Abstract
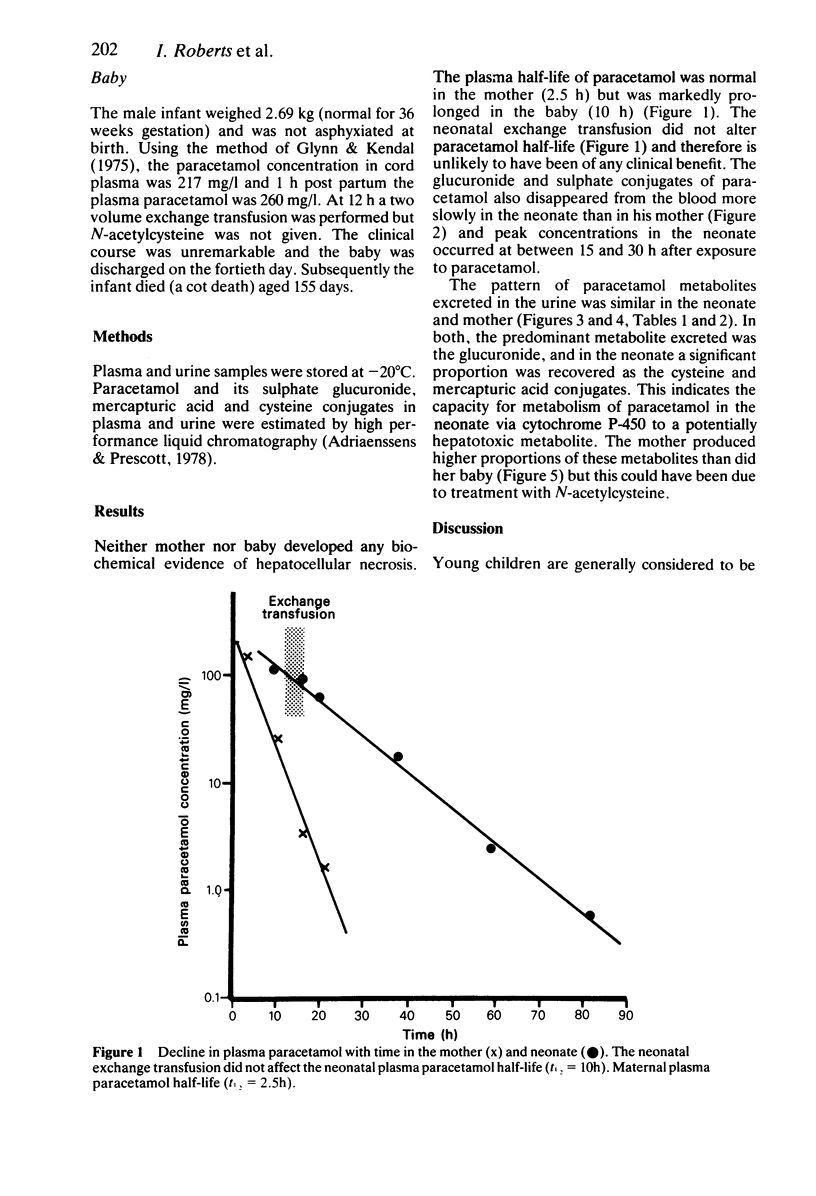
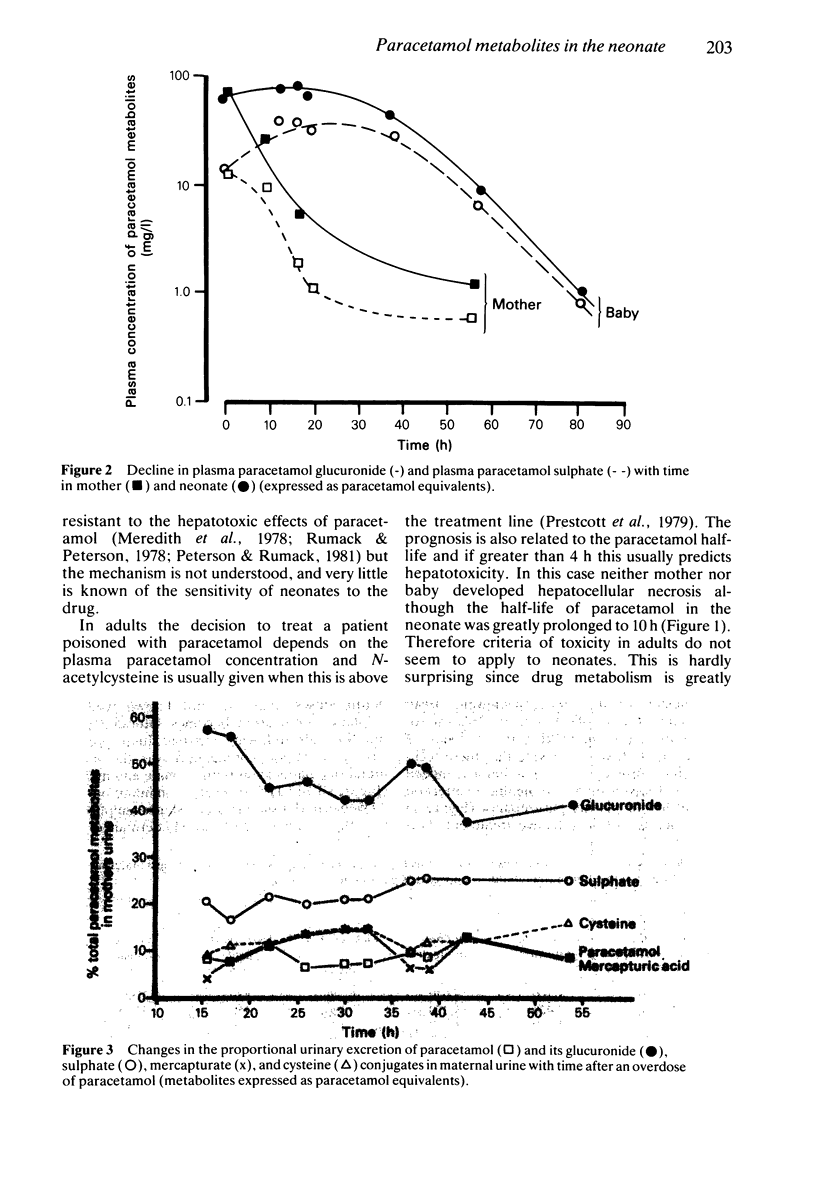
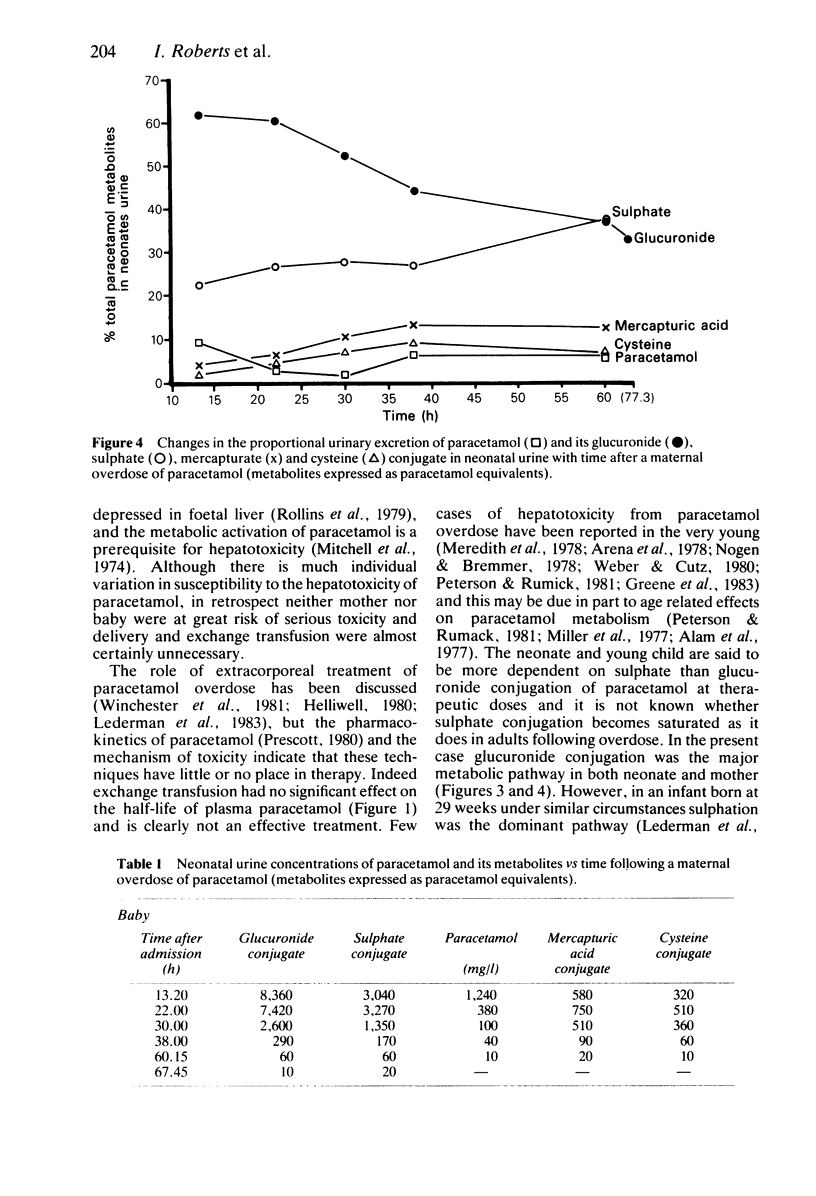
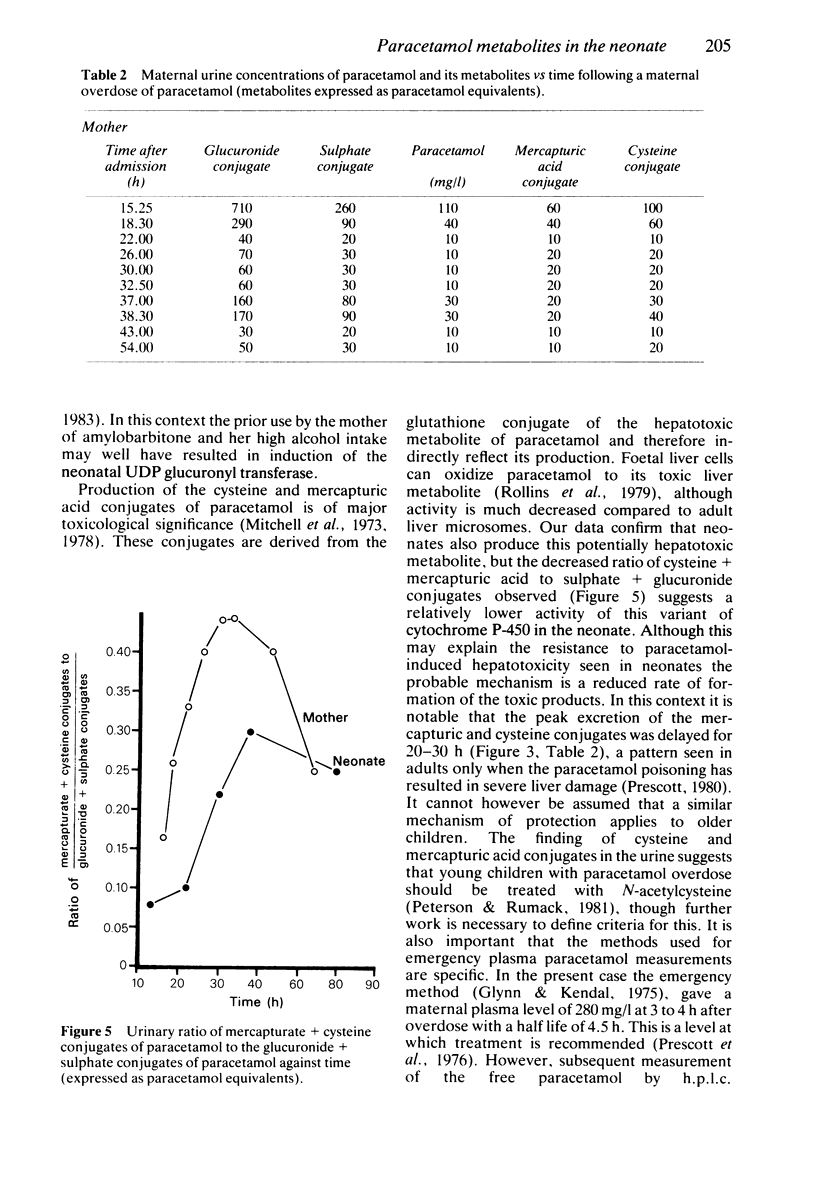
A case of paracetamol overdose in a 36 week pregnant woman is described. The baby was delivered by Caesarian section 6 h after the overdose. The mother but not the baby was treated with N-acetylcysteine and neither suffered liver damage. The plasma paracetamol half-life was prolonged to 10 h in the neonate compared to 2.5 h in the mother and was unaffected by a two volume exchange transfusion. The pattern of urinary metabolites in the neonate was similar to that observed in the mother, but there was a marked delay in the time taken to reach peak plasma concentrations of metabolites. This is consistent with a very slow biotransformation of the drug and may explain the relative resistance of very young children to the hepatotoxicity of paracetamol. There was no evidence of limited or decreasing capacity in sulphate conjugation nor was sulphation the major metabolic pathway. In retrospect both the obstetrical intervention and the exchange transfusion were unnecessary.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adriaenssens P. I., Prescott L. F. High performance liquid chromatographic estimation of paracetamol metabolites in plasma. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;6(1):87–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam S. N., Roberts R. J., Fischer L. J. Age-related differences in salicylamide and acetaminophen conjugation in man. J Pediatr. 1977 Jan;90(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80787-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arena J. M., Rourk M. H., Jr, Sibrack C. D. Acetaminophen: report of an unusual poisoning. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):68–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. W., Craft L., Ghishan F. Acetaminophen poisoning in infancy. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Apr;137(4):386–387. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140300064018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helliwell M. Severe barbiturate and paracetamol overdose: the simultaneous removal of both poisons by haemoperfusion. Postgrad Med J. 1980 May;56(655):363–365. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.56.655.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman S., Fysh W. J., Tredger M., Gamsu H. R. Neonatal paracetamol poisoning: treatment by exchange transfusion. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Aug;58(8):631–633. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.8.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith T. J., Newman B., Goulding R. Paracetamol poisoning in children. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 12;2(6135):478–479. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6135.478-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith T. J., Vale J. A., Goulding R. The epidemiology of acute acetaminophen poisoning in England and Wales. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Feb 23;141(3 Spec No):397–400. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. P., Roberts R. J., Fischer L. J. Acetaminophen elimination kinetics in neonates, children, and adults. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Mar;19(3):284–294. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976193284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. R., Jollow D. J., Potter W. Z., Davis D. C., Gillette J. R., Brodie B. B. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. I. Role of drug metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Oct;187(1):185–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. R., McMurtry R. J., Statham C. N., Nelson S. D. Molecular basis for several drug-induced nephropathies. Am J Med. 1977 Apr;62(4):518–526. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. R., Thorgeirsson S. S., Potter W. Z., Jollow D. J., Keiser H. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury: protective role of glutathione in man and rationale for therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Oct;16(4):676–684. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974164676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogen A. G., Bremner J. E. Fatal acetaminophen overdosage in a young child. J Pediatr. 1978 May;92(5):832–833. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. G., Rumack B. H. Age as a variable in acetaminophen overdose. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Feb 23;141(3 Spec No):390–393. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. G., Rumack B. H. Pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen in children. Pediatrics. 1978 Nov;62(5 Pt 2 Suppl):877–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Illingworth R. N., Critchley J. A., Stewart M. J., Adam R. D., Proudfoot A. T. Intravenous N-acetylcystine: the treatment of choice for paracetamol poisoning. Br Med J. 1979 Nov 3;2(6198):1097–1100. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6198.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F. Kinetics and metabolism of paracetamol and phenacetin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;10 (Suppl 2):291S–298S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Roscoe P., Wright N., Brown S. S. Plasma-paracetamol half-life and hepatic necrosis in patients with paracetamol overdosage. Lancet. 