Full text
PDF

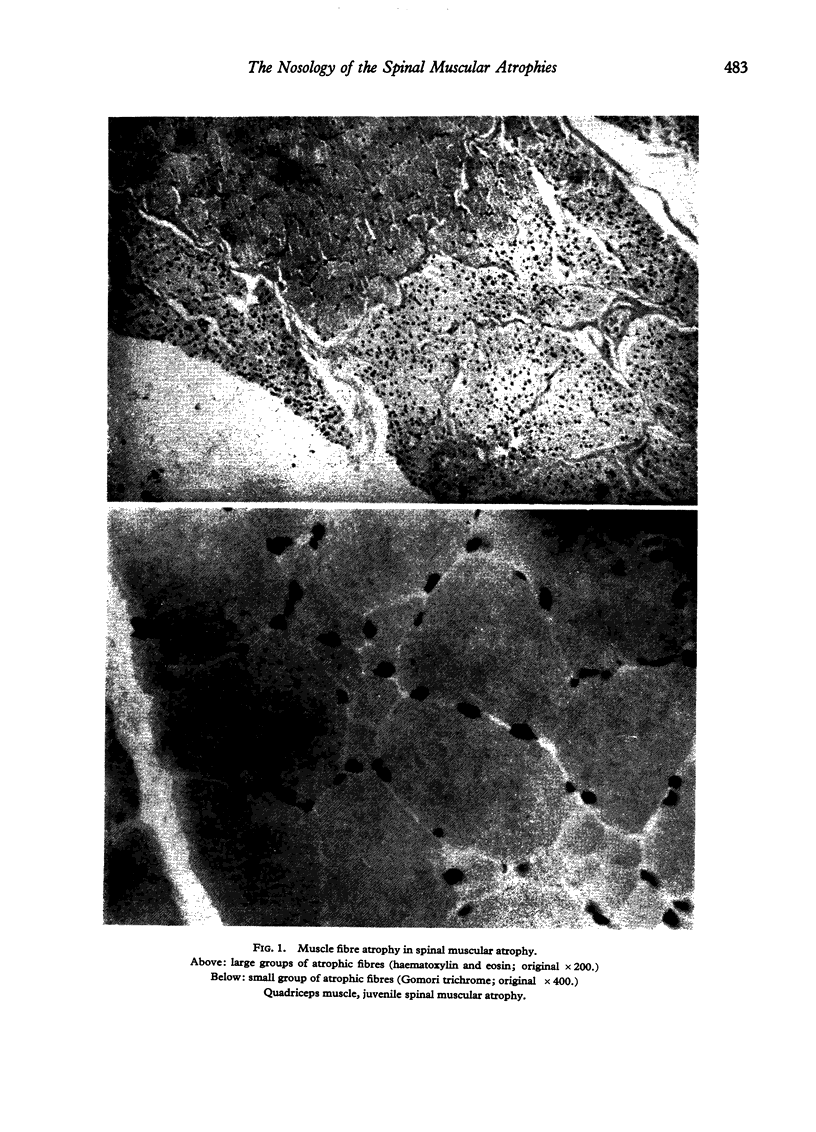
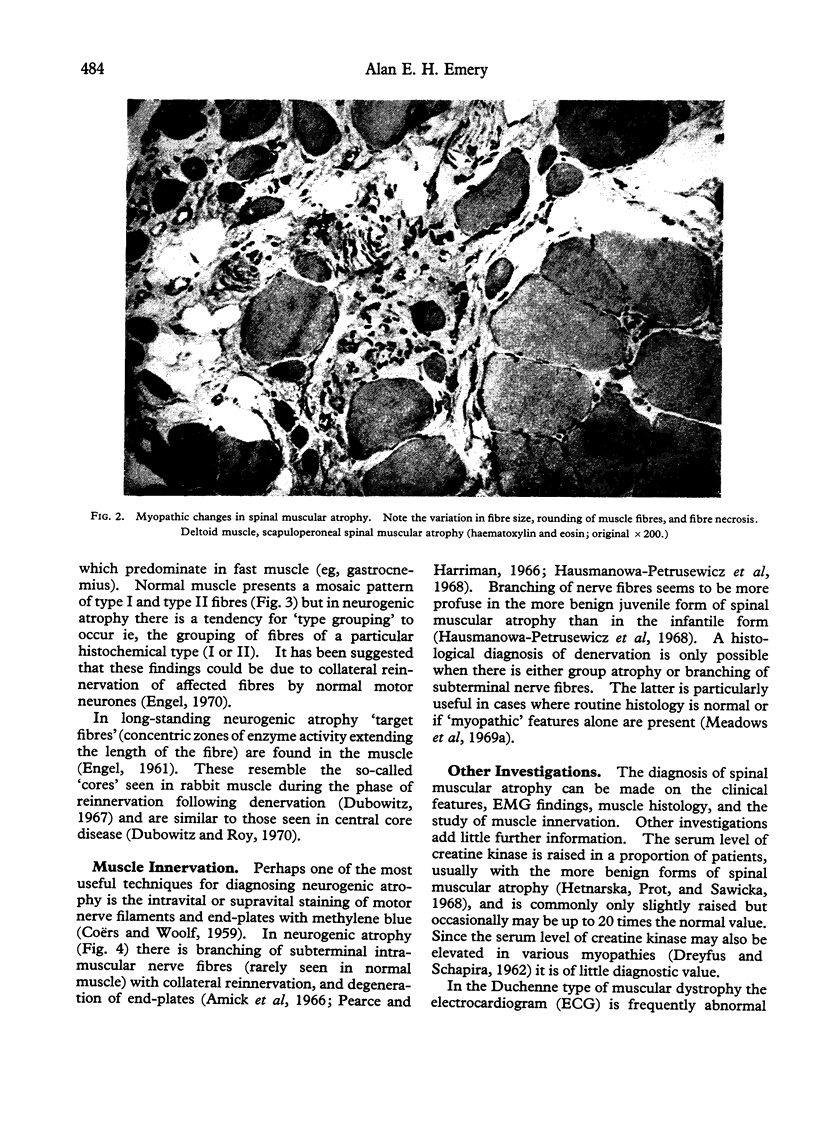
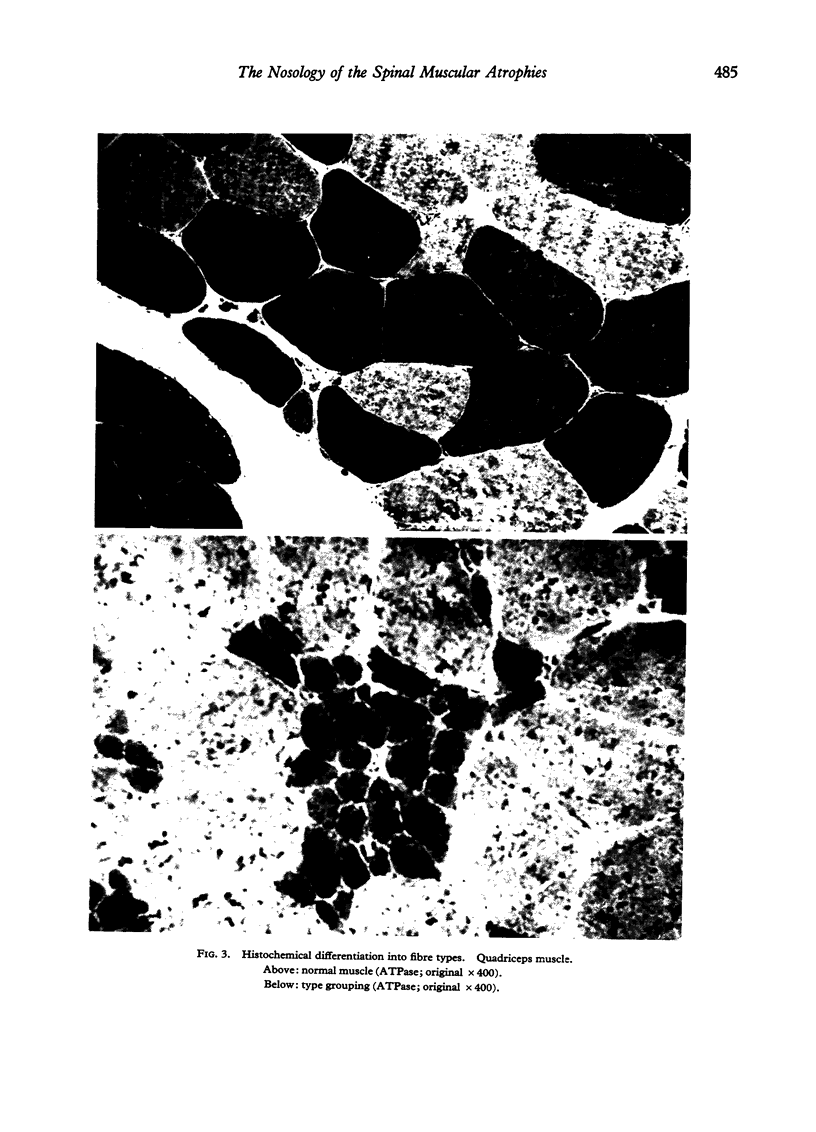


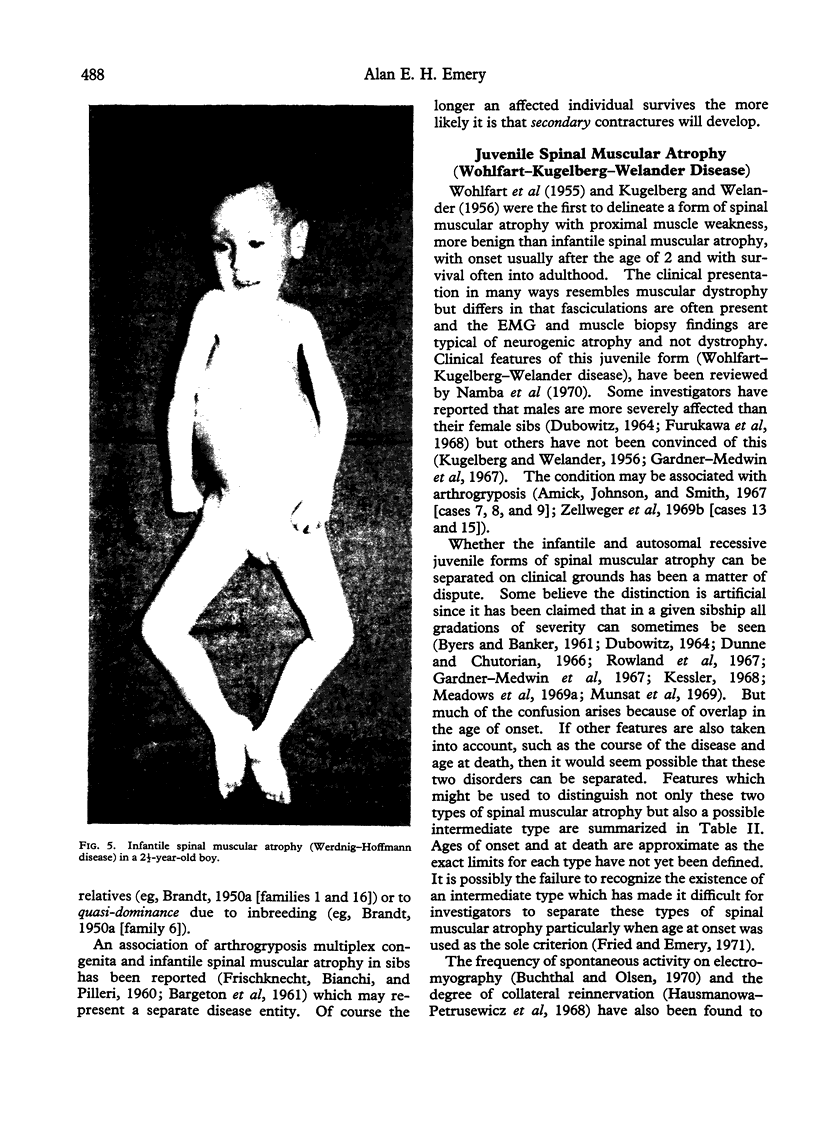






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberfeld D. C., Namba T. Progressive ophthalmoplegia in Kugelberg-Welander disease. Report of a case. Arch Neurol. 1969 Mar;20(3):253–256. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480090041005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almog C., Tal E. A family with Kugelberg-Welander sydrome. Hereditary proximal spinal muscul atrophy--some additional features. Confin Neurol. 1968;30(5):313–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amick L. D., Johnson W. W., Smith H. L. Electromyographic and histopathologic correlations in arthrogryposis. Arch Neurol. 1967 May;16(5):512–523. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470230064009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amick L. D., Smith H. L., Johnson W. W. An unusual spectrum of progressive spinal muscular atrophy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1966;42(3):275–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1966.tb01183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. M., Fogelson M. H., Silberberg D. H. Familial proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1966 Feb;14(2):208–212. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470080092014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER P. E. ATROPHIA MUSCULORUM SPINALIS PSEUDOMYOPATHICA. HEREDITAERE NEUROGENE PROXIMALE AMYOTROPHIE VON KUGELBERG UND WELANDER. Z Mensch Vererb Konstitutionsl. 1963 Dec 17;37:193–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDT S. Course and symptoms of progressive infantile muscular atrophy; a follow-up study of 112 cases in Denmark. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1950 Feb;63(2):218–228. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1950.02310200026003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS R. K., BANKER B. Q. Infantile muscular atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1961 Aug;5:140–164. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1961.00450140022003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R., Manz F., Moser R. Gehäuftes "sporadisches" Vorkommen spinaler progressiver Muskelatrophien im Kindesalter. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1970 Feb;118(2):41–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Johns R. J. Abnormal motor nerve excitability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1970 Jul;127(1):55–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal F., Olsen P. Z. Electromyography and muscle biopsy in infantile spinal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1970;93(1):15–30. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTAIGNE P., CAMBIER J., LAPLANE D., ESCOUROLLE R., BOUDOURESQUES J., DE PAILLERETS F. AMYOTROPHIE NEUROG'ENE FAMILIALE PSEUDO-MYOPATHIQUE DE LA SECONDE ENFANCE. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1963 Jul;109:13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzato G. Le amiotrofie spinali progressive pseudomiopatiche dell'adulto. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1969 May-Jun;24(3):341–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOWITZ V. INFANTILE MUSCULAR ATROPHY. A PROSPECTIVE STUDY WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO A SLOWLY PROGRESSIVE VARIETY. Brain. 1964 Dec;87:707–718. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., Murphy S. R., Nigam M. P., Hills J. R. "Myopathic" changes in chronically denervated muscle. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jan;16(1):14–24. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470190018002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz V., Roy S. Central core disease of muscle: clinical, histochemical and electron microscopic studies of an affected mother and child. Brain. 1970;93(1):133–146. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W., Strich S. J. An hereditary motor neurone disease with progressive denervation of muscle in the mouse: the mutant 'wobbler'. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Dec;31(6):535–542. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.6.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Lambert E. H. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. I. Neurologic, genetic, and electrophysiologic findings in hereditary polyneuropathies. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jun;18(6):603–618. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470360025002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Lambert E. H. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. II. Neurologic, genetic, and electrophysiologic findings in various neuronal degenerations. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jun;18(6):619–625. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470360041003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL W. K. Muscle target fibres, a newly recognized sign of denervation. Nature. 1961 Jul 22;191:389–390. doi: 10.1038/191389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. Abnormalities of the electrocardiogram in female carriers of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Br Med J. 1969 May 17;2(5654):418–420. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5654.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E., Spikesman A. Evidence against the existence of a subclinical form of X-linked Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Jun;10(6):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery E. S., Fenichel G. M., Eng G. A spinal muscular atrophy with scapuloperoneal distribution. Arch Neurol. 1968 Feb;18(2):129–133. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470320031003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K. Selective and nonselective susceptibility of muscle fiber types. A new approach to human neuromuscular diseases. Arch Neurol. 1970 Feb;22(2):97–117. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480200003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenichel G. M., Emery E. S., Hunt P. Neurogenic atrophy simulating facioscapulohumeral dystrophy. A dominant form. Arch Neurol. 1967 Sep;17(3):257–260. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470270035005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried K., Emery A. E. Spinal muscular atrophy type II. A separate genetic and clinical entity from type I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease) and type 3 (Kugelberg-Welander disease). Clin Genet. 