Full text
PDF







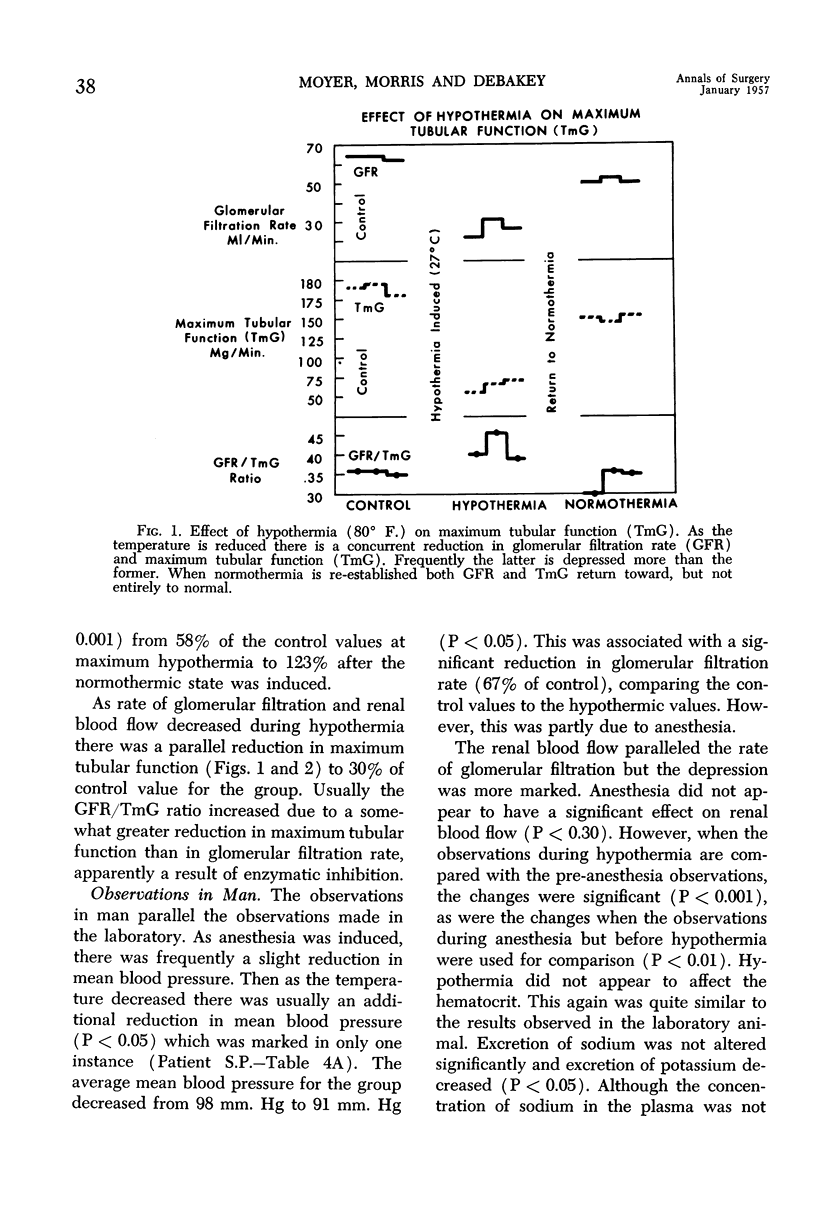
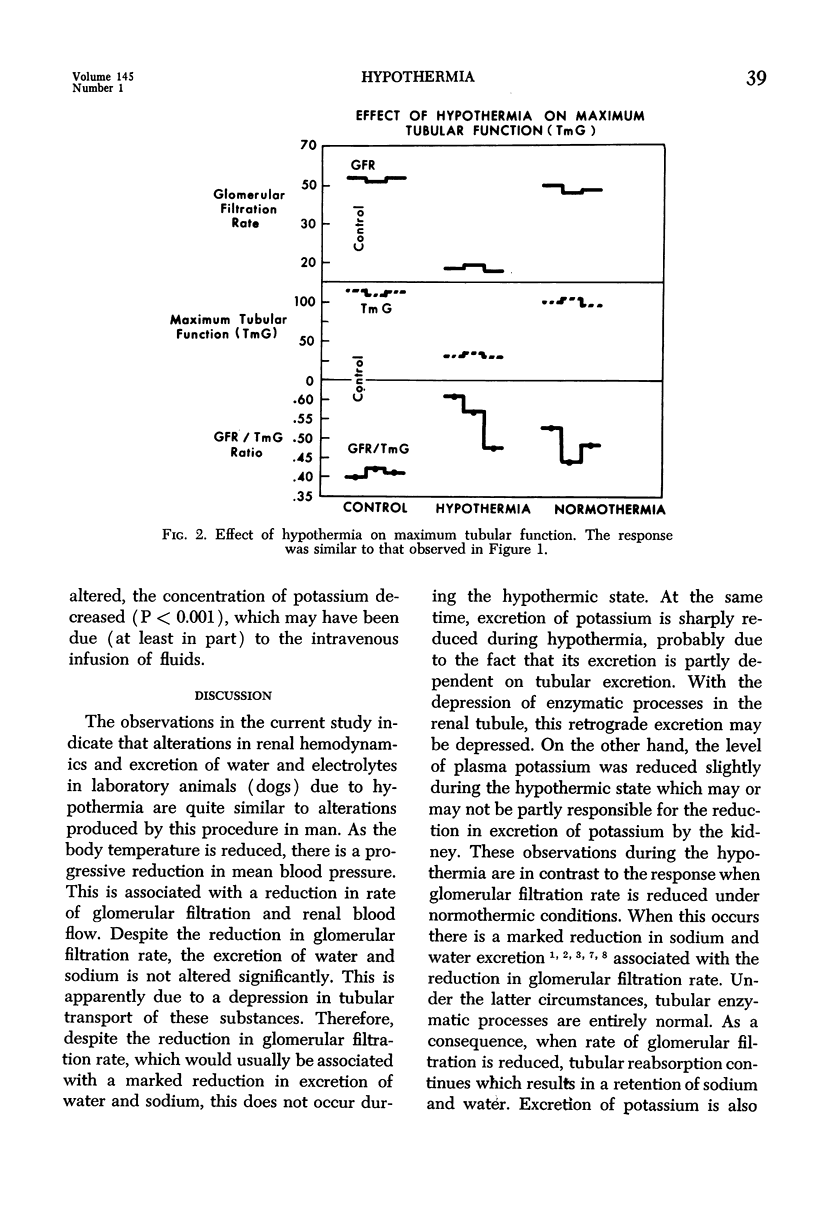

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HANDLEY C. A., MOYER J. H. Changes in sodium and water excretion produced by vaso-active and by ganglionic and adrenergic blocking agents. Am J Physiol. 1954 Aug;178(2):309–314. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS J. M., BUIE R. M., SEVIER S. M., HARRISON T. R. The effect of posture and of congestion of the head on sodium excretion in normal subjects. Circulation. 