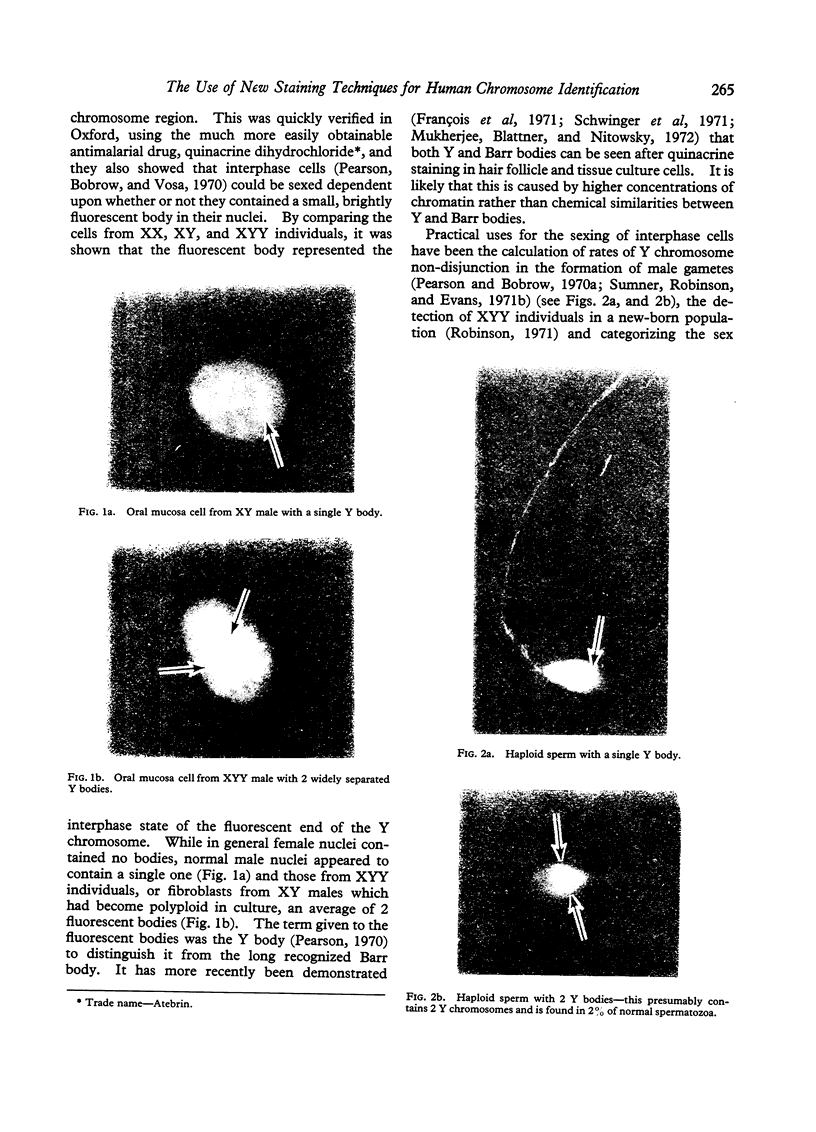
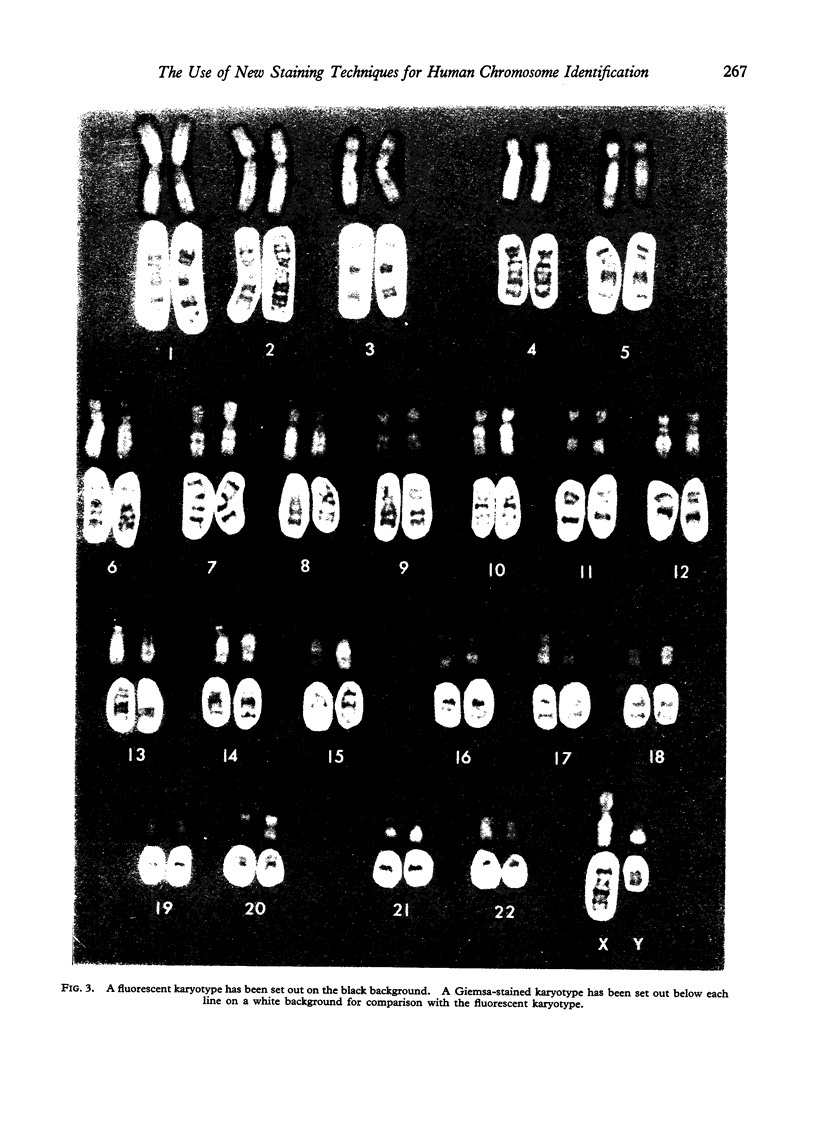
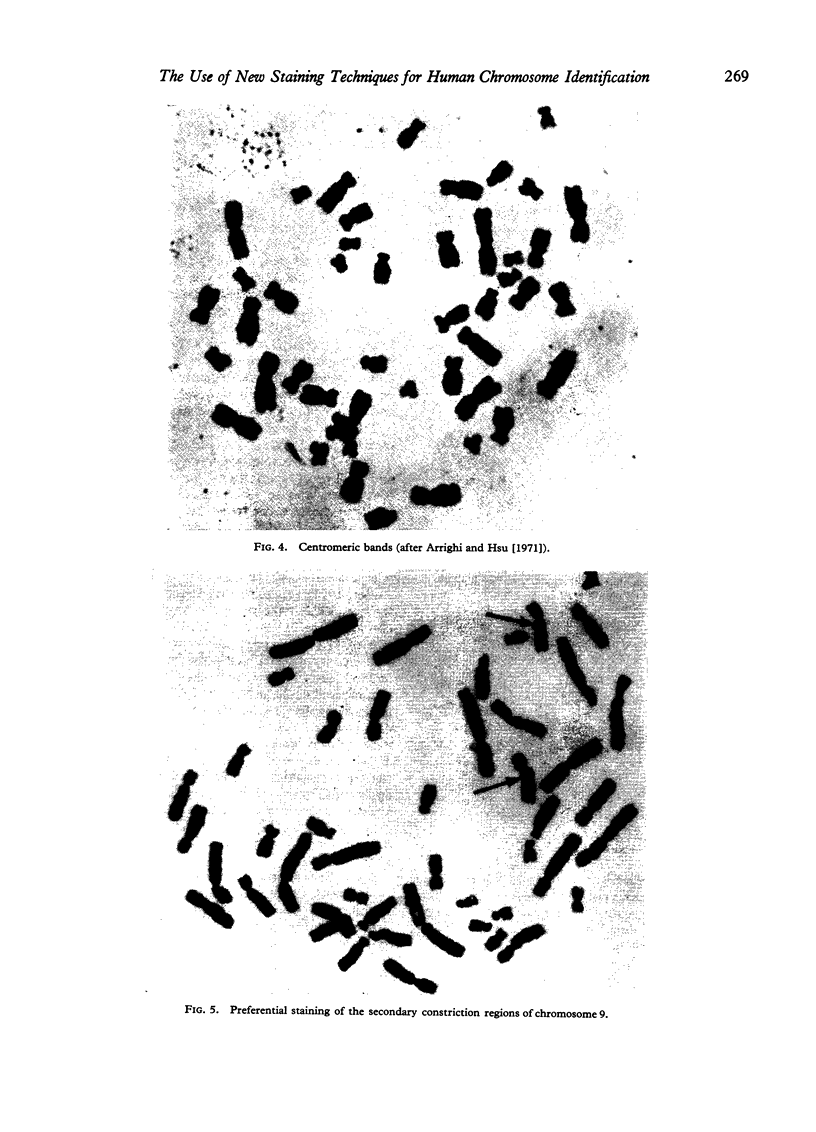
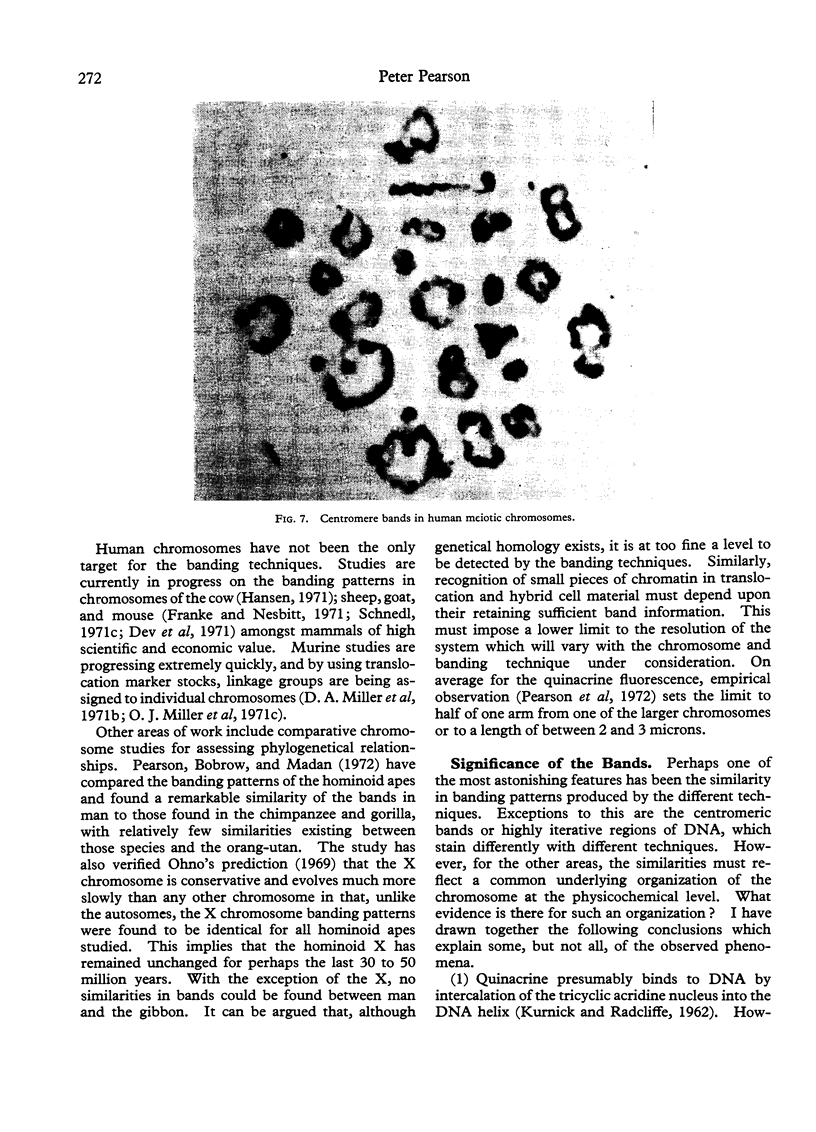
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrighi F. E., Hsu T. C. Localization of heterochromatin in human chromosomes. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(2):81–86. doi: 10.1159/000130130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M., Pearson P. L., Collacott H. E. Para-nucleolar position of the human Y chromosome in interphase nuclei. Nature. 1971 Aug 20;232(5312):556–557. doi: 10.1038/232556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M., Pearson P. L., Pike M. C., el-Alfi O. S. Length variation in the quinacrine-binding segment of human Y chromosomes of different sizes. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(3):190–198. doi: 10.1159/000130138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M., Pearson P. L. The use of quinacrine fluorescence in the identification of B and E group chromosomes involved in structural abnormalities. J Med Genet. 1971 Jun;8(2):240–243. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgaonkar D. S., Hollander D. H. Quinacrine fluorescence of the human Y chromosome. Nature. 1971 Mar 5;230(5288):52–52. doi: 10.1038/230052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breg W. R., Miller O. J., Miller D. A., Allderdice P. W. Distinctive fluorescence of quinacrine-labelled human G group chromosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 30;231(26):276–277. doi: 10.1038/newbio231276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler E. M., Frey R., Müller H., Joegelin M., Stalder G. R. Fluorescence pattern of a dicentric Y. Humangenetik. 1971;12(2):170–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00291474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Castleman K. R., Lomakka G., Modest E. J., Moller A., Nathan R., Wall R. J., Zech L. Automatic karyotyping of quinacrine mustard stained human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):233–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90645-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., De la Chapelle A., Lindsten J., Schröder J., Zech L. Absence of brightly fluorescent Y material in XX men. Ann Genet. 1971 Sep;14(3):173–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Farber S., Foley G. E., Kudynowski J., Modest E. J., Simonsson E., Wagh U., Zech L. Chemical differentiation along metaphase chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jan;49(1):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90538-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Gahrton G., Lindsten J., Zech L. Identification of the Philadelphia chromosome as a number 22 by quinacrine mustard fluorescence analysis. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Nov;63(1):238–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Hultén M., Lindsten J., Zech L. Chromatid interchange resulting in duplication of the short arm of chromosome number 7 in man. Ann Genet. 