Abstract
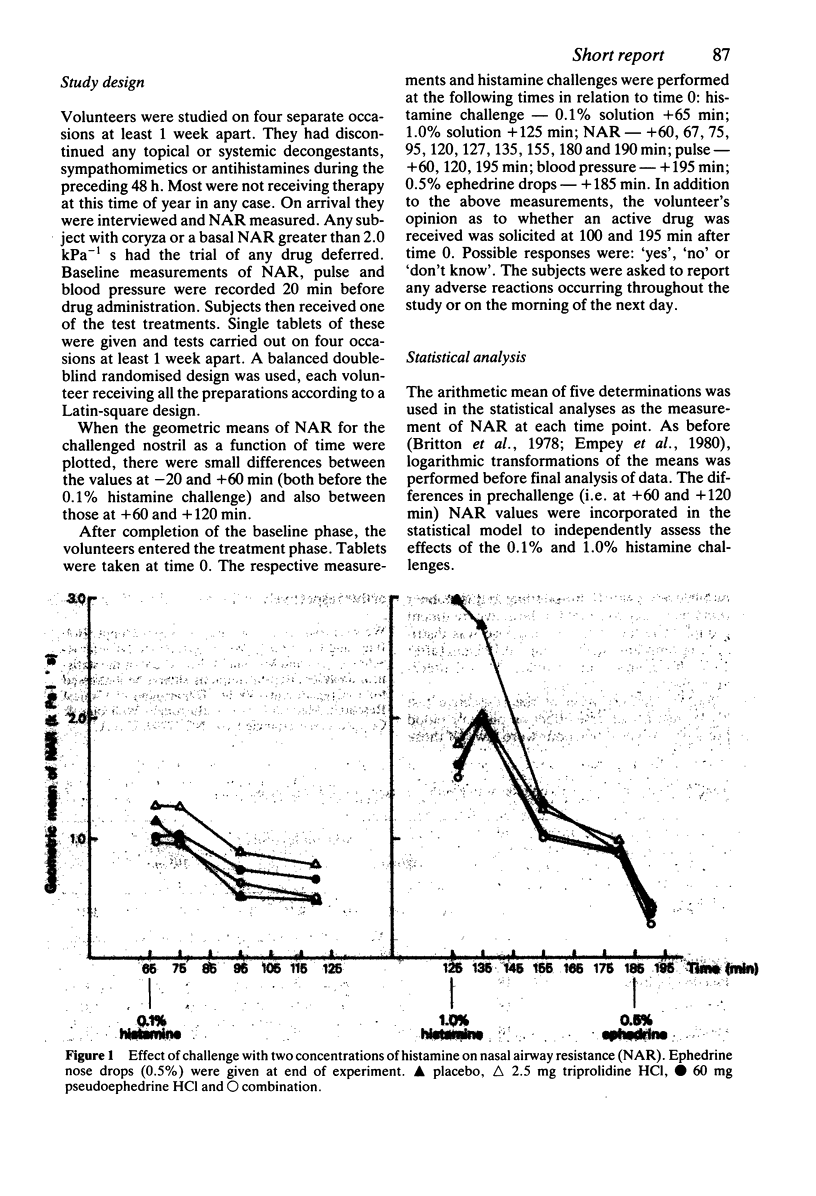
The abilities of triprolidine 2.5 mg and pseudoephedrine 60 mg, alone and in combination, to protect against an increase in nasal airway resistance (NAR) after histamine challenge were determined in eighteen individuals with grass pollen allergy. The study was conducted outside the pollen season using a double-blind, placebo controlled crossover design. The prior administration of pseudoephedrine 60 mg and triprolidine 2.5 mg alone or in combination was superior to placebo in reducing the increase in NAR after challenge with 1.0% histamine. However, such NAR measurements did not differentiate between pseudoephedrine 60 mg and triprolidine 2.5 mg administered alone or in combination. Challenge with 0.1% histamine failed to discriminate between any of the test medications.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britton M. G., Empey D. W., John G. C., McDonnell K. A., Hughes D. T. Histamine challenge and anterior nasal rhinometry: their use in the assessment of pseudoephedrine and triprolidine as nasal decongestants in subjects with hayfever. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;6(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell J. T., Williams B. O., Allen S., Cato A., Perkins J. G. A double-blind controlled evaluation of Actifed and its individual constituents in allergic rhinitis. J Int Med Res. 1982;10(5):341–347. doi: 10.1177/030006058201000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Empey D. W., Young G. A., Letley E., John G. C., Smith P., McDonnell K. A., Bagg L. R., Hughes D. T. Dose-response study of the nasal decongestant and cardiovascular effects of pseudoephedrine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;9(4):351–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Ollier S., Davies R. J. Use of anterior rhinometry in nasal provocation challenges with allergen and evaluation of the effects of ketotifen, clemastine and sodium cromoglycate on these responses. Respiration. 1980;39 (Suppl 1):26–31. doi: 10.1159/000195035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