1971;2(4):203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Nakao K., Sugita H., Tsukagoshi H. Kugelberg-Welander disease with particular reference to sex-influenced manifestations. Arch Neurol. 1968 Aug;19(2):156–162. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480020042004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Tsukagoshi H., Sugita H., Toyokura Y. Neurogenic muscular atrophy simulating facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy with particular reference to the heterogeneity of Kugelberg-Welander disease. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Sep-Oct;9(2):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMEZ M. R., CLERMONT V., BERNSTEIN J. Progressive bulbar paralysis in childhood (Fazio-Londe's disease). Report of a case with pathologic evidence of nuclear atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1962 Apr;6:317–323. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.00450220059009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamstorp I. Progressive spinal muscular atrophy with onset in infancy or early childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967 Jul;56(4):408–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb15400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin D., Hudgson P., Walton J. N. Benign spinal muscular atrophy arising in childhood and adolescence. J Neurol Sci. 1967 Jul-Aug;5(1):121–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(67)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvie J. M., Woolf A. L. Kugelberg-Welander syndrome (hereditary proximal spinal muscular atrophy). Br Med J. 1966 Jun 11;1(5501):1458–1461. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5501.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. Proximal spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):29–34. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Górecka A. Aminoacydria i aminoacydemia w chorobach mieśni pochodzenia rdzeniowego. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 1969 Sep-Oct;3(5):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSMANOWA-PETRUSEWICZ I., SOBKOWICZ H., ZIELINSKA S., DOBOSZ I. [Apropos of heredofamilial juvenile muscular atrophy]. Schweiz Arch Neurol Neurochir Psychiatr. 1962;90:255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ L., LAPRESLE J., GARCIN R. [Neurogenic muscular atrophy of proximal and symmetrical topography simulating a myopathy. Study of 2 cases]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1961 Feb;104:97–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Askanas W., Badurska B., Emeryk B., Fidziańska A., Garbalińska W., Hetnarska L., Kamieniecka Z., Prot J., Niebrój-Dobosz I. Infantile and juvenile spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Mar-Apr;6(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetnarska L., Prot J., Sawicka E. Creatine phospholinase activity in spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Mar-Apr;6(2):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogenhuis L. A., Spaulding S. W., Engel W. K. Neuronal RNA metabolism in infantile spinal muscular atrophy (Werdnig-Hoffmann's disease) studied by radioautography: a new technic in the investigation of neurological disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Apr;26(2):335–341. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IONASESCU V., LUCA N., PETRESCU A., CALCAIANU G. HEREDITARY PROXIMAL SPINAL MUSCULAR ATROPHY. BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS. Confin Neurol. 1965;25:79–86. doi: 10.1159/000103802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUGELBERG E., WELANDER L. Heredofamilial juvenile muscular atrophy simulating muscular dystrophy. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1956 May;75(5):500–509. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1956.02330230050005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeser H. E. Scapuloperoneal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1965 Jun;88(2):407–418. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy W. R., Alter M., Sung J. H. Progressive proximal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy of late onset. A sex-linked recessive trait. Neurology. 1968 Jul;18(7):671–680. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.7.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler G. B. Non-progressive proximal and generalized spinal muscular atrophy in siblings. Bull Los Angeles Neurol Soc. 1968 Jan;33(1):21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn R. Postmortem findings in a case of Wohlfart-Kugelberg-Welander disease. Confin Neurol. 1968;30(4):253–260. doi: 10.1159/000103537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Tsubaki T., Sakamoto F. The Ryukyuan muscular atrophy. An obscure heritable neuromuscular disease found in the islands of southern Japan. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Oct;11(4):359–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY J. A., WITTIG E. O. [Familial proximal muscular atrophy]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 1962 Sep;20:233–237. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x1962000300006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGEE K. R., DEJONG R. N. Neurogenic muscular atrophy simulating muscular dystrophy. Arch Neurol. 1960 Jun;2:677–682. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1960.03840120083009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGEE K. R. Familial progressive bulbar-spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 1960 Mar;10:295–305. doi: 10.1212/wnl.10.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANNING G. W., CROPP G. J. The electrocardiogram in progressive muscular dystrophy. Br Heart J. 1958 Jul;20(3):416–420. doi: 10.1136/hrt.20.3.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARQUARDT J. E., MACLOWRY J., PERRY R. E. Infantile progressive spinal muscular atrophy in indentical Negro twins. N Engl J Med. 1962 Aug 23;267:386–388. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196208232670804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows J. C., Marsden C. D. A distal form of chronic spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 1969 Jan;19(1):53–58. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows J. C., Marsden C. D., Harriman D. G. Chronic spinal muscular atrophy in adults. 1. The Kugelberg-Welander syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Nov-Dec;9(3):527–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows J. C., Marsden C. D., Harriman D. G. Chronic spinal muscular atrophy in adults. 2. Other forms. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Nov-Dec;9(3):551–566. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L., Woods R., Fowler W., Pearson C. M. Neurogenic muscular atrophy of infancy with prolonged survival. The variable course of Werdnig-Hoffmann Disease. Brain. 1969 Mar;92(1):9–24. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Aberfeld D. C., Grob D. Chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Nov;11(5):401–423. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perloff J. K., Roberts W. C., de Leon A. C., Jr, O'Doherty D. The distinctive electrocardiogram of Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy. An electrocardiographic-pathologic correlative study. Am J Med. 1967 Feb;42(2):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perloff J. K., de Leon A. C., Jr, O'Doherty D. The cardiomyopathy of progressive muscular dystrophy. Circulation. 1966 Apr;33(4):625–648. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.33.4.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. A., Opitz J. M., Goto I., Reese H. H. The benign proximal spinal progressive muscular atrophies. Acta Neurol Scand. 1968;44(5):542–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1968.tb05591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., DeVivo D. C., Engel W. K., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Familial adult-onset proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Report of a family with type II hyperlipoproteinemia. Arch Neurol. 1970 Jun;22(6):541–549. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480240061009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu H., Seceleanu A., Migea C., Török Z., Bordeianu L., Seceleanu S. La pseudomyopathie neurogène de Kugelberg-Welander. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1966 May;66(5):409–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricker K., Mertens H. G., Schimrigk K. The neurogenic scapulo-peroneal syndrome. Eur Neurol. 1968;1(5):257–274. doi: 10.1159/000113668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOTT J., JACOBI M., WALD M. A. Electrocardiographic patterns in the differential diagnosis of progressive muscular dystrophy. Am J Med Sci. 1955 May;229(5):517–524. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195505000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKYRING A., McKUSICK V. A. Clinical, genetic and electrocardiographic studies in childhood muscular dystrophy. Am J Med Sci. 1961 Nov;242:534–547. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196111000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. B., PATEL A. THE WOHLFART-KUGELBERG-WELANDER DISEASE; REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND REPORT OF A CASE. Neurology. 1965 May;15:469–473. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.5.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRA R. Neurogenic, familial, girdle type muscular atrophy. (Clinical, electromyographic and pathological study). Confin Neurol. 1963;23:245–255. doi: 10.1159/000104301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchmann L. Spinal muscular atrophy of the scapulo-peroneal-type. Z Kinderheilkd. 1970;109(2):118–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00438809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro A. J., Fogelson M. H., Goldberg A. C. Microcephaly and mental subnormalitiy in chronic progressive spinal muscular atrophy of childhood. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1967 Oct;9(5):594–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1967.tb02330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIEFFRY S., ARTHUIS M., BARGETON E. Quarante cas de maladie de Werdnig-Hoffmann avec onze examens anatomiques. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1955 Oct;93(4):621–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUKAGOSHI H., NAKANISHI T., KONDO K., TSUBAKI T. HEREDITARY PROXIMAL NEUROGENIC MUSCULAR ATROPHY IN ADULT. Arch Neurol. 1965 Jun;12:597–603. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1965.00460300045005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trillet M., Girard P. F., Schott B., Ramel P., Woehrle R. La paralysie bulbo-ontine chronique progressive avec surdité. A propos d'une observation clinique. Presse Med. 1970 Jan 17;78(3):129–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi H., Shoji H., Furukawa T. Proximal neurogenic muscular atrophy in adolescence and adulthood with X-linked recessive inheritance. Kugelberg-Welander disease and its variant of late onset in one pedigree. Neurology. 1970 Dec;20(12):1188–1193. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.12.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi H., Sugita H., Furukawa T., Tsubaki T., Ono E. Kugelberg-welander syndrome with dominant inheritance. Arch Neurol. 1966 Apr;14(4):378–381. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470100034004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Laere J. Paralysie bulbo-pontine chronique progressive familiale avec surdité. Un cas de syndrome de Klippel-Trenaunay dans la même fratrie. Problèmes diagnostiques et génétiques. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1966 Aug;115(2):289–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verger P., Vital C., Guillard J. M., Eschapasse P., Le Pennec J. J. Les formes intermédiaires de l'amyotrophie spinale infantile (a propos de six observations nouvelles) Pediatrie. 1969 Mar;24(2):131–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTON J. N. Amyotonia congenita: a follow-up study. Lancet. 1956 Jun 30;270(6931):1023–1027. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTON J. N. The limp child. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 May;20(2):144–154. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLFART G., FEX J., ELIASSON S. Hereditary proximal spinal muscular atrophy, a clinical entity simulating progressive muscular dystrophy. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand. 1955;30(1-2):395–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger H., McCormick W. F. Scapuloperoneal dystrophy and scapuloperoneal atrophy. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1968 Dec;23(6):643–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger H., Schneider H. J., Schuldt D. R., Mergner W. Heritable spinal muscular atrophies. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1969 Feb;24(1):92–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger H., Schneider H., Schuldt D. R. A new genetic variant of spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 1969 Sep;19(9):865–869. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.9.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]