1971 Jun;14(2):143–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Hultén M., Lindsten J., Zech L. Distinction between extra G-like chromosomes by quinacrine mustard fluorescence analysis. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Nov;63(1):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Hultén M., Lindsten J., Zech L. Identification of chromosome bivalents in human male meiosis by quinacrine mustard fluorescence analysis. Hereditas. 1972;67(1):147–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1971.tb02368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Lindsten J., Zech L., Buckton K. E., Price W. H. Four patients with trisomy 8 identified by the fluorescence and Giemsa banding techniques. J Med Genet. 1972 Mar;9(1):1–7. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Lindsten J., Zech L. The nature of structural X chromosome aberrations in Turner's syndrome as revealed by quinacrine mustard fluorescence analysis. Hereditas. 1970;66(2):287–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1970.tb02352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Modest E. J., Foley G. E., Wagh U., Simonsson E. Chemical differentiation with fluorescent alkylating agents in Vicia faba metaphase chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Nov;58(1):128–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Modest E. J., Foley G. E., Wagh U., Simonsson E. DNA-binding fluorochromes for the study of the organization of the metaphase nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Nov;58(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. R., Ruddle F. H. Karyotype analysis utilizing differentially stained constitutive heterochromatin of human and murine chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1971;34(1):51–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00285516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernay P. R., Hsu L. Y., Streicher H., Hirschhorn K. Human chromosome identification by differential staining: G goup (21-22-Y). Cytogenetics. 1971;10(3):219–224. doi: 10.1159/000130141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. J., Felsenfeld G. Structure of chromatin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):101–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio229101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Shaw M. W., MacCluer J. W. Racial differences in the length of the human Y chromosome. Cytogenetics. 1966;5(1):34–52. doi: 10.1159/000129883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Heterochromatin of the Indian muntjac. Replication, condensation, DNA ultracentrifugation, fluorescent and heterochromatin staining. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):441–460. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90430-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Cunha A. B., Pavan C., Morgante J. S., Garrido M. C. Studies on cytology and differentiation in sciaridae. II. DNA redundancy in salivary gland cells of Hybosciara fragilis (Diptera, Sciaridae). Genetics. 