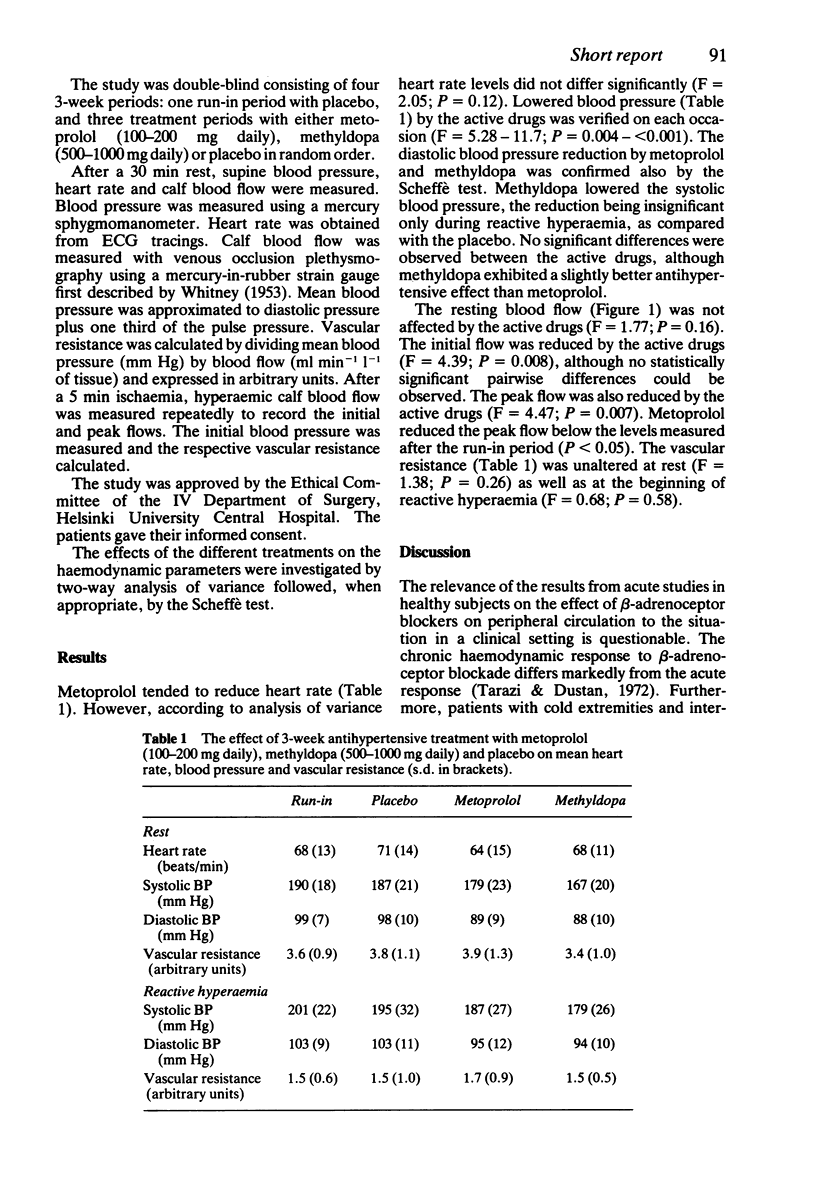
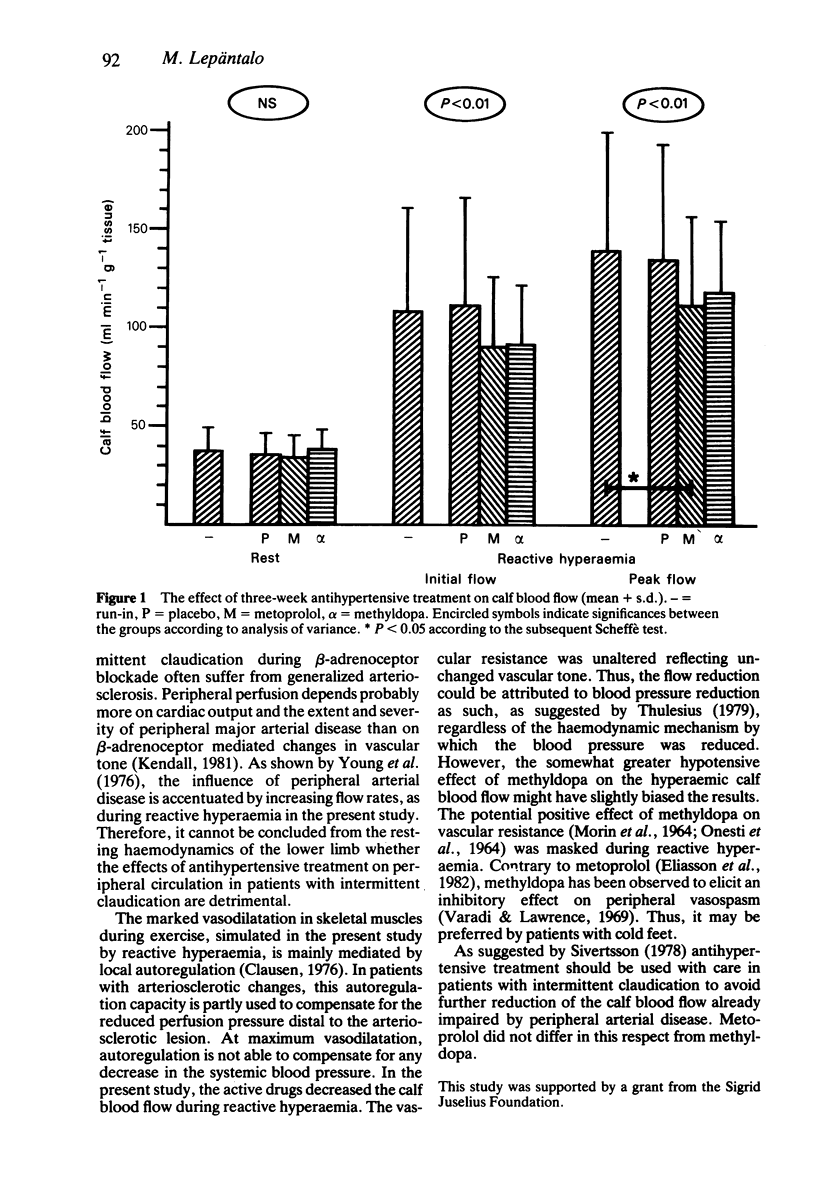
Abstract
In a placebo-controlled double-blind study 14 hypertensive patients with intermittent claudication were treated with metoprolol (100-200 mg daily) and methyldopa (500-1000 mg daily) for 3 weeks and their effects on heart rate, blood pressure as well as on resting and hyperaemic calf blood flow and vascular resistance were compared. In their antihypertensive effect metoprolol and methyldopa did not differ significantly. In 23 diseased limbs the calf blood flow and vascular resistance remained unchanged at rest during the trial. The active drugs reduced hyperaemic flow (P less than 0.05). The peak flow was reduced by 20% (P greater than 0.01) with metoprolol and by 15% with methyldopa below the initial level and by 17% and by 12% below the level recorded on placebo, respectively. Neither of the drugs influenced vascular resistance during reactive hyperaemia. Thus, in patients with intermittent claudication antihypertensives should be used with care.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clausen J. P. Circulatory adjustments to dynamic exercise and effect of physical training in normal subjects and in patients with coronary artery disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1976 May-Jun;18(6):459–495. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(76)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson K., Lins L. E., Sundqvist K. Peripheral vasospasm during beta-receptor blockade - a comparison between metoprolol and pindolol. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1982;665:109–112. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1982.tb00417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J. Are selective beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs an advantage? J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1981 Jan;15(1):33–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepäntalo M., Tötterman K. J. Effect of long-term beta-adrenergic-blockade on calf blood flow in hypertensive patients. Clin Physiol. 