1950 Dec;2(6):822–827. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.2.6.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS L. C., MOYER J. H. The acute effects of hexamethonium on renal hemodynamics in normotensive and hypertensive human subjects. Am J Med Sci. 1953 Jul;226(1):1–15. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195307000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
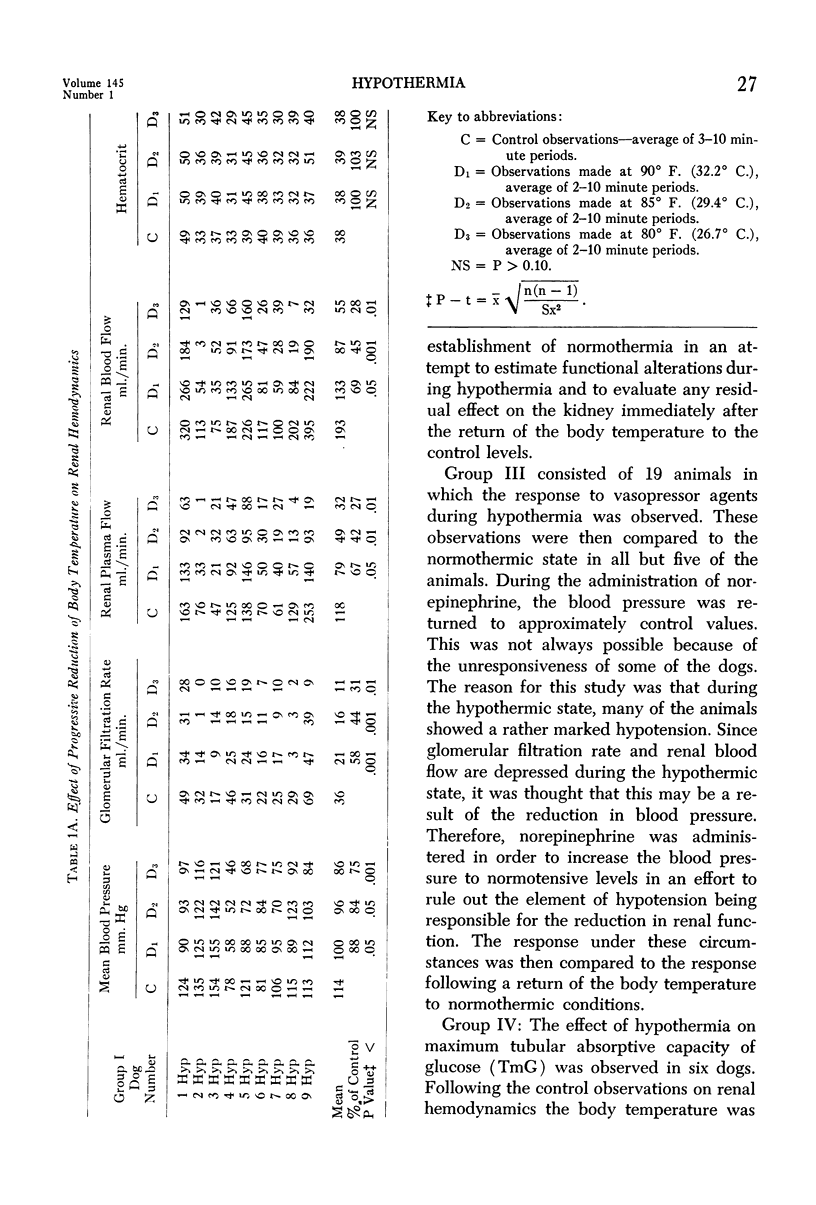
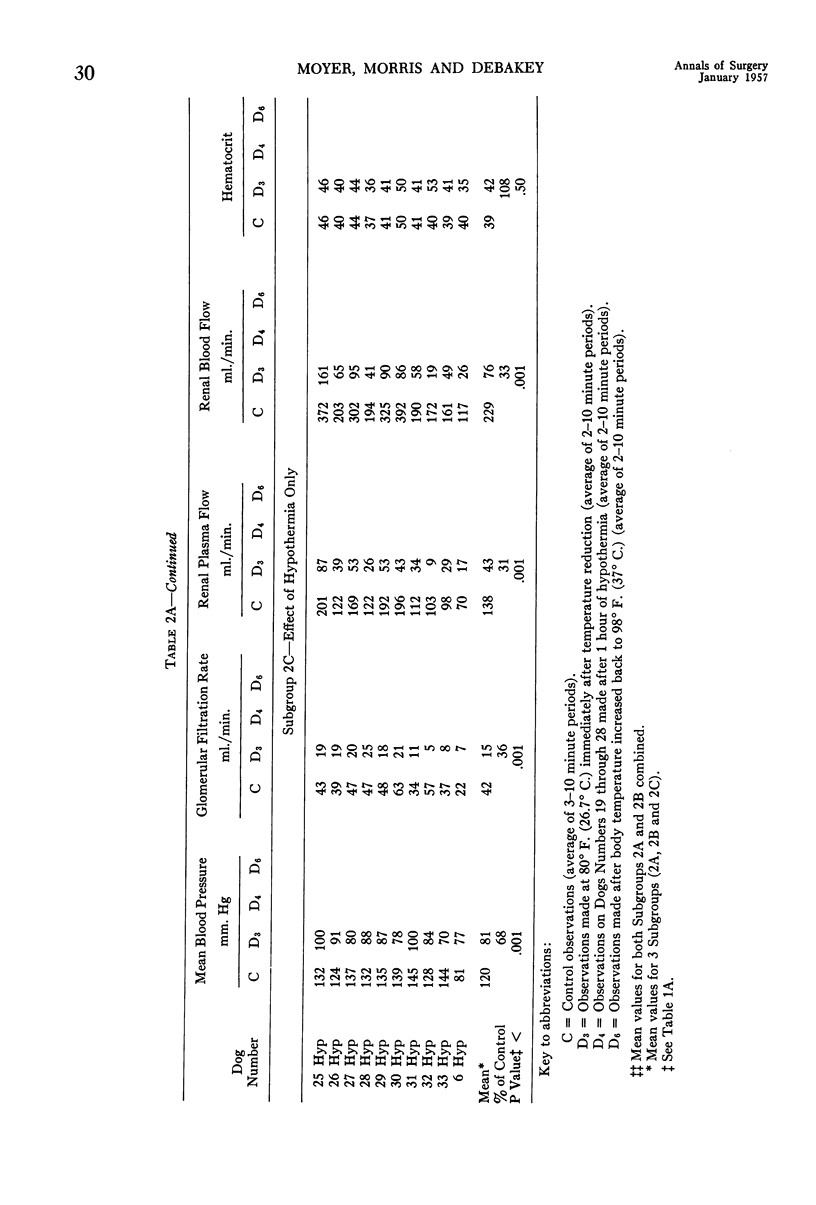
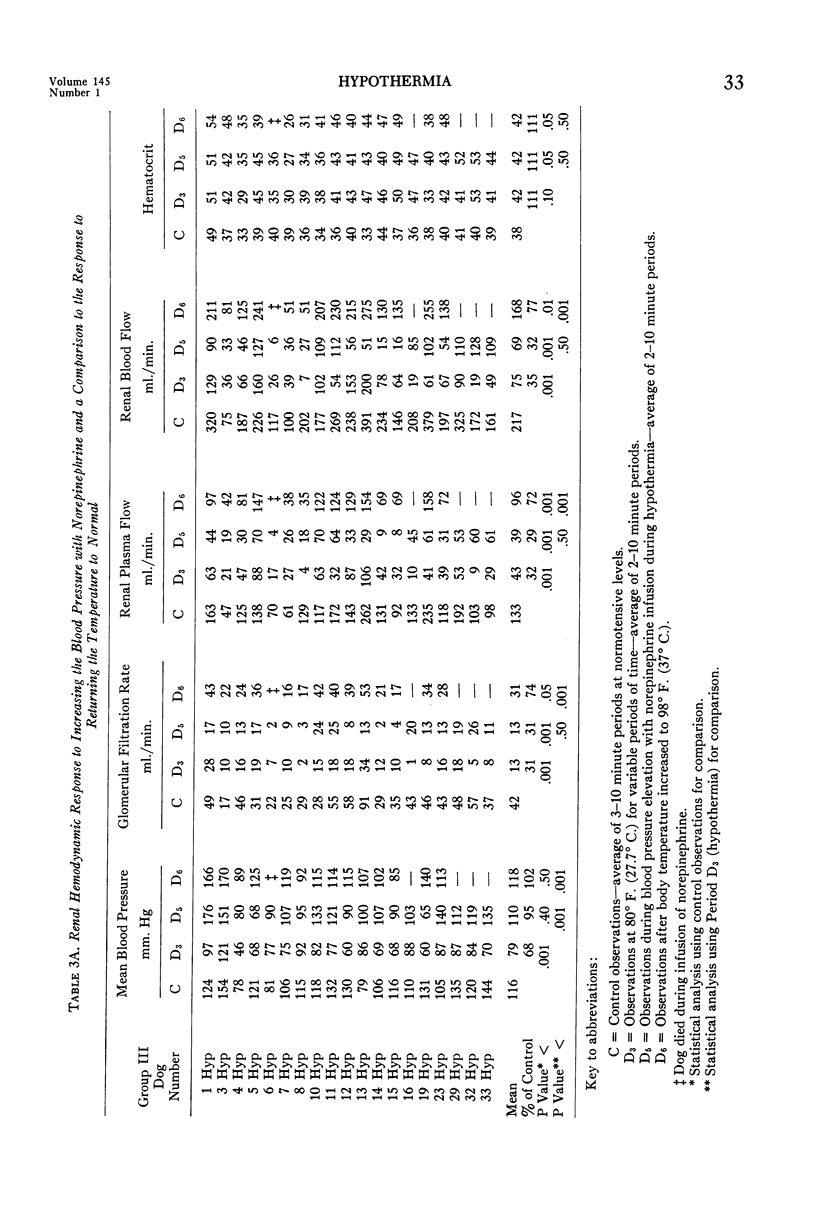
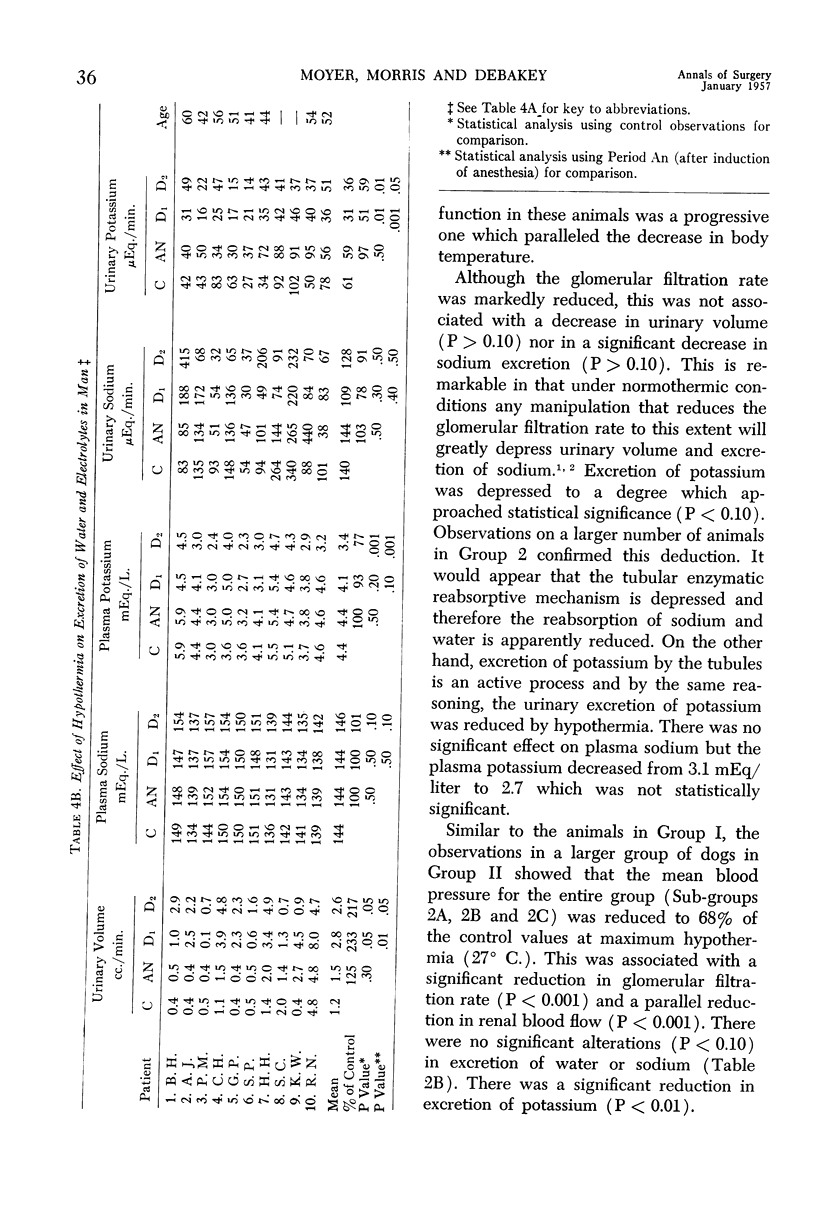
- MORRIS G. C., Jr, MOYER J. H., COLLEY D. A., BROCKMAN H. L. The renal hemodynamic response to hypothermia and to clamping of the thoracic aorta with and without hypothermia. Surg Forum. 1955;5:219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER J. H., HANDLEY C. A. Renal and cardiovascular hemodynamic response to ganglionic blockade with pendiomide and a comparison with hexamethonium and arfonad. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Apr;113(4):383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER J. H., MILLS L. C., FORD R. V., SPURR C. The effect of a head-up tilted position and ambulation on renal hemodynamics and water and electrolyte excretion in patients with hypertension, with and without renal damage. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Feb;45(2):179–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER J. H., MILLS L. C. Hexamethonium-its effect on glomerular filtration rate, maximal tubular function and renal excretion of electrolytes. J Clin Invest. 1953 Feb;32(2):172–184. doi: 10.1172/JCI102725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni T. G., Rehberg P. B. On the influence of posture on kidney function. J Physiol. 1931 Mar 23;71(3):331–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