1969;61(1 Suppl):335–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dev V. G., Grewal M. S., Miller D. A., Kouri R. E., Hutton J. J., Miller O. J. The quinacrine fluorescence karyotype of Mus musculus and demonstration of strain differences in secondary constrictions. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(6):436–451. doi: 10.1159/000130164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drets M. E., Shaw M. W. Specific banding patterns of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2073–2077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Lejeune J. Sur une nouvelle technique d'analyse du caryotype humain. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 May 17;272(20):2638–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., de Grouchy J., Finaz C., Lejeune J. Mise en évidence de la structure fine des chromosomes humains par digestion enzymatique (pronase en particulier. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Aug 2;273(5):587–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. J., Buckton K. E., Sumner A. T. Cytological mapping of human chromosomes: results obtained with quinacrine fluorescence and the acetic-saline-Giemsa techniques. Chromosoma. 1971;35(3):310–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00326281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Thomas E. D., Bryant J. I., Neiman P. E. Leukaemic transformation of engrafted human marrow cells in vivo. Lancet. 1971 Feb 6;1(7693):251–255. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90998-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fran cois J., Mation-van Leuven M. T., Acosta J. Male and female sex determination in hair roots. Clin Genet. 1971;2(2):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1971.tb00258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Nesbitt M. Identification of the mouse chromosomes by quinacrine mustard staining. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(5):356–366. doi: 10.1159/000130154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagne R., Laberge C. Morphologie du corpuscule fluorescent interphasique mis en evidence par la quinacrine chez l'homme. Can J Genet Cytol. 1971 Mar;13(1):128–130. doi: 10.1139/g71-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G. The genes for ribosomal RNA during oögenesis. Genetics. 1969;61(1 Suppl):121–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George K. P., Polani P. E. Y heterochromatin and XX males. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1215–1216. doi: 10.1038/2281215b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik K. H., Allderdice P. W., Grzeschik A., Opitz J. M., Miller O. J., Siniscalco M. Cytological mapping of human X-linked genes by use of somatic cell hybrids involving an X-autosome translocation (mouse-hamster-human X-linked markers). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):69–73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M., Pearson P. L. Fluorescent evidence for spermatocytes with two Y chromosomes in an XYY male. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Feb;34(3):273–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1971.tb00239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W., Corneo G. Location of satellite and homogeneous DNA sequences on human chromosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 27;233(43):268–271. doi: 10.1038/newbio233268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURNICK N. B., RADCLIFFE I. E. Reaction between DNA and quinacrine and other antimalarials. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Oct;60:669–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasten F. H. Cytochemical studies with acridine orange and the influence of dye contaminants in the staining of nucleic acids. Int Rev Cytol. 1967;21:141–202. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60814-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomholt B., Mohr J. Human karyotyping by heat-Giemsa staining and comparison with fluorochrome techniques. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 24;234(47):109–110. doi: 10.1038/newbio234109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpuech G., Raynaud E. J., Belin J., Godeneche P., de Grouchy J. Délétion du bras court du 18 par translocation t(G-;18p+). Une étude en fluorescence par la moutarde de quinacrine. Ann Genet. 1971 Sep;14(3):213–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolov G., Manolova Y., Levan A., Klein G. Fluorescent pattern of apparently normal chromosomes in Burkitt lymphomas. Hereditas. 1971;68(1):160–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1971.tb02396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson N. A., Robertson J. W. Effects of dextran 40 on postoperative renal haemodynamics. Lancet. 1966 Jul 30;2(7457):251–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92541-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlree M. E., Price W. H., Brown W. M., Tulloch W. S., Newsam J. E., Maclean N. Chromosome studies on testicular cells from 50 subfertile men. Lancet. 1966 Jul 9;2(7454):69–71. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91803-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Allderdice P. W., Miller O. J., Breg W. R. Quinacrine fluorescence patterns of human D group chromosomes. Nature. 1971 Jul 2;232(5305):24–27. doi: 10.1038/232024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Kouri R. E., Dev V. G., Grewal M. S., Hutton J. J., Miller O. J. Assignment of four linkage groups to chromosomes in Mus musculus and a cytogenetic method for locating their centromeric ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2699–2702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Allderdice P. W., Miller D. A., Breg W. R., Migeon B. R. Human thymidine kinase gene locus: assignment to chromosome 17 in a hybrid of man and mouse cells. Science. 