Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive overview of the pharmacokinetic parameters used from in vivo and in vitro studies that are important in order to understand the major conceptual approaches of toxicokinetics and the disposition of environmental chemicals. In vitro biochemical information concerning the detoxication of environmental chemicals is also presented. The discussion leads to a more complete appreciation for the use of in vitro measurements for in vivo correlations. The concept of interspecies scaling in the interpolation and extrapolation of fundamental biochemical metabolic processes is illustrated with a number of examples. Additional examples of in vitro-in vivo correlations are presented in the evaluation of the impact of chemical exposure to humans. Finally, several important metabolic detoxication enzymes are presented, including the mammalian microsomal cytochrome P450 and flavin-containing monooxygenases as well as carboxylesterases and glucuronosyltransferases, to provide insight into the processes of chemical detoxication in mammalian tissue and blood. Because interspecies scaling and the pharmacokinetics of chemical disposition have already shown their usefulness in understanding some examples of chemical disposition, our summary focuses on showing the usefulness of the pharmacokinetic equations and providing confidence in using the approach for in vitro-in vivo correlations. Ultimately, the presentation may provide the reader with a conceptual framework for future evaluation of the human health risks associated with environmental toxicants.
Full text
PDF



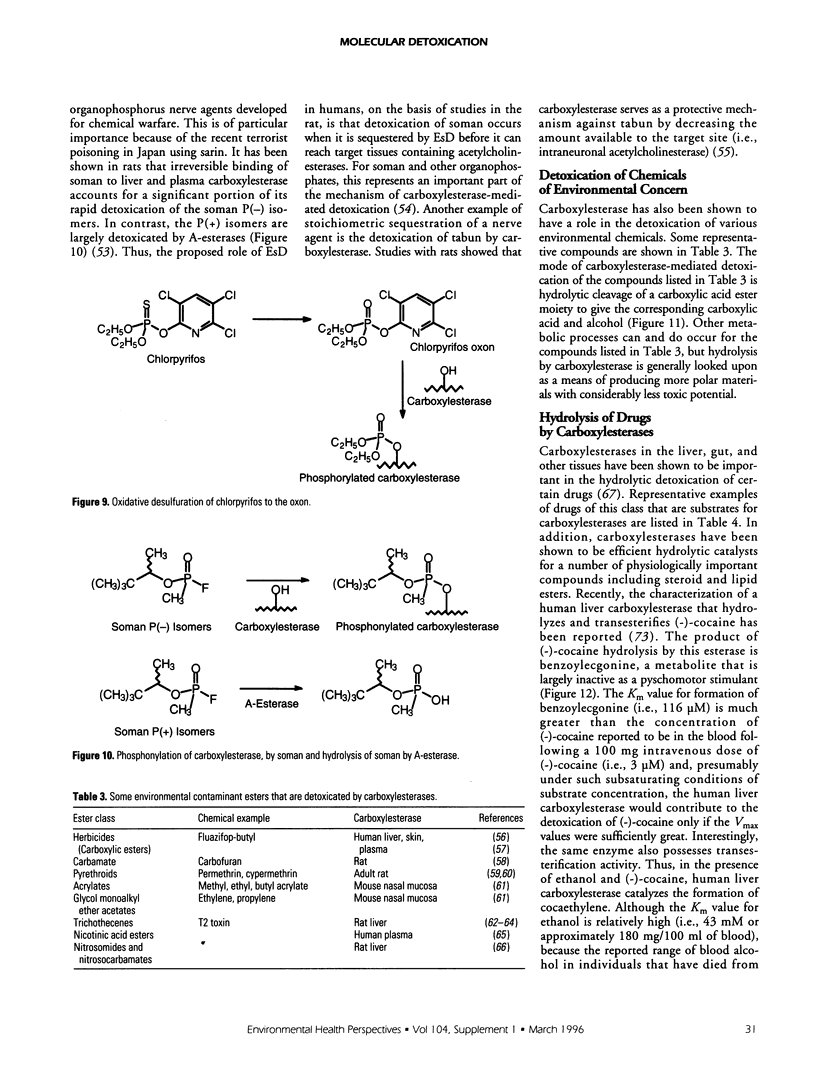
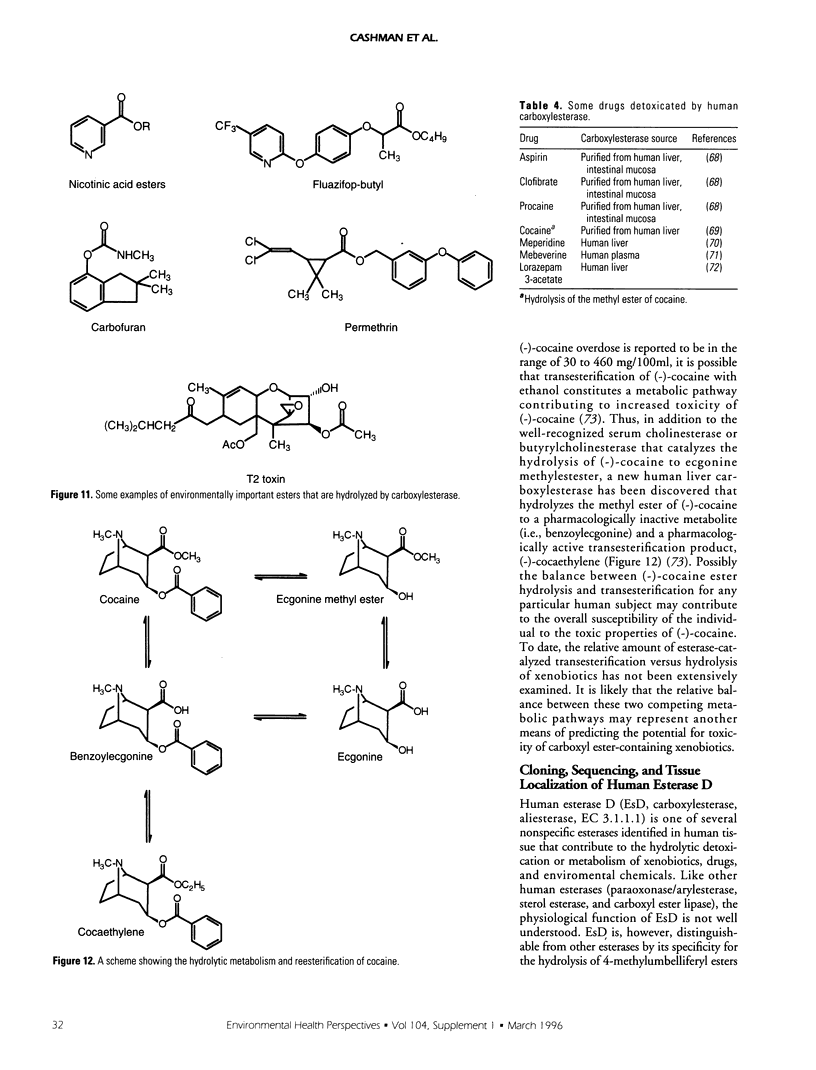

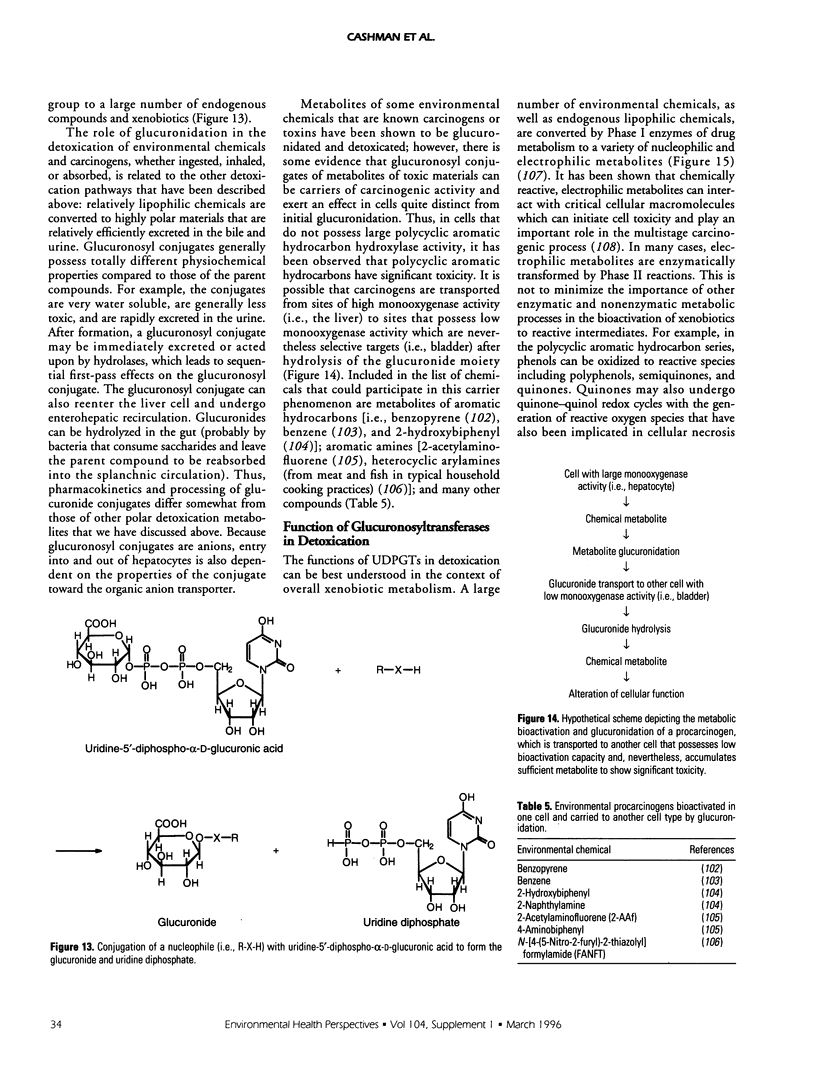
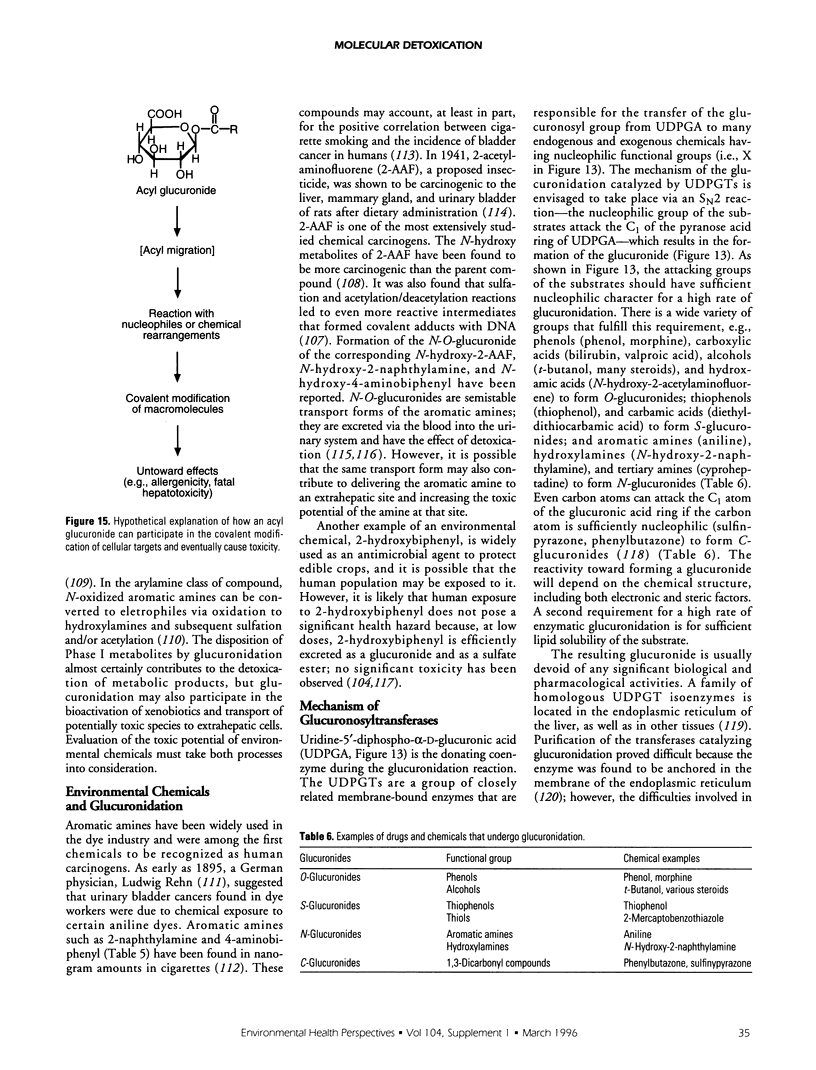





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen M. E., Clewell H. J., 3rd, Gargas M. L., Smith F. A., Reitz R. H. Physiologically based pharmacokinetics and the risk assessment process for methylene chloride. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;87(2):185–205. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aukerman S. L., Brundrett R. B., Hartman P. E. Detoxification of nitrosamides and nitrosocarbamates in blood plasma and tissue homogenates. Environ Mutagen. 1984;6(6):835–849. doi: 10.1002/em.2860060610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggot J. D. Application of interspecies scaling to the bispyridinium oxime HI-6. Am J Vet Res. 1994 May;55(5):689–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet L. Z., Galeazzi R. L. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Aug;68(8):1071–1074. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkman C. E., Park S. B., Wrighton S. A., Cashman J. R. In vitro-in vivo correlations of human (S)-nicotine metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Aug 8;50(4):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00168-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernareggi A., Rowland M. Physiologic modeling of cyclosporin kinetics in rat and man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1991 Feb;19(1):21–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01062191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock K. W. UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and their role in metabolism and disposition of carcinogens. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;27:367–383. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanffy M. S., Kee C. R., Hinchman C. A., Trela B. A. Metabolism of dibasic esters by rat nasal mucosal carboxylesterase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1991 Jan-Feb;19(1):124–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H., Fertig J. B. Scaling of antipyrine intrinsic clearance of unbound drug in 15 mammalian species. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1984 Apr-Jun;9(2):177–183. doi: 10.1007/BF03189622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. Interspecies scaling, allometry, physiological time, and the ground plan of pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1982 Apr;10(2):201–227. doi: 10.1007/BF01062336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H., Ronfeld R. Interspecies pharmacokinetic scaling and the Dedrick plots. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):R768–R775. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.245.6.R768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branchereau S., Ferry N., Myara A., Sato H., Kowai O., Trivin F., Houssin D., Danos O., Heard J. Correction du déficit en bilirubine glucuronyl-transférase chez le rat Gunn par transfert de gène dans le foie au moyen de vecteurs rétroviraux. Chirurgie. 1993;119(10):642–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockmöller J., Roots I. Assessment of liver metabolic function. Clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1994 Sep;27(3):216–248. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199427030-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. B., Reid W. D., Cho A. K., Sipes G., Krishna G., Gillette J. R. Possible mechanism of liver necrosis caused by aromatic organic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):160–164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzezinski M. R., Abraham T. L., Stone C. L., Dean R. A., Bosron W. F. Purification and characterization of a human liver cocaine carboxylesterase that catalyzes the production of benzoylecgonine and the formation of cocaethylene from alcohol and cocaine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Nov 1;48(9):1747–1755. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90461-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRIGLER J. F., Jr, NAJJAR V. A. Congenital familial nonhemolytic jaundice with kernicterus. Pediatrics. 1952 Aug;10(2):169–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantalamessa F. Acute toxicity of two pyrethroids, permethrin, and cypermethrin in neonatal and adult rats. Arch Toxicol. 1993;67(7):510–513. doi: 10.1007/BF01969923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardona R. A., King C. M. Activation of the O-glucuronide of the carcinogen N-hydroxy-N-2-fluorenylacetamide by enzymatic deacetylation in vitro: formation of fluorenylamine-tRNA adducts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 May 1;25(9):1051–1056. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman J. R., Park S. B., Yang Z. C., Wrighton S. A., Jacob P., 3rd, Benowitz N. L. Metabolism of nicotine by human liver microsomes: stereoselective formation of trans-nicotine N'-oxide. Chem Res Toxicol. 1992 Sep-Oct;5(5):639–646. doi: 10.1021/tx00029a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman J. R. Structural and catalytic properties of the mammalian flavin-containing monooxygenase. Chem Res Toxicol. 1995 Mar;8(2):166–181. doi: 10.1021/tx00044a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casida J. E., Ueda K., Gaughan L. C., Jao L. T., Soderlund D. M. Structure-biodegradability relationships in pyrethroid insecticides. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1975;3(4):491–500. doi: 10.1007/BF02220819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. E., Chambers H. W. Time course of inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and aliesterases following parathion and paraoxon exposures in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 May;103(3):420–429. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(90)90315-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. E., Ma T., Boone J. S., Chambers H. W. Role of detoxication pathways in acute toxicity levels of phosphorothionate insecticides in the rat. Life Sci. 1994;54(18):1357–1364. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. P., Hartgraves S. L., Murphy M. R., Wayner M. J., Kumar N., Valdes J. J. Effects of three reputed carboxylesterase inhibitors upon rat serum esterase activity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1991 Spring;15(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri N. K., Servando O. A., Manniello M. J., Luders R. C., Chao D. K., Bartlett M. F. Metabolism of tripelennamine in man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 Jul-Aug;4(4):372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark N. W., Scott R. C., Blain P. G., Williams F. M. Fate of fluazifop butyl in rat and human skin in vitro. Arch Toxicol. 1993;67(1):44–48. doi: 10.1007/BF02072034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates P. M., Mestriner M. A., Hopkinson D. A. A preliminary genetic interpretation of the esterase isozymes of human tissues. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 Jul;39(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius C. E. Fasting hyperbilirubinemia in Bolivian squirrel monkeys with a Gilbert's-like syndrome. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1993;37:127–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cretton E. M., Sommadossi J. P. Modulation of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine catabolism by probenecid and acetaminophen in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 12;42(7):1475–1480. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90461-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davila D. G., Williams D. E. The etiology of lung cancer. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993 Feb;68(2):170–182. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R., Bischoff K. B., Zaharko D. S. Interspecies correlation of plasma concentration history of methotrexate (NSC-740). Cancer Chemother Rep. 1970 Apr;54(2):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson R. G., Baker P. V., Franklin M. E., Hooper W. D. Facile hydrolysis of mebeverine in vitro and in vivo: negligible circulating concentrations of the drug after oral administration. J Pharm Sci. 1991 Oct;80(10):952–957. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600801010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulik D. M., Fenselau C. Species-dependent glucuronidation of drugs by immobilized rabbit, rhesus monkey, and human UDP-glucuronyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):473–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan A. M., Morgan C., Gallie B. l., Phillips R. A., Squire J. Re-evaluation of the sublocalization of esterase D and its relation to the retinoblastoma locus by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(2-3):153–157. doi: 