. Oxidation phenotype--a major determinant of metoprolol metabolism and response. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 16;307(25):1558–1560. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212163072505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard M. S., Silas J. H., Freestone S., Trevethick J. Defective metabolism of metoprolol in poor hydroxylators of debrisoquine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;14(2):301–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo M. W., Silber B., Riegelman S. An automated HPLC method for the assay of propranolol and its basic metabolites in plasma and urine. J Chromatogr Sci. 1982 Mar;20(3):126–131. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/20.3.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang K. S., Rowland M. Hepatic clearance of drugs. I. Theoretical considerations of a "well-stirred" model and a "parallel tube" model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding, and the hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1977 Dec;5(6):625–653. doi: 10.1007/BF01059688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneck D. W., Pritchard J. F., Gibson T. P., Vary J. E., Hayes A. H., Jr Effect of dose and uremia on plasma and urine profiles of propranolol metabolites. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Jun;27(6):744–755. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Nuckolls E. M., Oates J. A. Plasma propranolol levels in adults with observations in four children. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Jan-Feb;11(1):112–120. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970111112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber B. M., Holford N. H., Riegelman S. Dose-dependent elimination of propranolol and its major metabolites in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Jul;72(7):725–732. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600720703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Bahr C., Hermansson J., Tawara K. Plasma levels of (+) and (-)-propranolol and 4-hydroxypropranolol after administration of racemic (+/-)-propranolol in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;14(1):79–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb04937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Walle U. K., Knapp D. R., Conradi E. C., Bargar E. M. Identification of major sulfate conjugates in the metabolism of propranolol in dog and man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 Jul-Aug;11(4):344–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle U. K., Walle T., Bai S. A., Olanoff L. S. Stereoselective binding of propranolol to human plasma, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, and albumin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Dec;34(6):718–723. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