1971 Jul 16;173(3993):244–245. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3993.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Miller D. A., Allderdice P. W., Dev V. G., Grewal M. S. Quinacrine fluorescent karyotypes of human diploid and heteroploid cell lines. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(5):338–346. doi: 10.1159/000130152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Miller D. A., Kouri R. E., Allderdice P. W., Dev V. G., Grewal M. S., Hutton J. J. Identification of the mouse karyotype by quinacrine fluorescence, and tentative assignment of seven linkage groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1530–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A. B., Blattner P. Y., Nitowsky H. M. Quinacrine mustard fluorescence of sex chromatin in human amniotic fluid cell cultures. Nature. 1972 Jan 28;235(5335):226–229. doi: 10.1038/235226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Riordan M. L., Robinson J. A., Buckton K. E., Evans H. J. Distinguishing between the chromosomes involved in Down's syndrome (trisomy 21) and cronic myeloid leukaemia (Ph1) by fluorescence. Nature. 1971 Mar 19;230(5290):167–168. doi: 10.1038/230167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil S. R., Merrick S., Lubs H. A. Identification of each human chromosome with a modified Giemsa stain. Science. 1971 Aug 27;173(3999):821–822. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3999.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. L., Bobrow M. Definitive evidence for the short arm of the Y chromosome associating with the X chromosome during miosis in the human male. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):959–961. doi: 10.1038/226959a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. L., Bobrow M. Fluorescent staining of the Y chromosome in meiotic stages of the human male. J Reprod Fertil. 1970 Jun;22(1):177–179. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0220177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. L., Bobrow M., Vosa C. G., Barlow P. W. Quinacrine fluorescence in mammalian chromosomes. Nature. 1971 Jun 4;231(5301):326–329. doi: 10.1038/231326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. L., Bobrow M., Vosa C. G. Technique for identifying Y chromosomes in human interphase nuclei. Nature. 1970 Apr 4;226(5240):78–80. doi: 10.1038/226078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polani P. E., Mutton D. E. Y-fluorescence of interphase nuclei, especially circulating lymphocytes. Br Med J. 1971 Jan 16;1(5741):138–142. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5741.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridler M. A. Banding patterns of metaphase chromosomes in Down's syndrome. Lancet. 1971 Aug 14;2(7720):354–356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritossa F. M., Atwood K. C., Lindsley D. L., Spiegelman S. On the chromosomal distribution of DNA complementary to ribosomal and soluble RNA. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:449–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. A., Buckton K. E. Quinacrine fluorescence of variant and abnormal human Y chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1971;35(3):342–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00326283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. Y chromosome fluorescence in buccal mucosa cells: a study on a newborn population. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Jul;35(1):61–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1956.tb01379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D., Bodmer W. F. Relationship of centromeric heterochromatin to fluorescent banding patterns of metaphase chromosomes in the mouse. Nature. 1971 Jun 25;231(5304):503–506. doi: 10.1038/231503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnedl W. Analysis of the human karyotype using a reassociation technique. Chromosoma. 1971;34(4):448–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00326316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnedl W. Fluorescenzuntersuchungen über die Längenvariabilität des Y-Chromosoms beim Menschen. Humangenetik. 1971;12(3):188–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00702774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnedl W. The karyotype of the mouse. Chromosoma. 1971;35(2):111–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00285731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinger E., Rakebrand E., Müller H. J., Bühler E. M., Tettenborn U. Y-body in hair roots. Humangenetik. 1971;12(1):79–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00291039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel C. M. Non-identity of apparently similar chromosome aberrations in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):555–556. doi: 10.1038/233555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson A. C., Bedford J., Barberton G. M. A patient with 45,X-46,XXq--46,XXq-dic karyotype. J Med Genet. 1971 Dec;8(4):513–516. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner A. T., Evans H. J., Buckland R. A. New technique for distinguishing between human chromosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 7;232(27):31–32. doi: 10.1038/newbio232031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner A. T., Robinson J. A., Evans H. J. Distingiishing between X, Y and YY-bearing human spermatozoa by fluorescence and DNA content. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 24;229(8):231–233. doi: 10.1038/newbio229231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Fedoroff S. Banding in human chromosomes treated with trypsin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):52–54. doi: 10.1038/newbio235052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Grouchy J., Turleau C., Léonard C. Etude en fluorescence d'une trisomie C mosaique, probablement 8: 46,XY-47,XY,?8+. Ann Genet. 1971 Mar;14(1):69–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]