Abstract
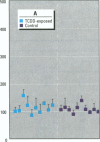
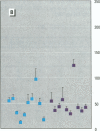
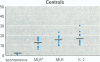
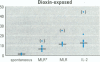
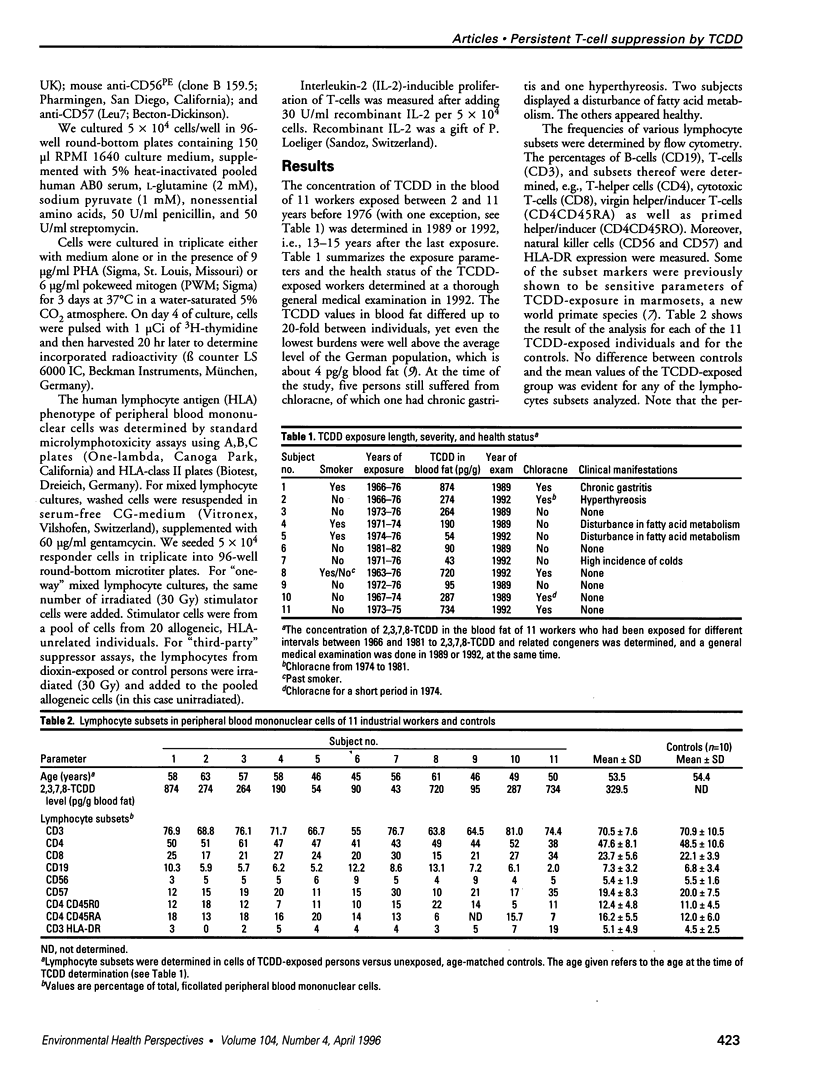
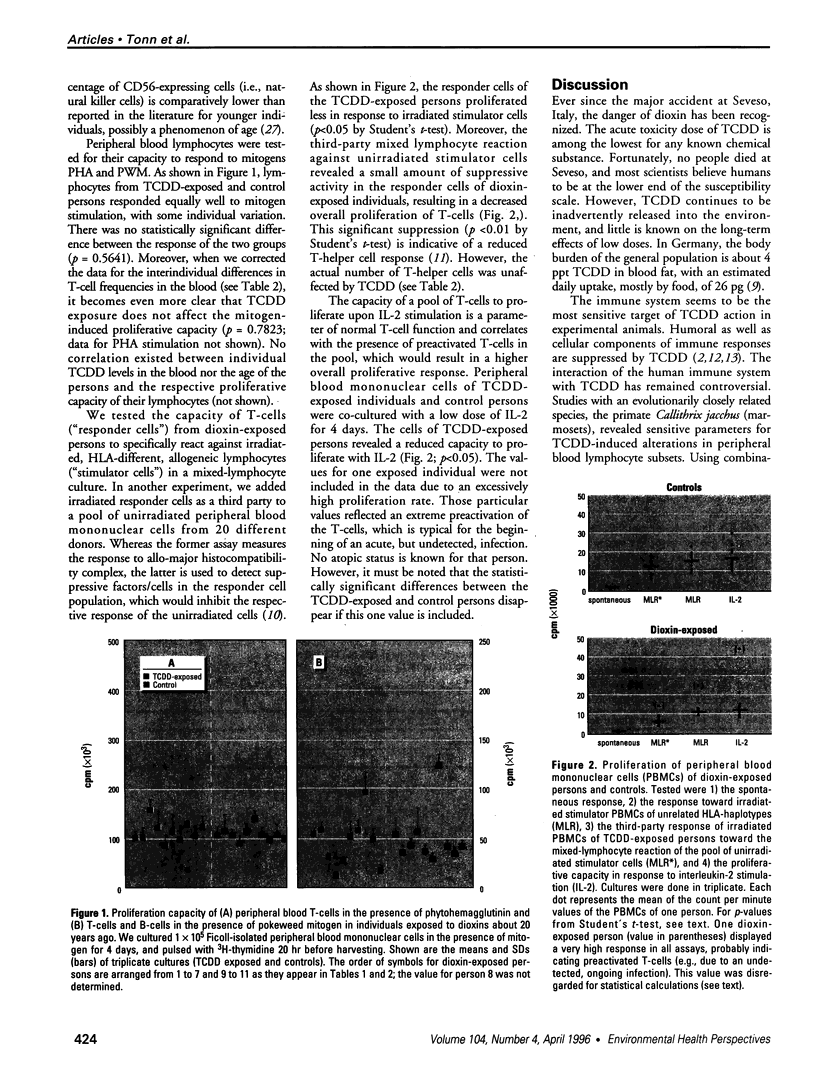
In experimentally exposed animals 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-n-dioxin (TCDD) causes severe immunosuppression. However, the overall susceptibility of humans for the different pathological effects of TCDD has remained unclear. We examined the long-term effects of TCDD in 11 industrial workers who were exposed to high doses of TCDD for several years 20 years ago. Current TCDD body burdens were still at least 10 times higher (between 43 and 874 pg/g blood far) in these exposed persons than in the average German population. To evaluate possible TCDD-induced changes in the percentage of different lymphocyte subsets, we determined a large panel of lymphocyte subsets in the blood by flow cytometric analysis. Immunocompetence of T-and B-lymphocytes was tested by nitrogen (phytohemagglutinin, pokeweed mitogen)- induced lymphoproliferation assays and by assays using sensitive mixed-lymphocyte cultures. No significant differences could be detected between the individuals tested and controls for surface marker distribution or mitogen-induced lymphoproliferation TCDD-exposed subjects showed a reduced response to human lymphocyte antigen-allogeneic lymphocytes and interleukin-2-boosted proliferation. Responder cells of the dioxin-exposed persons proliferated less in response to irradiated stimulator cells (p < or = 0.05), and the third-party mixed lymphocyte reaction against unirradiated stimulator cells revealed suppressive activity in the responder cell fraction compared to the controls (p < or = 0.01). Furthermore, the capacity of a pool of T cells isolated from TCDD-exposed subjects to proliferate upon interleukin-2 stimulation was significantly diminished (p < or = 0.05). TCDD has a long-term immunosuppressive-effect on T-helper cell function, which is mediated more likely by a reduced functionality of individual cells rather than by a reduction in absolute cell numbers in the peripheral blood.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark D. A., Gauldie J., Szewczuk M. R., Sweeney G. Enhanced suppressor cell activity as a mechanism of immunosuppression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Nov;168(2):290–299. doi: 10.3181/00379727-168-41275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley R. K., Holsapple M. P. Elucidation of cellular targets responsible for tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-induced suppression of antibody responses: I. The role of the B lymphocyte. Immunopharmacology. 1988 Nov-Dec;16(3):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(88)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser C., Welzel M. Ontogenic development of murine fetal thymocytes is accelerated by 3,3',4,4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1993 Nov;15(8):841–852. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(93)90001-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faith R. E., Luster M. I. Investigations on the effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on parameters of various immune functions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:564–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsapple M. P., Snyder N. K., Wood S. C., Morris D. L. A review of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced changes in immunocompetence: 1991 update. Toxicology. 1991;69(3):219–255. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(91)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. M., Wild G., Ward J. D., Ward A. M. Immunological abnormalities 17 years after accidental exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Oct;45(10):701–704. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.10.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutsen A. P. Immunologic effects of TCDD exposure in humans. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1984 Dec;33(6):673–681. doi: 10.1007/BF01625599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. W., Kremer J., Gleichmann E., Esser C. 3,3',4,4'-Tetrachlorobiphenyl inhibits proliferation of immature thymocytes in fetal thymus organ culture. Scand J Immunol. 1994 May;39(5):480–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L., Snyder N. K., Gokani V., Blair R. E., Holsapple M. P. Enhanced suppression of humoral immunity in DBA/2 mice following subchronic exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;112(1):128–132. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(92)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert D., Neubert R., Stahlmann R., Helge H. Immuno-toxicology and -pharmacology. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1989;22(12):1457–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert R., Golor G., Helge H., Neubert D. Risk assessment for possible effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and related substances on components and functions of the immune system. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1994;11(2-3):163–171. doi: 10.1159/000424207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert R., Stahlmann R., Korte M., van Loveren H., Vos J. G., Golor G., Webb J. R., Helge H., Neubert D. Effects of small doses of dioxins on the immune system of marmosets and rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 23;685:662–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb35931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D. G., Jr, Hampton L., Lapeza C. R., Jr, Belser W. T., Green V., Alexander L., Needham L. L. High-resolution gas chromatographic/high-resolution mass spectrometric analysis of human serum on a whole-weight and lipid basis for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Anal Chem. 1987 Aug 1;59(15):2000–2005. doi: 10.1021/ac00142a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelec G., Schneider E. M., Wernet P. Cloned human T lymphocytes with lymphostimulatory capacity preferentially activate suppressor cells. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Apr;14(4):335–340. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelec G., Wernet P., Rehbein A., Balko I., Schneider E. M. Alloproliferative human T cell clones primed and cultured in vitro lose proliferative and gain suppressive activity with age. Hum Immunol. 1984 Jun;10(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocchiari F., Silano V., Zampieri A. Human health effects from accidental release of tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) at Seveso, Italy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Knutson J. C. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:517–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehr P. A., Stein G., Webb K., Schramm W., Gedney W. B., Donnell H. D., Ayres S., Falk H., Sampson E., Smith S. J. A pilot epidemiologic study of possible health effects associated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin contaminations in Missouri. Arch Environ Health. 1986 Jan-Feb;41(1):16–22. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1986.9935760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson H. I., Bradfield C. A. The AH-receptor: genetics, structure and function. Pharmacogenetics. 1993 Oct;3(5):213–230. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199310000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognoni G., Bonaccorsi A. Epidemiological problems with TCDD (a critical view). Drug Metab Rev. 1982;13(3):447–469. doi: 10.3109/03602538209029989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb K. B., Evans R. G., Knutsen A. P., Roodman S. T., Roberts D. W., Schramm W. F., Gibson B. B., Andrews J. S., Jr, Needham L. L., Patterson D. G. Medical evaluation of subjects with known body levels of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1989;28(2):183–193. doi: 10.1080/15287398909531339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe W. H., Michalek J. E., Miner J. C., Rahe A., Silva J., Thomas W. F., Grubbs W. D., Lustik M. B., Karrison T. G., Roegner R. H. Health status of Air Force veterans occupationally exposed to herbicides in Vietnam. I. Physical health. JAMA. 1990 Oct 10;264(14):1824–1831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zober M. A., Ott M. G., Päpke O., Senft K., Germann C. Morbidity study of extruder personnel with potential exposure to brominated dioxins and furans. I. Results of blood monitoring and immunological tests. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Aug;49(8):532–544. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.8.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]