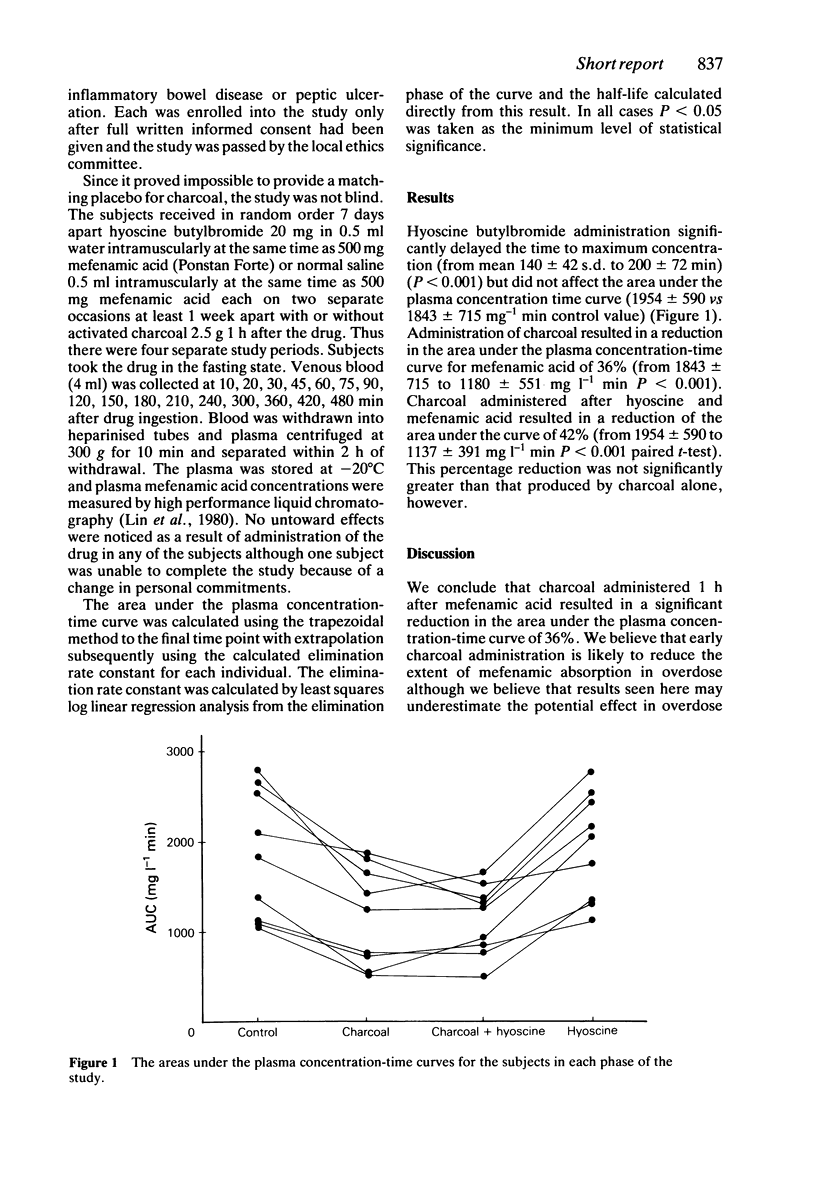
Abstract
Mefenamic acid 500 mg orally was administered to nine healthy volunteers on four occasions 7 days apart. On two occasions allocated at random, activated charcoal (2.5 g of medicoal) was administered 1 h after the drug. Hyoscine butylbromide (20 mg intramuscularly) was given immediately after mefenamic acid on one of these occasions, and on one occasion after mefenamic acid without charcoal. Hyoscine significantly delayed the time to maximum mefenamic acid concentrations but did not affect the area under the plasma concentration-time curve. Charcoal reduced the area under the plasma concentration curve by 36% and charcoal and hyoscine reduced the area under the plasma concentration curve by 42% from their respective control values. We conclude that early charcoal administration in a ratio of 5 g to 1 g of drug effectively reduces the area under the plasma concentration-time curve after oral mefenamic acid administration. Early charcoal administration may be of value therefore in reducing the toxicity of mefenamic acid after deliberate or accidental overdosage.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balali-Mood M., Critchley J. A., Proudfoot A. T., Prescott L. F. Mefenamic acid overdosage. Lancet. 1981 Jun 20;1(8234):1354–1356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92528-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Houston J. B. Effect of activated charcoal on acetaminophen absorption. Pediatrics. 1976 Sep;58(3):432–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Tsuchiya T. Effect of activated charcoal on aspirin absorption in man. Part I. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 May-Jun;13(3):317–322. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972133317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. K., Lee C. S., Perrin J. H. Determination of two fenamates in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Sci. 1980 Jan;69(1):95–97. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600690128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


