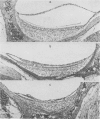
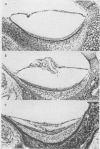
Full text
PDF





















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALTMANN F. Malformations, anomalies, and vestigial structures of the inner ear. AMA Arch Otolaryngol. 1953 Jun;57(6):591–602. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1953.00710030615001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARNVIG J. Vestibular function in deafness and severe hardness of hearing. Acta Otolaryngol. 1955 Jul-Aug;45(4):283–288. doi: 10.3109/00016485509124281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATSAKIS J. G., NISHIYAMA R. H. Deafness with sporadic goiter. Pendred's syndrome. Arch Otolaryngol. 1962 Nov;76:401–406. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1962.00740050413004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATTEN E. H. The origin of the acoustic ganglion in the sheep. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1958 Dec;6(4):597–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIELSCHOWSKY M., SCHOFIELD G. C. Studies on megacolon in piebald mice. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1962 Oct;40:395–403. doi: 10.1038/icb.1962.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLINGHAM R. E., SILVERS W. K. The melanocytes of mammals. Q Rev Biol. 1960 Mar;35:1–40. doi: 10.1086/402951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOSHER S. K., HALLPIKE C. S. OBSERVATIONS ON THE HISTOLOGICAL FEATURES, DEVELOPMENT AND PATHOGENESIS OF THE INNER EAR DEGENERATION OF THE DEAF WHITE CAT. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Apr 13;162:147–170. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUNG C. S., ROBINSON O. W., MORTON N. E. A note on deaf mutism. Ann Hum Genet. 1959 Dec;23:357–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1959.tb01479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN M. M., CASSADY G., HANNA B. L. A genetic study of hereditary renal dysfunction with associated nerve deafness. Am J Hum Genet. 1961 Dec;13:379–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNY-BROWN D. Hereditary sensory radicular neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1951 Nov;14(4):237–252. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.14.4.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEOL M. S., ROBINS M. W. The spinner mouse. J Hered. 1962 May-Jun;53:133–136. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deol M. S., Green M. C. Snell's waltzer, a new mutation affecting behaviour and the inner ear in the mouse. Genet Res. 1966 Dec;8(3):339–345. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300010193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deol M. S., Lane P. W. A new gene affecting the morphogenesis of the vestibular part of the inner ear in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966 Dec;16(3):543–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn L. C. A New Gene Affecting Behavior and Skeleton in the House Mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1934 Apr;20(4):230–232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.20.4.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVERBERG G. Labyrinthine disease in identical twins. Acta Otolaryngol. 1955 May-Jun;45(3):198–206. doi: 10.3109/00016485509118150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erway L., Hurley L. S., Fraser A. Neurological defect: manganese in phenocopy and prevention of a genetic abnormality of inner ear. Science. 1966 Jun 24;152(3730):1766–1768. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3730.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINMESSER M., ZELIG S. Congenital deafness associated with onychodystrophy. Arch Otolaryngol. 1961 Nov;74:507–508. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1961.00740030518004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER H. Morphologische und mikroskopisch-anatomische Untersuchungen am Innenohr eines Stammes spontanmutierter Hausmäuse (Dreher). Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1956;62(3):348–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCH L. Deafness as part of an hereditary syndrome. J Laryngol Otol. 1959 Jun;73:355–382. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100055420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. R., FROGGATT P., JAMES T. N. CONGENITAL DEAFNESS ASSOCIATED WITH ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES, FAINTING ATTACKS AND SUDDEN DEATH. A RECESSIVE SYNDROME. Q J Med. 1964 Jul;33:361–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. R., FROGGATT P., MURPHY T. GENETICAL ASPECTS OF THE CARDIO-AUDITORY SYNDROME OF JERVELL AND LANGE-NIELSEN (CONGENITAL DEAFNESS AND ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES). Ann Hum Genet. 