Abstract
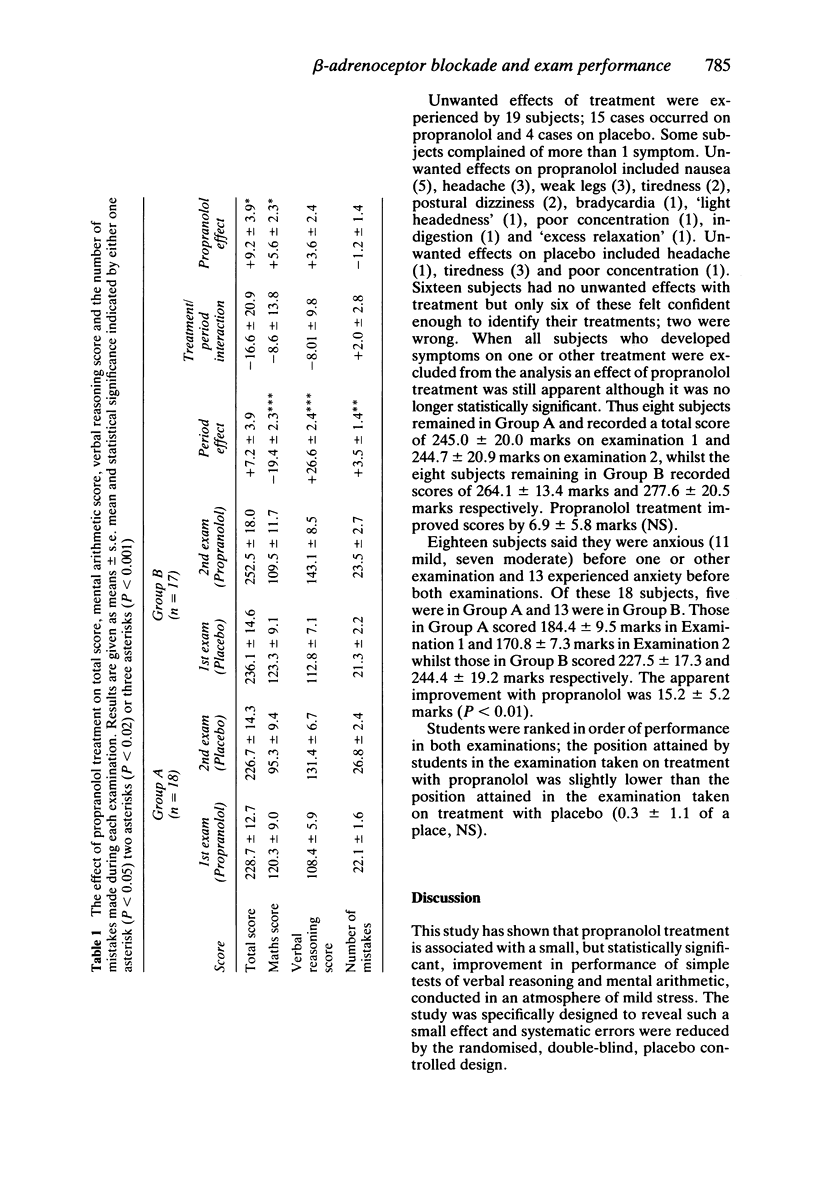
Simple tests of verbal reasoning and mental arithmetic, taken under mildly stressful conditions, have been shown to give a reproducible test of intellectual function within groups of normal subjects. Using these tests, in two separate examinations, a double-blind cross-over study was performed on 35 medical students to assess the effects of acute beta-adrenoceptor blockade with propranolol on intellectual function. With placebo treatment, students recorded an average total score of 231.3 marks, with average scores of 108.9 marks on the mental arithmetic paper and 122.4 marks on the verbal reasoning paper. Treatment with propranolol was associated with an improvement in total score of 9.2 +/- 3.9 marks (P less than 0.05), an improvement in mental arithmetic score of 5.6 +/- 2.3 marks (P less than 0.05) and an improvement in verbal reasoning score of 3.6 +/- 2.4 marks (NS). Eighteen out of the 35 students said that they were mildly anxious before one examination and 13 students said they were anxious before both examinations. Those students who admitted anxiety seemed to benefit the most, in terms of improved examination performance, from treatment with propranolol.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bai T. R., Webb D., Hamilton M. Treatment of hypertension with beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1982 Oct;16(4):239–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer C. Beneficial effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on "exam. nerves". Lancet. 1972 Aug 26;2(7774):435–435. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91840-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltart D. J., Shand D. G. Plasma propranolol levels in the quaniitative assessment of beta-adrenergic blockade in man. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 26;3(5725):731–734. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5725.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills M., Armitage P. The two-period cross-over clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;8(1):7–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb05903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack D. B., Dean S., Kendall M. J. Detection of some antihypertensive drugs and their metabolites in urine by thin-layer chromatography. Five commonly used beta blockers and hydralazine. J Chromatogr. 1980 Jan 4;187(1):277–280. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)87901-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. M., Burgoyne W., Savage I. T. Effect of pindolol on stress-related disturbances of musical performance: preliminary communication. J R Soc Med. 1983 Mar;76(3):194–196. doi: 10.1177/014107688307600308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. M., Griffith D. N., Pearson R. M., Newbury P. Effect of oxprenolol on stage-fright in musicians. Lancet. 1977 Nov 5;2(8045):952–954. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90890-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson G., Regàrdh C. G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of beta-adrenoreceptor blocking drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1976;1(4):233–263. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197601040-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