1971 Mar 13;1(7698):519–522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Sutherland G. R., Park J., Smith I. J., Proudfoot A. T. Cysteamine, methionine, and penicillamine in the treatment of paracetamol poisoning. Lancet. 1976 Jul 17;2(7977):109–113. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92842-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F. Treatment of severe acetaminophen poisoning with intravenous acetylcysteine. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Feb 23;141(3 Spec No):386–389. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.3.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. E., von Bahr C., Glaumann H., Moldéus P., Rane A. Acetaminophen: potentially toxic metabolite formed by human fetal and adult liver microsomes and isolated fetal liver cells. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1414–1416. doi: 10.1126/science.38505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumack B. H., Meredith T. J., Peterson R. G., Prescott L. F., Vale J. A. Panel discussion. Management of acetaminophen overdose. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Feb 23;141(3 Spec No):401–403. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumack B. H., Peterson R. G. Acetaminophen overdose: incidence, diagnosis, and management in 416 patients. Pediatrics. 1978 Nov;62(5 Pt 2 Suppl):898–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Cutz E. Liver failure in an infant. Can Med Assoc J. 1980 Jul 19;123(2):112–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester J. F., Gelfand M. C., Helliwell M., Vale J. A., Goulding R., Schreiner G. E. Extracorporeal treatment of salicylate or acetaminophen poisoning--is there a role? Arch Intern Med. 1981 Feb 23;141(3 Spec No):370–374. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.3.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


