Abstract
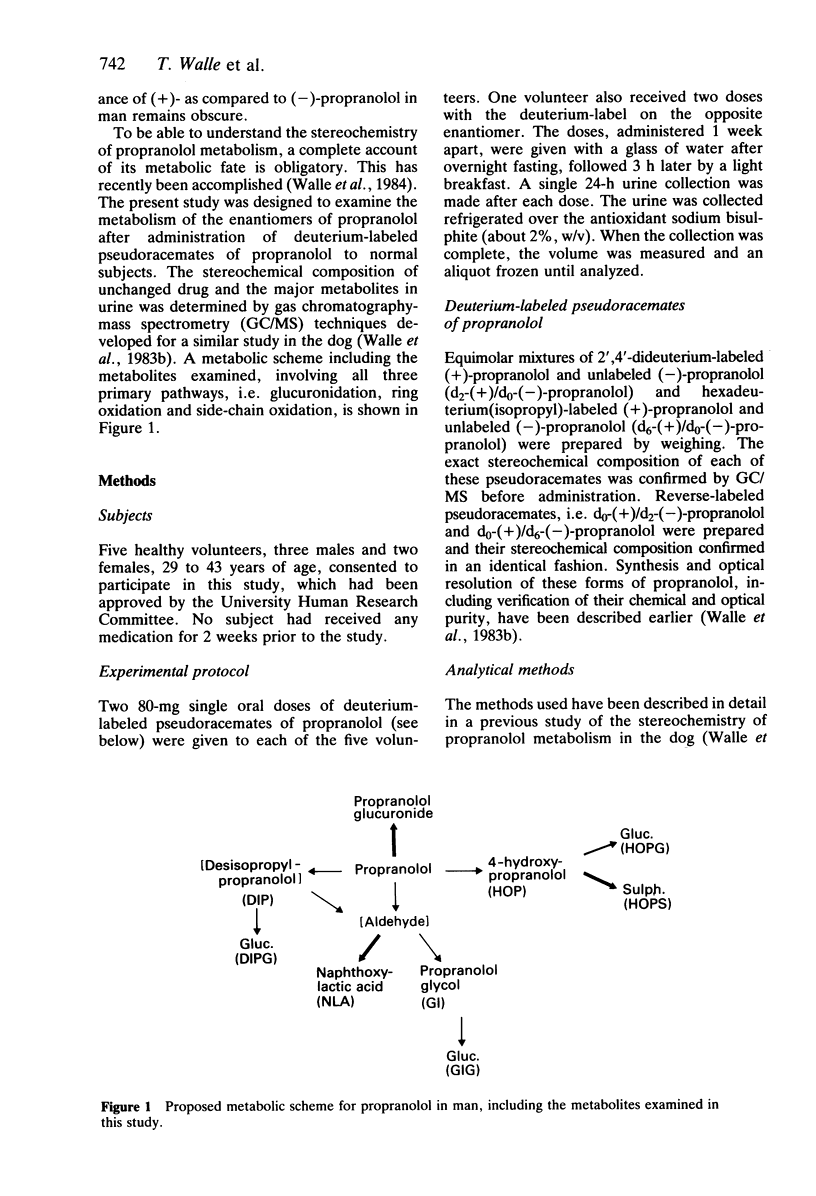
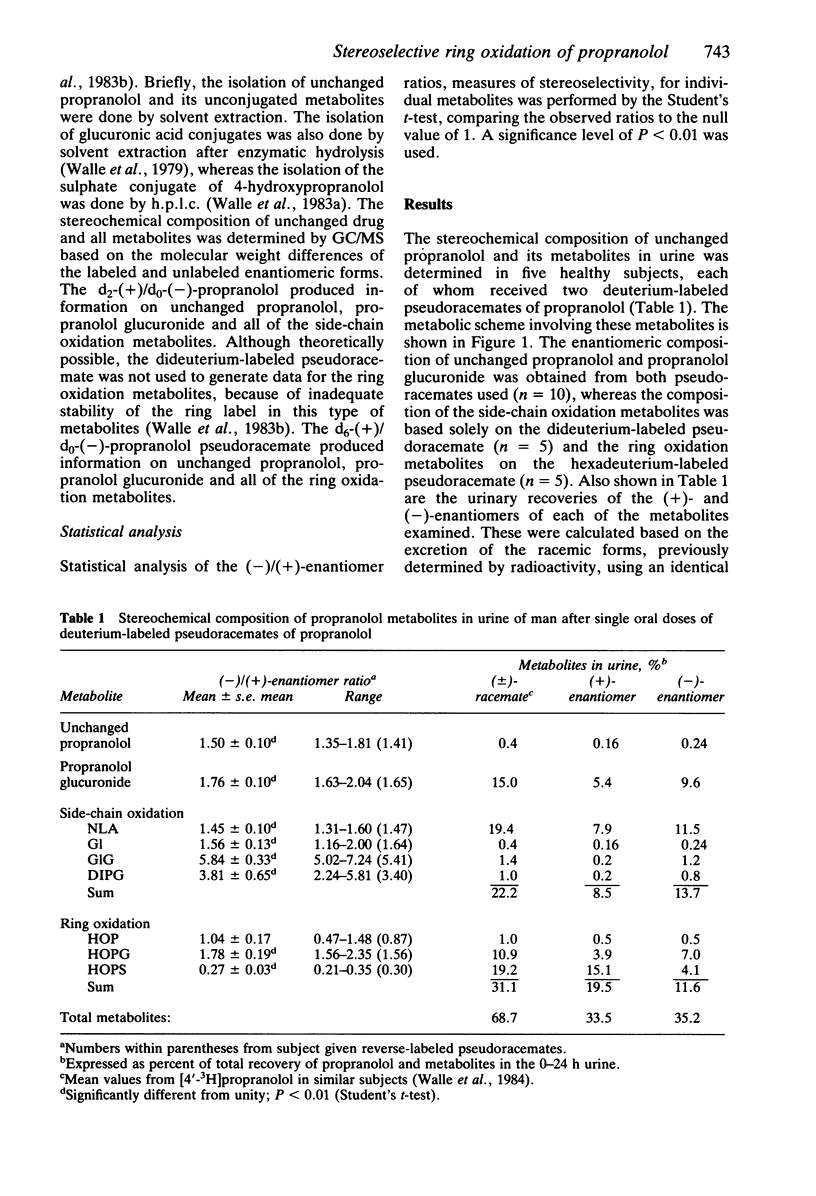
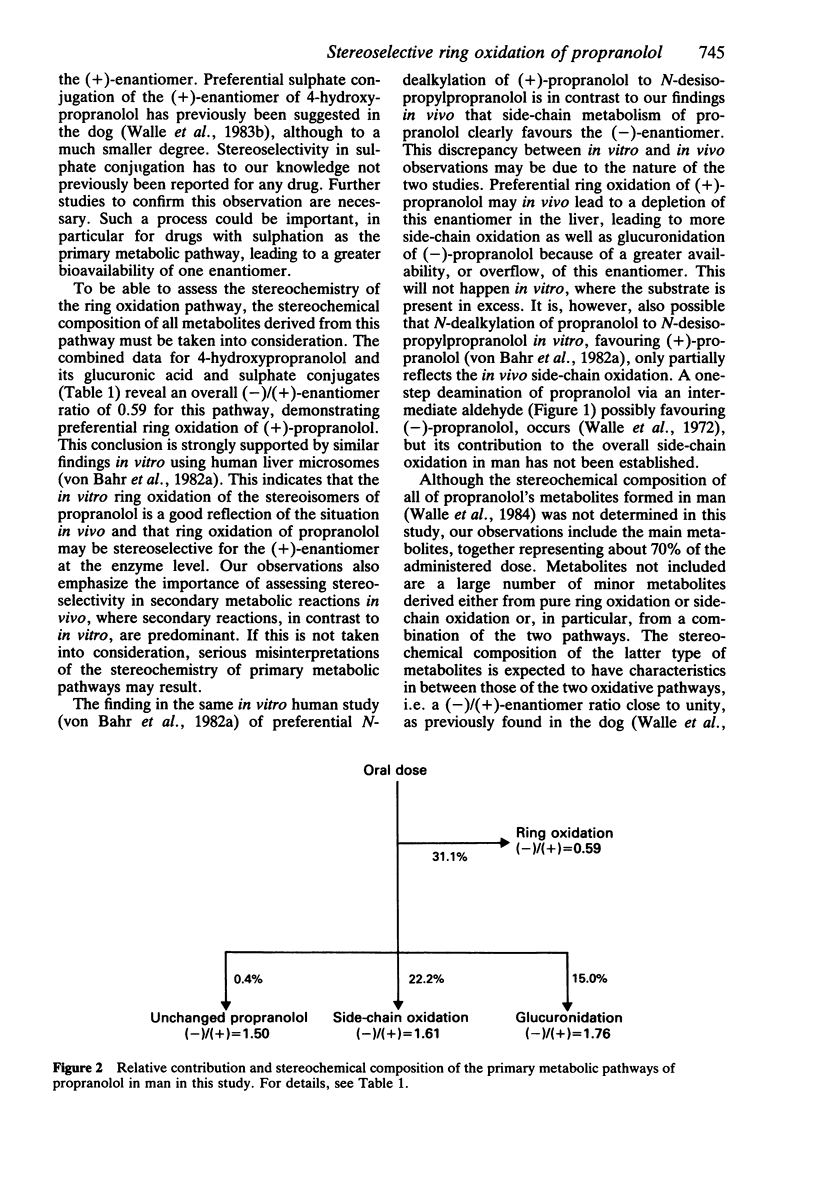
The objective of this study was to elucidate stereoselective mechanisms of propranolol metabolism in man. Five normal subjects were given single 80 mg oral doses of deuterium-labeled pseudoracemates of propranolol, and the stereochemical composition of propranolol and its major metabolites in urine was determined by GC/MS. The (-)/(+)-enantiomer ratios for unchanged propranolol, 1.50 +/- 0.10 (mean +/- s.e. mean), and propranolol glucuronide, 1.76 +/- 0.10, were similar to previous findings in plasma. All products of side-chain oxidation also consisted mainly of the (-)-enantiomer, with an overall (-)/(+) ratio of 1.61 +/- 0.11. A (-)/(+) ratio of 1.04 +/- 0.17 for 4-hydroxypropranolol did not indicate stereoselectivity in ring oxidation. However, the ratio for its glucuronic acid conjugate of 1.78 +/- 0.19 and for its sulphate conjugate of 0.27 +/- 0.03 suggested stereoselectivity in either the glucuronidation or sulphation of 4-hydroxypropranolol, or both. When the stereoselectivity in these secondary pathways was taken into consideration, the overall ring oxidation strongly favoured (+)-propranolol with a (-)/(+)-enantiomer ratio of 0.59 +/- 0.09. The composite observations of the stereochemistry of propranolol metabolism in man are consistent with stereoselective ring oxidation of (+)-propranolol, leading to a greater bioavailability of the pharmacologically more active (-)-propranolol and subsequent preferential side-chain oxidation and glucuronidation of this enantiomer.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bai S. A., Wilson M. J., Walle U. K., Walle T. Stereoselective increase in propranolol bioavailability during chronic dosing in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Nov;227(2):360–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargar E. M., Walle U. K., Bai S. A., Walle T. Quantitative metabolic fate of propranolol in the dog, rat, and hamster using radiotracer, high performance liquid chromatography, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry techniques. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 May-Jun;11(3):266–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltart D. J., Shand D. G. Plasma propranolol levels in the quaniitative assessment of beta-adrenergic blockade in man. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 26;3(5725):731–734. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5725.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. H., Shand D. G. Disposition of propranolol. V. Drug accumulation and steady-state concentrations during chronic oral administration in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Jul-Aug;14(4):487–493. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973144part1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. D., O'Donnell S. R. Pharmacology of 4-hydroxypropranolol, a metabolite of propranolol. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;43(1):222–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. L., Powell M. L. Evidence for an arene oxide-NIH shift pathway in the metabolic conversion of propranolol to 4'-hydroxypropranolol in the rat and in man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1979 Nov-Dec;7(6):351–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oatis J. E., Jr, Russell M. P., Knapp D. R., Walle T. Ring-hydroxylated propranolol: synthesis and beta-receptor antagonist and vasodilating activities of the seven isomers. J Med Chem. 1981 Mar;24(3):309–314. doi: 10.1021/jm00135a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olanoff L. S., Walle T., Walle U. K., Cowart T. D., Gaffney T. E. Stereoselective clearance and distribution of intravenous propranolol. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Jun;35(6):755–761. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Rangno R. E. The disposition of propranolol. I. Elimination during oral absorption in man. Pharmacology. 