Full text
PDF
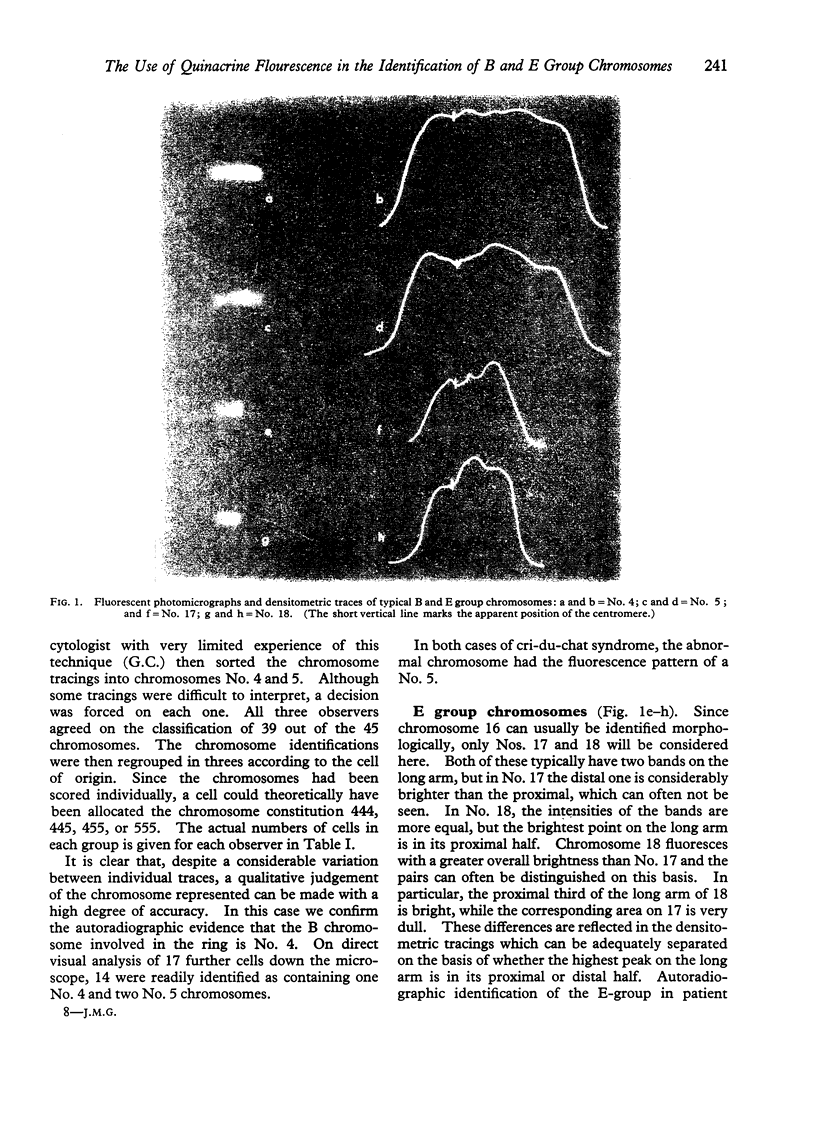
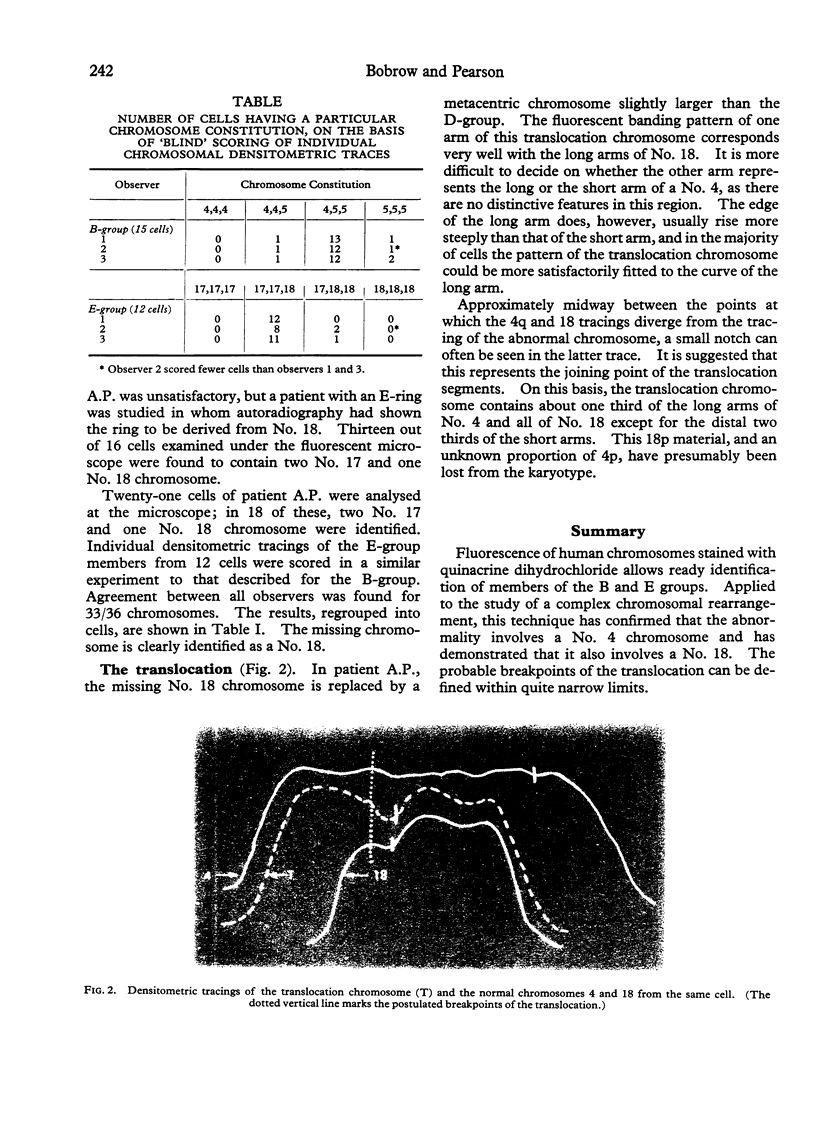

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caspersson T., Lindsten J., Zech L. Identification of the abnormal B group chromosome in the "cri du chat" syndrome by QM-fluorescence. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):475–476. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90479-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C., Modest E. J. Identification of human chromosomes by DNA-binding fluorescent agents. Chromosoma. 1970;30(2):215–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00282002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C. Quinacrine mustard-fluorescence of human chromosomes 4, 5 and X. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):474–475. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90478-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. L., Bobrow M., Vosa C. G. Technique for identifying Y chromosomes in human interphase nuclei. Nature. 1970 Apr 4;226(5240):78–80. doi: 10.1038/226078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]