1983 Feb;3(1):35–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1983.tb00696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIN Y., TURMEL L., FORTIER J. METHYLDOPA: CLINICAL STUDIES IN ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Dec;248:633–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONESTI G., BREST A. N., NOVACK P., KASPARIAN H., MOYER J. H. PHARMACODYNAMIC EFFECTS OF ALPHA-METHYL DOPA IN HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS. Am Heart J. 1964 Jan;67:32–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(64)90395-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger J. C., Sheldon C. D., Lerski R. A., Livingstone W. R. Intermittent claudication complicating beta-blockade. Br Med J. 1976 May 8;1(6018):1125–1125. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6018.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivertsson R. Effect of blood pressure reduction on tissue perfusion. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1979;628:13–16. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb00763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Warren D. J. Effect of beta-blocking drugs on peripheral blood flow in intermittent claudication. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):2–4. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198201000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarazi R. C., Dustan H. P. Beta adrenergic blockade in hypertension. Practical and theoretical implications of long-term hemodynamic variations. Am J Cardiol. 1972 May;29(5):633–640. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadi D. P., Lawrence A. M. Suppression of Raynaud's phenomenon by methyldopa. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Jul;124(1):13–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITNEY R. J. The measurement of volume changes in human limbs. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):1–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. F., Cholvin N. R., Kirkeeide R. L., Roth A. C. Hemodynamics of arterial stenoses at elevated flow rates. Circ Res. 1977 Jul;41(1):99–107. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


