Abstract
1 The design origins of the potent non-mercapto angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors enalaprilat and its mono ethyl ester enalapril are described.
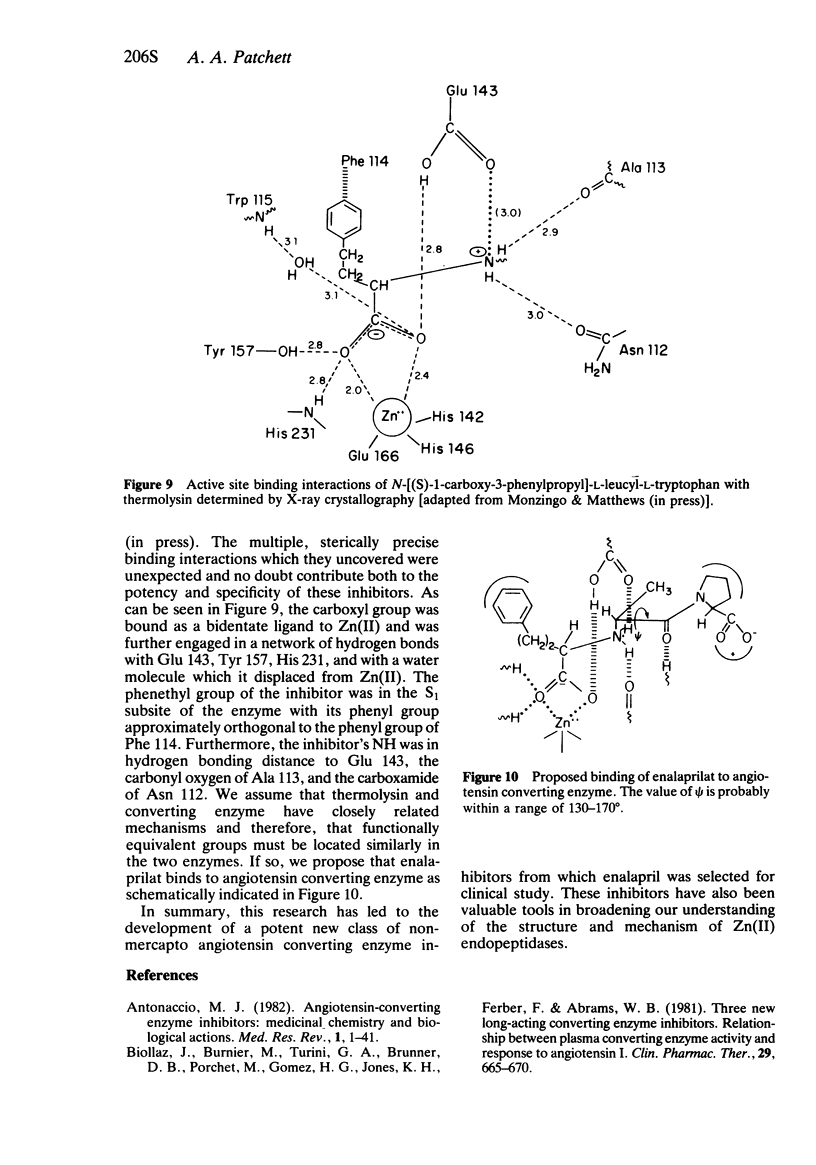
2 Lactam analogues of enalaprilat have provided some insight into the conformation of this inhibitor when it is bound to converting enzyme.
3 X-ray crystallographic studies of a related enzyme/inhibitor complex offer an explanation for the high potency and specificity of these and related inhibitors.
Keywords: enalapril, enalaprilat, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biollaz J., Burnier M., Turini G. A., Brunner D. B., Porchet M., Gomez H. J., Jones K. H., Ferber F., Abrams W. B., Gavras H. Three new long-acting converting-enzyme inhibitors: relationship between plasma converting-enzyme activity and response to angiotensin I. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 May;29(5):665–670. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers L. D., Wolfenden R. A potent reversible inhibitor of carboxypeptidase A. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 25;247(2):606–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers L. D., Wolfenden R. Binding of the by-product analog benzylsuccinic acid by carboxypeptidase A. Biochemistry. 1973 May 22;12(11):2070–2078. doi: 10.1021/bi00735a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S., Sabo E. F., Ondetti M. A. Design of potent competitive inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Carboxyalkanoyl and mercaptoalkanoyl amino acids. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5484–5491. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Pluscec J., Williams N. J., Weaver E. R., Sabo E. F., Kocy O., Cheung H. S., Ondetti M. A. Inhibition of angiotensin-coverting enzyme by analogs of peptides from Bothrops jararaca venom. Experientia. 1973 Aug 15;29(8):1032–1035. doi: 10.1007/BF01930447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maycock A. L., DeSousa D. M., Payne L. G., ten Broeke J., Wu M. T., Patchett A. A. Inhibition of thermolysin by N-carboxymethyl dipeptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 15;102(3):963–969. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91632-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Cushman D. W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):441–444. doi: 10.1126/science.191908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchett A. A., Harris E., Tristram E. W., Wyvratt M. J., Wu M. T., Taub D., Peterson E. R., Ikeler T. J., ten Broeke J., Payne L. G. A new class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):280–283. doi: 10.1038/288280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrillo E. W., Jr, Ondetti M. A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: medicinal chemistry and biological actions. Med Res Rev. 1982 Jan-Mar;2(1):1–41. doi: 10.1002/med.2610020103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C. S. Pharmacological properties of the converting enzyme inhibitor, enalapril maleate (MK-421). Fed Proc. 1983 Feb;42(2):167–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidt D. G., Bravo E. L., Fouad F. M. Medical intelligence drug therapy: captopril. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jan 28;306(4):214–219. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198201283060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


