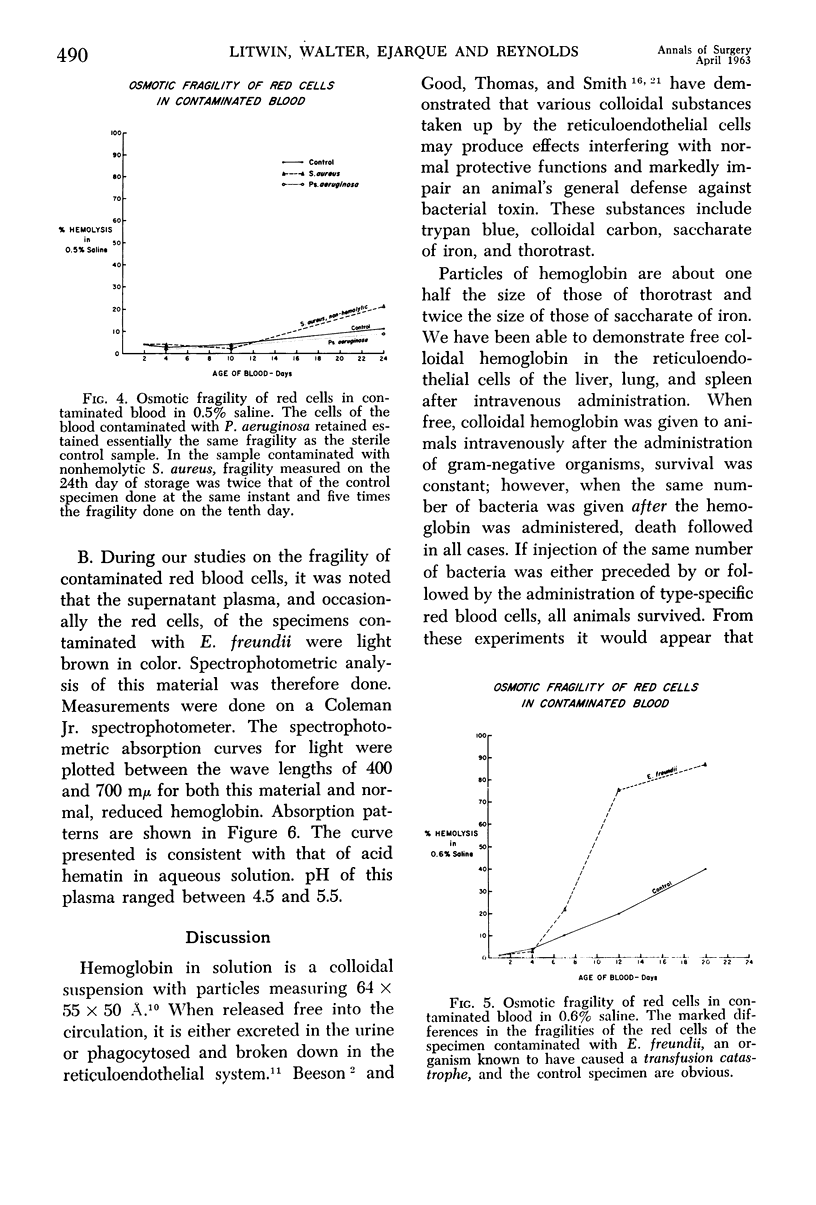
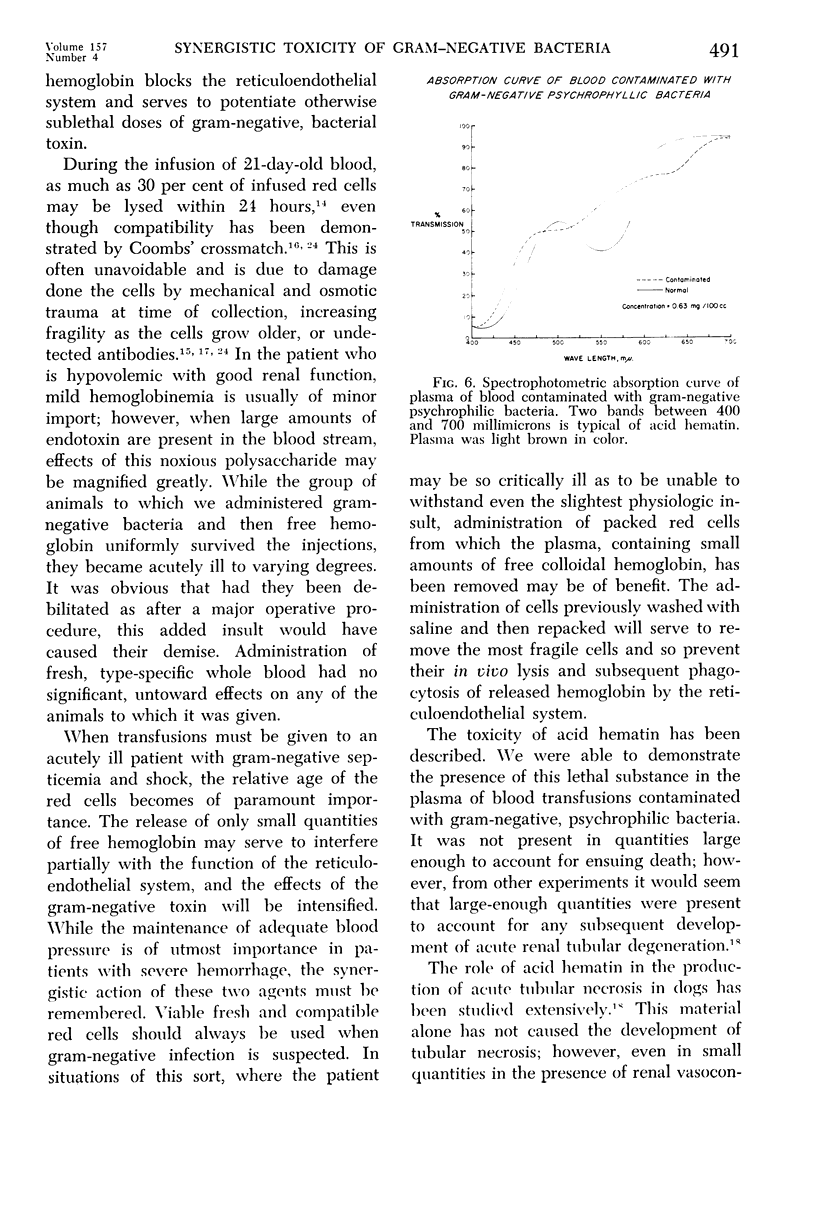
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRE R., GERMAIN A., POLACCO E. [Apropos of a transfusional complication due to bacterial contamination of the preserved blood by a gram-negative bacillus. Clinical, physipathological and therapeutic considerations]. Bull Mem Soc Med Hop Paris. 1959 Oct 9;75:811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORDEN C. W., HALL W. H. Fatal transfusion reactions from massive bacterial contamination of blood. N Engl J Med. 1951 Nov 15;245(20):760–765. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195111152452003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SANFORD J. P., BARTLETT J. E., MALLERY O. T., Jr Effects and clinical significance of bacterial contaminants in transfused blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Jun;39(6):902–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I. Transfusion reactions from contaminated blood; their recognition and treatment. N Engl J Med. 1958 Jun 26;258(26):1289–1293. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195806262582603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., WILLIAMS D., SIEMENSKI J., MURPHY R. Shock-like state due to transfusion of blood contaminated with gram-negative bacilli; successful treatment with antibiotics and arterenol. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1953 Jul;92(1):75–84. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1953.00240190087006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLER P., JAWETZ E. Experimental studies on bacterial contamination of bank blood. I. The nature of toxicity of contaminated blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 May;43(5):696–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLER P., MERRILL E. R., JAWETZ E. Experimental studies on bacterial contamination of band blood. II. Observations on bacteremia in mice and the influence of antibiotics in preventing death. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Jun;45(6):943–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON J. G., 2nd, MURPHY W. P., Jr, REES S. B., SCHEITLIN W. A. The influence of extracelluar factors involved in the collection of blood in ACD on maintenance of red cell viability during refrigerated storage. Am J Clin Pathol. 1956 Aug;26(8):855–873. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/26.8.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD R. A., THOMAS L. Studies on the generalized Shwartzman reaction. II. The production of bilateral cortical necrosis of the kidneys by a single injection of bacterial toxin in rabbits previously treated with thorotrast or trypan blue. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):625–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUDSMIT R., KRIJNEN H. W. Increased destruction of compatible red cells. Vox Sang. 1957 Oct;2(5):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1957.tb03958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. G., Evans R. D., Aub J. C., Sack T., Peacock W. C. THE POST-TRANSFUSION SURVIVAL OF PRESERVED HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES STORED AS, WHOLE BLOOD OR IN RESUSPENSION, AFTER REMOVAL OF PLASMA, BY MEANS OF TWO ISOTOPES OF RADIOACTIVE IRON. J Clin Invest. 1947 Jul;26(4):715–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI101855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES J. D., STOKES E. J. Effect of temperature on survival of bacteria in blood for transfusion; with a note on contamination by cold-growing organisms. Br Med J. 1957 Dec 14;2(5058):1389–1395. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5058.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITWIN M. S., WALTER C. W., JACKSON N. Experimental production of acute renal tubular necrosis. I. The role of gram-negative bacteria. II. The toxicity of acid hematin. III. Acid hematin -- the etiologic pigment. Ann Surg. 1960 Dec;152:1010–1025. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196012000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN M. A study of bacteria implicated in transfusion reactions and of bacteria isolated from blood products. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Aug;42(2):273–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. T., THOMAS L., GOOD R. A. Generalized Shwartzman reaction. V. Intravenous injection of collidal iron or carbon on response of rabbits to meningococcal toxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Apr;82(4):712–715. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENS A. R., Jr, LEGG J. S., HENRY B. S., DILLE J. M., KIRBY W. M., FINCH C. A. Fatal transfusion reactions from contamination of stored blood by cold growing bacteria. Ann Intern Med. 1953 Dec;39(6):1228–1239. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-39-6-1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYMINSKI W. [Manifest and latent hemolysis of preserved blood]. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 1959;29:511–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTER C. W., KUNDSIN R. B., BUTTON L. N. New technic for detection of bacterial contamination in a blood bank using plastic equipment. N Engl J Med. 1957 Aug 22;257(8):364–369. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195708222570803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





