Abstract
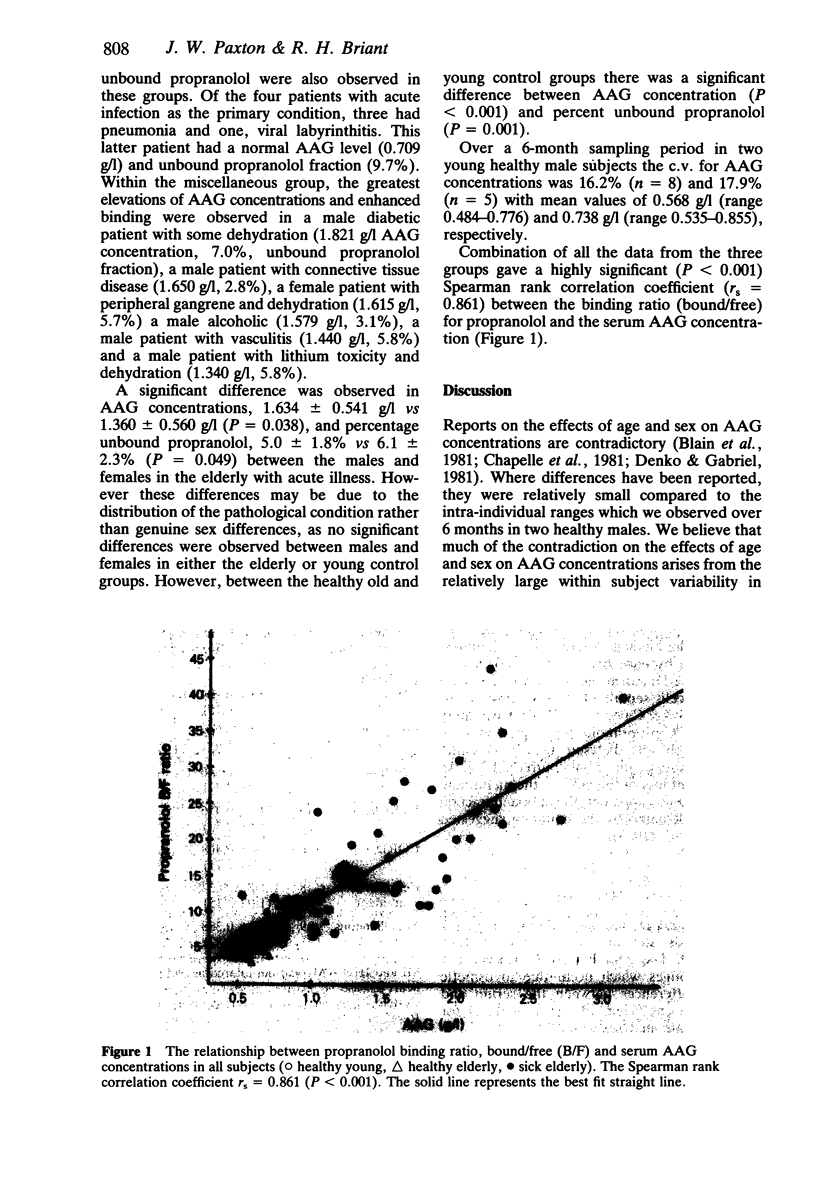
Alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) concentrations and propranolol binding were investigated in the serum of elderly hospitalized patients with acute illness, and healthy elderly and young subjects. Significantly greater AAG concentrations and reduced unbound propranolol fraction were observed in the elderly with acute disease compared to the elderly controls. The greatest changes (up to five-fold) occurred with cancer, with lesser changes associated with myocardial infarction and ischaemic heart disease, acute infection, heart failure, chronic obstructive respiratory disease, and cerebrovascular accident. Various miscellaneous conditions were also associated with high AAG concentrations and enhanced propranolol binding. The healthy elderly had higher AAG concentrations and lower unbound propranolol fractions than the healthy young group. Overall there was a highly significant correlation between the propranolol binding ratio (bound/free) and the serum AAG concentration. These results suggest that the elderly population may be particularly susceptible to changes in AAG concentrations, and that during acute illness interpretation of serum concentrations of drugs which bind mainly to AAG, may require knowledge of their free fractions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson F. P. Methadone plasma protein binding: alterations in cancer and displacement from alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Nov;32(5):652–658. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booker H. E., Darcey B. Serum concentrations of free diphenylhydantoin and their relationship to clinical intoxication. Epilepsia. 1973 Jun;14(2):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1973.tb03954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgå O., Piafsky K. M., Nilsen O. G. Plasma protein binding of basic drugs. I. Selective displacement from alpha 1-acid glycoprotein by tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Nov;22(5 Pt 1):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle J. P., Albert A., Smeets J. P., Heusghem C., Kulbertus H. E. The prognostic significance of serum alpha 1-acid glycoprotein changes in acute myocardial infarction. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Sep 10;115(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denko C. W., Gabriel P. Age and sex related levels of albumin, ceruloplasmin, alpha 1 antitrypsin, alpha 1 acid glycoprotein, and transferrin. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1981 Jan-Feb;11(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. D., Oie S. Effect of altered disopyramide binding on its pharmacologic response in rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):469–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Craig W. A., Kornguth M., Monson R. Influence of binding on the pharmacologic activity of antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Nov 26;226:214–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb20483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima J. J., Boudoulas H., Blanford M. Concentration-dependence of disopyramide binding to plasma protein and its influence on kinetics and dynamics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Dec;219(3):741–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt D. G., Frisk-Holmberg M., Hollifield J. W., Shand D. G. Plasma binding and the affinity of propranolol for a beta receptor in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Aug;20(2):152–157. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976202152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meffin P. J., Robert E. W., Winkle R. A., Harapat S., Peters F. A., Harrison D. C. Role of concentration-dependent plasma protein binding in disopyramide disposition. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1979 Feb;7(1):29–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01059439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxton J. W. Alpha 1 -acid glycoprotein and binding of basic drugs. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;5(9):635–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxton J. W., Calder R. L. Propranolol binding in serum: comparison of methods and investigation of effects of drug concentration, pH, and temperature. J Pharmacol Methods. 1983 Aug;10(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(83)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M., Borgá O., Odar-Cederlöf I., Johansson C., Sjöqvist F. Increased plasma protein binding of propranolol and chlorpromazine mediated by disease-induced elevations of plasma alpha1 acid glycoprotein. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1435–1439. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Stargel W. W., Wagner G. S., Shand D. G. Increased plasma propranolol binding in myocardial infarction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;9(4):438–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozer T. N., Gambertoglio J. G., Furst D. E., Avery D. S., Holford N. H. Volume shifts and protein binding estimates using equilibrium dialysis: application to prednisolone binding in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Dec;72(12):1442–1446. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600721218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand U. W., Hintze K. L., Slattery J. T., Levy G. Protein binding of several drugs in serum and plasma of healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Mar;27(3):297–300. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo E., Greenblatt D. J. Pharmacokinetic and clinical implications of quinidine protein binding. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Apr;68(4):466–470. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