1964 Nov;28:133–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1964.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. R., MORGANS M. E., TROTTER W. R. The syndrome of sporadic goitre and congenital deafness. Q J Med. 1960 Apr;29:279–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. R. PROFOUND CHILDHOOD DEAFNESS. J Med Genet. 1964 Dec;1(2):118–151. doi: 10.1136/jmg.1.2.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn P., Aird R. B. A neuroectodermal syndrome of dominant inheritance. J Neurol Sci. 1965 Mar-Apr;2(2):161–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(65)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grüneberg H., Burnett J. B., Snell G. D. The Origin of Jerker, a New Gene Mutation of the House Mouse, and Linkage Studies Made with It. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1941 Dec 15;27(12):562–565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.27.12.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLEY G. The placodal relations of the neural crest in the domestic cat. J Anat. 1955 Apr;89(2):133–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRMANN C., Jr, AGUILAR M. J., SACKS O. W. HEREDITARY PHOTOMYOCLONUS ASSOCIATED WITH DIABETES MELLITUS, DEAFNESS, NEPHROPATHY, AND CEREBRAL DYSFUNCTION. Neurology. 1964 Mar;14:212–221. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLANDER C. S., PROUT T. E., RIENHOFF M., RUBEN R. J., ASPER S. P., Jr CONGENITAL DEAFNESS AND GOITER. STUDIES OF A PATIENT WITH A COCHLEAR DEFECT AND INADEQUATE FORMATION OF IODOTHYRONINES. Am J Med. 1964 Oct;37:630–637. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUGHTON N. I. WAARDENBURG'S SYNDROME WITH DEAFNESS AS THE PRESENTING SYMPTOM. REPORT OF TWO CASES. N Z Med J. 1964 Feb;63:83–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLEY L. S., EVERSON G. J., GEIGER J. F. Manganese deficiency in rats: congenital nature of ataxia. J Nutr. 1958 Nov 10;66(3):309–319. doi: 10.1093/jn/66.3.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERVELL A., LANGE-NIELSEN F. Congenital deaf-mutism, functional heart disease with prolongation of the Q-T interval and sudden death. Am Heart J. 1957 Jul;54(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(57)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSEN S. Familial deafness and goitre in persons with a low serum level of protein-bound iodine: preliminary report. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1958;140:168–182. doi: 10.3109/00016485809124412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R. Extra-toes: anew mutant gene causing multiple abnormalities in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1967 Jun;17(3):543–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloepfer H. W., Laguaite J. K. The hereditary syndrome of congenital deafness and retinitis pigmentosa. (Usher's syndrome). Laryngoscope. 1966 May;76(5):850–862. doi: 10.1288/00005537-196605000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koroxenidis G. T., Webb N. C., Jr, Moschos C. B., Lehan P. H. Congenital heart disease, deaf-mutism and associated somatic malformations occurring in several members of one family. Am J Med. 1966 Jan;40(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSAY J. R., CARUTHERS D. G., HEMENWAY W. G., HARRISON S. Inner ear pathology following maternal rubella. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1953 Dec;62(4):1201–1218. doi: 10.1177/000348945306200419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSAY J. R., HEMENWAY W. G. Inner ear pathology due to measles. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1954 Sep;63(3):754–771. doi: 10.1177/000348945406300310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Hereditary absence of otoliths in the house mouse. J Physiol. 1951 Jul;114(3):410–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. W. Association of megacolon with two recessive spotting genes in the mouse. J Hered. 1966 Jan-Feb;57(1):29–31. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS E. A new hereditary syndrome--sex linked deafmutism associated with total albinism. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1962;12:12–19. doi: 10.1159/000151176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL D. Ectodermal dysplasia; report of kindred with ocular abnormalities and hearing defect. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Apr;45(4 Pt 2):143–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKAELIAN D. O., RUBEN R. J. HEARING DEGENERATION IN SHAKER-1 MOUSE. CORRELATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS WITH BEHAVIORAL RESPONSES AND WITH COCHLEAR ANATOMY. Arch Otolaryngol. 1964 Oct;80:418–430. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1964.00750040430011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKAELIAN D., ALFORD B. R., RUBEN R. J. COCHLEAR POTENTIALS AND 8 NERVE ACTION POTENTIALS IN NORMAL AND GENETICALLY DEAF MICE. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1965 Mar;74:146–157. doi: 10.1177/000348946507400113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOHR J., MAGEROY K. Sex-linked deafness of a possibly new type. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1960;10:54–62. doi: 10.1159/000151118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUCKLE T. J., WELLSM Urticaria, deafness, and amyloidosis: a new heredo-familial syndrome. Q J Med. 1962 Apr;31:235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULROW P. J., ARON A. M., GATHMAN G. E., YESNER R., LUBS H. A. HEREDITARY NEPHRITIS. REPORT OF A KINDRED. Am J Med. 1963 Dec;35:737–748. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer T. C. The development of piebald spotting in mice. Dev Biol. 1965 Jun;11(3):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(65)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD F. C. The pathology of congenital deafness. J Laryngol Otol. 1960 Dec;74:919–950. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100057376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER N. Congenital deafness due to a sex-linked recessive gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1958 Jun;10(2):196–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS B. W. Sex-linked deaf-mutism. Ann Hum Genet. 1963 Feb;26:195–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1963.tb01975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S C. The Inheritance and Expression of Fused, a New Mutation in the House Mouse. Genetics. 1937 Jan;22(1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/genetics/22.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETTELMAYER J. R., HOGAN M. Waardenburg's syndrome--report of a case in a non-Dutch family. N Engl J Med. 1961 Mar 9;264:500–501. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196103092641008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATIS H. M. Comments on the inheritance of deaf mutism in Northern Ireland. Ann Hum Genet. 1958 Feb;22(2):153–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1957.tb01930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN K. F., HUBER S. A. Morphology and behavior of Waltzertype mice. J Morphol. 1960 Mar;106:197–203. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051060206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENSON A. C., CHEESEMAN E. A. Hereditary deaf mutism, with particular reference to Northern Ireland. Ann Hum Genet. 1956 Feb;20(3):177–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1956.tb01367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. F., Glover R. A. Abnormal Segregation in Hereditary Renal Disease with Deafness. Am J Hum Genet. 1961 Mar;13(1 Pt 1):89–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman M., Ray B. A., Sidman R. L., Klinger J. M. Hearing and vision in neurological mutant mice: a method for their evaluation. Exp Neurol. 1966 Dec;16(4):377–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIETZ W. A syndrome of deaf-mutism associated with albinism showing dominant autosomal inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1963 Sep;15:259–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAARDENBURG P. J. A new syndrome combining developmental anomalies of the eyelids, eyebrows and nose root with pigmentary defects of the iris and head hair and with congenital deafness. Am J Hum Genet. 1951 Sep;3(3):195–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHALEN R. E., HUANG S., PESCHEL E., McINTOSH H. D. Hereditary nephropathy, deafness and renal foam cells. Am J Med. 1961 Aug;31:171–186. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILDERVANCK L. S. PERCEPTIVE DIAFNESS ASSOCIATED WITH SPLIT-HAND AND -FOOT, A NEW SYNDROME? Acta Genet Stat Med. 1963;13:161–169. doi: 10.1159/000151796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. A. Alport's syndrome of hereditary nephritis with deafness. Lancet. 1961 Dec 16;2(7216):1321–1323. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90899-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIPRKOWSKI L., ADAM A. RECESSIVE TOTAL ALBINISM AND CONGENITAL DEAF-MUTISM. Arch Dermatol. 1964 Jan;89:151–155. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1964.01590250157028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIPRKOWSKI L., KRAKOWSKI A., ADAM A., COSTEFF H., SADE J. Partial albinism and deaf-mutism due to a recessive sex-linked gene. Arch Dermatol. 1962 Oct;86:530–539. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1962.01590100144027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]