Abstract
Endocrine disrupting chemicals can potentially alter the reproductive physiology of fishes. To test this hypothesis, serum was collected from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) at five riverine locations in Minnesota. Male fish collected from an effluent channel below the St. Paul metropolitan sewage treatment plant had significantly elevated serum egg protein (vitellogenin) concentrations and significantly decreased serum testosterone concentrations compared to male carp collected from the St. Croix River, classified as a National Wild and Scenic River. Carp collected from the Minnesota River, which receives significant agricultural runoff, also exhibited depressed serum testosterone concentrations, but no serum vitellogenin was apparent. These data suggest that North American rivers are receiving estrogenic chemicals that are biologically active, as has been reported in Great Britain.
Full text
PDF
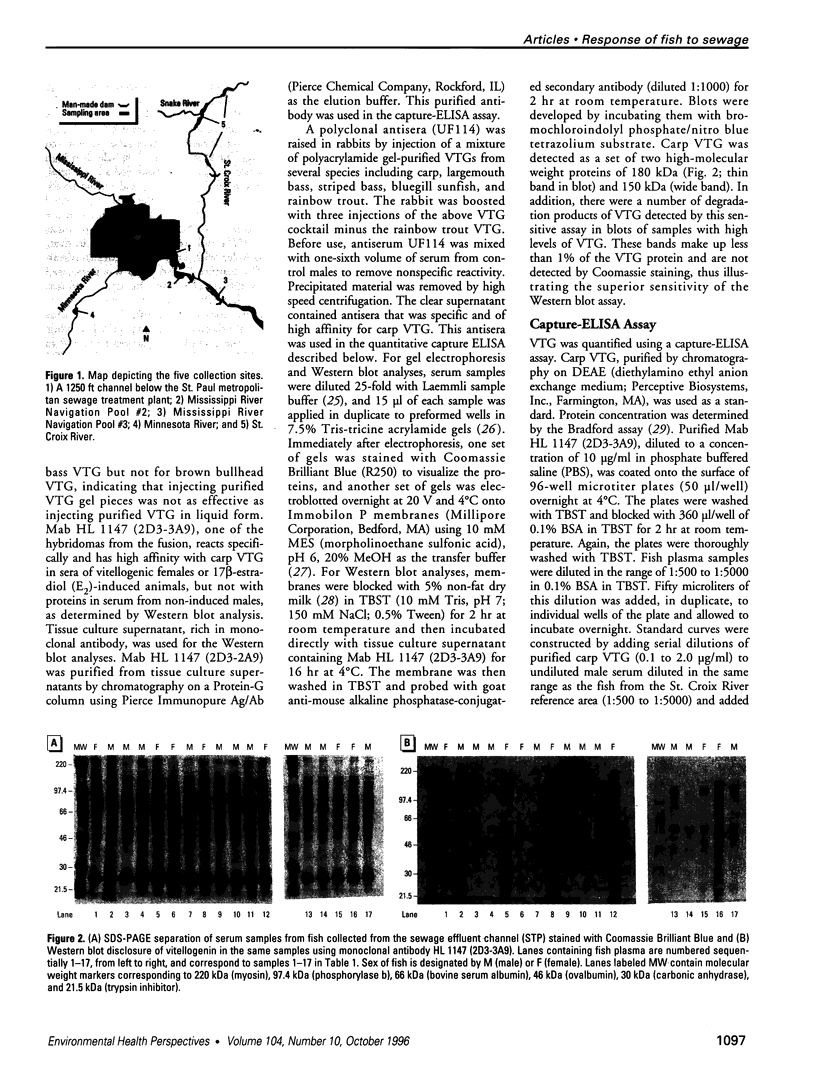

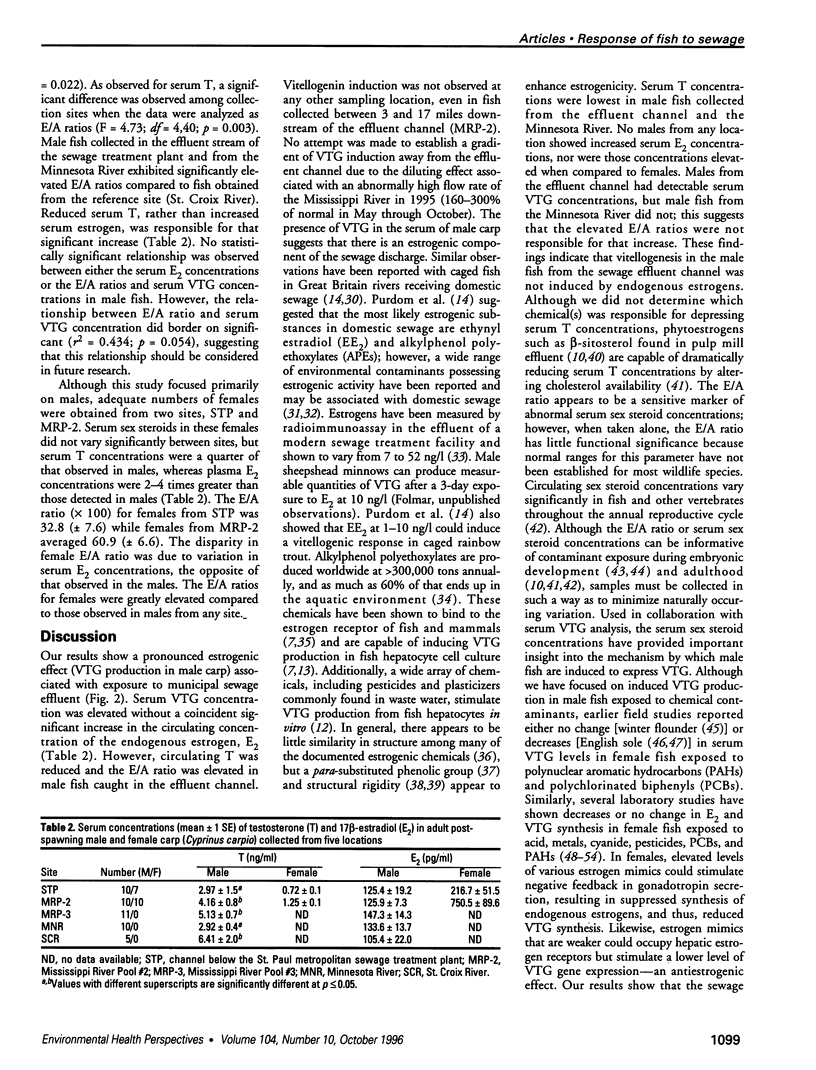


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitman J., Cecil H. C. Estrogenic activity of DDT analogs and polychlorinated biphenyls. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 Nov-Dec;18(6):1108–1112. doi: 10.1021/jf60172a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali O., Mosconi G., Yamamoto K., Kobayashi T., Kikuyama S., Polzonetti-Magni A. M. Hormonal control of in vitro vitellogenin synthesis in Rana esculenta liver: effects of mammalian and amphibian growth hormone. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;88(3):406–414. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(92)90235-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali O., Mosconi G., Yamamoto K., Kobayashi T., Kikuyama S., Polzonetti-Magni A. M. In-vitro effects of mammalian and amphibian prolactins on hepatic vitellogenin synthesis in Rana esculenta. J Endocrinol. 1993 Jun;137(3):383–389. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1370383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carragher J. F., Sumpter J. P., Pottinger T. G., Pickering A. D. The deleterious effects of cortisol implantation on reproductive function in two species of trout, Salmo trutta L. and Salmo gairdneri Richardson. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;76(2):310–321. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(89)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carragher J. F., Sumpter J. P. The effect of cortisol on the secretion of sex steroids from cultured ovarian follicles of rainbow trout. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;77(3):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(90)90230-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravorty S., Lal B., Singh T. P. Effect of endosulfan (thiodan) on vitellogenesis and its modulation by different hormones in the vitellogenic catfish Clarias batrachus. Toxicology. 1992 Nov 15;75(3):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(92)90001-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland P. A., Sumpter J. P., Walker T. K., Croft M. Vitellogenin levels in male and female rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson) at various stages of the reproductive cycle. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;83(2):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland P. A., Thomas P. The measurement of plasma vitellogenin levels in a marine teleost, the spotted seatrout (Cynoscion nebulosus) by homologous radioimmunoassay. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1988;91(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(88)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. L., Lim E. H., Lam T. J. Cortisol-induced hepatic vitellogenin mRNA in Oreochromis aureus (Steindachner). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1994 Nov;96(2):276–287. doi: 10.1006/gcen.1994.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin A. E., Grizzle J. M., Bradley J. T., Estridge B. H. Monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay of vitellogenin in the blood of male channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1992 Mar;101(3):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(92)90025-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillette L. J., Jr, Gross T. S., Gross D. A., Rooney A. A., Percival H. F. Gonadal steroidogenesis in vitro from juvenile alligators obtained from contaminated or control lakes. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 May;103 (Suppl 4):31–36. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillette L. J., Jr, Gross T. S., Masson G. R., Matter J. M., Percival H. F., Woodward A. R. Developmental abnormalities of the gonad and abnormal sex hormone concentrations in juvenile alligators from contaminated and control lakes in Florida. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Aug;102(8):680–688. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobling S., Reynolds T., White R., Parker M. G., Sumpter J. P. A variety of environmentally persistent chemicals, including some phthalate plasticizers, are weakly estrogenic. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Jun;103(6):582–587. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan V. C., Mittal S., Gosden B., Koch R., Lieberman M. E. Structure-activity relationships of estrogens. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Sep;61:97–110. doi: 10.1289/ehp.856197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korach K. S., Sarver P., Chae K., McLachlan J. A., McKinney J. D. Estrogen receptor-binding activity of polychlorinated hydroxybiphenyls: conformationally restricted structural probes. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;33(1):120–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Guellec K., Lawless K., Valotaire Y., Kress M., Tenniswood M. Vitellogenin gene expression in male rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1988 Sep;71(3):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(88)90264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLatchy D. L., Van Der Kraak G. J. The phytoestrogen beta-sitosterol alters the reproductive endocrine status of goldfish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;134(2):305–312. doi: 10.1006/taap.1995.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney J. D., Waller C. L. Polychlorinated biphenyls as hormonally active structural analogues. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Mar;102(3):290–297. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan J. A. Functional toxicology: a new approach to detect biologically active xenobiotics. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Oct;101(5):386–387. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Struck R. F., James R. Estrogenic activities of chlorinated hydrocarbons. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1978 Mar-May;4(2-3):325–339. doi: 10.1080/15287397809529664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelissero C., Bennetau B., Babin P., Le Menn F., Dunogues J. The estrogenic activity of certain phytoestrogens in the Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baeri. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;38(3):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90100-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelissero C., Flouriot G., Foucher J. L., Bennetau B., Dunoguès J., Le Gac F., Sumpter J. P. Vitellogenin synthesis in cultured hepatocytes; an in vitro test for the estrogenic potency of chemicals. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;44(3):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(93)90086-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottinger T. G., Pickering A. D. The effect of cortisol administration on hepatic and plasma estradiol-binding capacity in immature female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;80(2):264–273. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(90)90171-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabelo E. M., Tata J. R. Thyroid hormone potentiates estrogen activation of vitellogenin genes and autoinduction of estrogen receptor in adult Xenopus hepatocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993 Oct;96(1-2):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(93)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore L. S., Gurevitz M., Shemesh M. Estrogen as an environmental pollutant. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1993 Sep;51(3):361–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00201753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N., Lal B., Singh T. P. Pesticides induced changes in circulating thyroid hormones in the freshwater catfish Clarias batrachus. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1991;100(1-2):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(91)90133-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto A. M., Sonnenschein C., Chung K. L., Fernandez M. F., Olea N., Serrano F. O. The E-SCREEN assay as a tool to identify estrogens: an update on estrogenic environmental pollutants. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Oct;103 (Suppl 7):113–122. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpter J. P., Jobling S. Vitellogenesis as a biomarker for estrogenic contamination of the aquatic environment. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Oct;103 (Suppl 7):173–178. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s7173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaj B. I., Nath P. Steroid-induced synthesis of vitellogenin in the catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1981 Feb;43(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(81)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kraak G. J., Munkittrick K. R., McMaster M. E., Portt C. B., Chang J. P. Exposure to bleached kraft pulp mill effluent disrupts the pituitary-gonadal axis of white sucker at multiple sites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;115(2):224–233. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(92)90327-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wester P. W. Histopathological effects of environmental pollutants beta-HCH and methyl mercury on reproductive organs in freshwater fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1991;100(1-2):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(91)90160-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Jobling S., Hoare S. A., Sumpter J. P., Parker M. G. Environmentally persistent alkylphenolic compounds are estrogenic. Endocrinology. 1994 Jul;135(1):175–182. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.1.8013351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]