1972;7(3):159–168. doi: 10.1159/000136285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber B., Holford N. H., Riegelman S. Stereoselective disposition and glucuronidation of propranolol in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Jun;71(6):699–704. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Hull J. E., Norris K. J. Glucuronidation of propranolol and 4'-hydroxypropranolol. Substrate specificity and stereoselectivity of rat liver microsomal glucuronyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos. 1981 Sep-Oct;9(5):466–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Bahr C., Hermansson J., Tawara K. Plasma levels of (+) and (-)-propranolol and 4-hydroxypropranolol after administration of racemic (+/-)-propranolol in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;14(1):79–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb04937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Conradi E. C., Walle U. K., Fagan T. C., Gaffney T. E. 4-Hydroxypropranolol and its glucuronide after single and long-term doses of propranolol. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Jan;27(1):22–31. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Conradi E. C., Walle U. K., Fagan T. C., Gaffney T. E. The predictable relationship between plasma levels and dose during chronic propranolol therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Dec;24(6):668–677. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978246668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Fagan T. C., Conradi E. C., Walle U. K., Gaffney T. E. Presystemic and systemic glucuronidation of propranolol. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Aug;26(2):167–172. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979262167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Ishizaki T., Gaffney T. E. Isopropylamine, a biologically active deamination product of propranolol in dogs: identification of deuterated and unlabeled isopropylamine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Dec;183(3):508–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Oatis J. E., Jr, Walle U. K., Knapp D. R. New ring-hydroxylated metabolites of propranolol: species differences and stereospecific 7-hydroxylation. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982 Mar-Apr;10(2):122–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Walle U. K., Knapp D. R., Conradi E. C., Bargar E. M. Identification of major sulfate conjugates in the metabolism of propranolol in dog and man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 Jul-Aug;11(4):344–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Walle U. K. Stereoselective oral bioavailability of (+/-)-propranolol in the dog. A GC-MS study using a stable isotope technique. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;23(3):453–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle T., Wilson M. J., Walle U. K., Bai S. A. Stereochemical composition of propranolol metabolites in the dog using stable isotope-labeled pseudoracemates. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):544–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walle U. K., Walle T., Bai S. A., Olanoff L. S. Stereoselective binding of propranolol to human plasma, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, and albumin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Dec;34(6):718–723. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. J., Carr K., Vestal R. E., Belcher S., Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Direct measurement of propranolol bioavailability during accumulation to steady-state. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;6(4):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb00862.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr C., Hermansson J., Lind M. Oxidation of (R)- and (S)-propranolol in human and dog liver microsomes. Species differences in stereoselectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):458–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