10.1159/000132361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrer A., Walther B., Racciatti A., Boss G., Testa B. Structure-metabolism relationships in the hydrolysis of nicotinate esters by rat liver and brain subcellular fractions. Pharm Res. 1991 Jul;8(7):832–839. doi: 10.1023/a:1015839109449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrich M., Cohen S. D. DDVP (dichlorvos) detoxification by binding and interactions with DDT, dieldrin, and malaoxon. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1977 Oct;3(3):491–500. doi: 10.1080/15287397709529581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer L. J., Thies R. L., Charkowski D., Donham K. J. Formation and urinary excretion of cyproheptadine glucuronide in monkeys, chimpanzees, and humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1980 Nov-Dec;8(6):422–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelfeld L., Sarova-Pinchas I., Meytes D., Barash V., Brok-Simoni F., Feigl D. Phosphofructokinase deficiency (Tarui disease) associated with hepatic glucuronyltransferase deficiency (Gilbert's syndrome): a case and family study. Isr J Med Sci. 1990 Jun;26(6):328–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsson J. L., Johansson P., Bondesson U., Paalzow L. K. Analysis of methadone disposition in the pregnant rat by means of a physiological flow model. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1985 Aug;13(4):355–372. doi: 10.1007/BF01061474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan K. N., Smolen A., Eckerson H. W., La Du B. N. Purification of human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase. Evidence for one esterase catalyzing both activities. Drug Metab Dispos. 1991 Jan-Feb;19(1):100–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón A. R., Calvo B., Hernández R. M., Domínguez-Gil A., Pedraz J. L. Interspecies scaling of cimetidine-theophylline pharmacokinetic interaction: interspecies scaling in pharmacokinetic interactions. Pharm Res. 1994 Jul;11(7):945–950. doi: 10.1023/a:1018914816137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti G., Kahn J. O., Lifson J., Williams R., Turin L., Volberding P. A., Gambertoglio J. G. Pharmacokinetics of GLQ223 in rats, monkeys, and patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2531–2537. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil F., Gonzalvo M. C., Hernandez A. F., Villanueva E., Pla A. Differences in the kinetic properties, effect of calcium and sensitivity to inhibitors of paraoxon hydrolase activity in rat plasma and microsomal fraction from rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Oct 18;48(8):1559–1568. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombar C. T., Harrington G. W., Pylypiw H. M., Jr, Anderson L. M., Palmer A. E., Rice J. M., Magee P. N., Burak E. S. Interspecies scaling of the pharmacokinetics of N-nitrosodimethylamine. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 15;50(14):4366–4370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud V. K., Polasa K., Krishnaswamy K. Effect of turmeric on xenobiotic metabolising enzymes. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 1993 Jul;44(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01088486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Kadel W. L. Concerted role of carboxylesterases in the potentiation of carbofuran toxicity by iso-OMPA pretreatment. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1989;26(4):447–457. doi: 10.1080/15287398909531268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Patterson G. T., Dettbarn W. D. Acute tabun toxicity; biochemical and histochemical consequences in brain and skeletal muscles of rat. Toxicology. 1987 Nov;46(3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(87)90213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding D., Fournel-Gigleux S., Jackson M. R., Burchell B. Cloning and substrate specificity of a human phenol UDP-glucuronosyltransferase expressed in COS-7 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8381–8385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann E., Hoppe W., Krüsselmann A., Tschoetschel C. Organophosphate sensitive and insensitive carboxylesterases in human skin. Chem Biol Interact. 1993 Jun;87(1-3):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(93)90045-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundle B. S., O'Brien D. A., Alberti M., Beyer P., Hearst J. E. Functional expression of zeaxanthin glucosyltransferase from Erwinia herbicola and a proposed uridine diphosphate binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9321–9325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim S. S., Boudinot F. D. Pharmacokinetics of 2',3'-dideoxycytidine in rats: application to interspecies scale-up. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;41(12):829–834. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1989.tb06381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Schiller N. L., Fukuto T. R. Malathion and phenthoate carboxylesterase activities in pulmonary alveolar macrophages as indicators of lung injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;70(1):140–147. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(83)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Morikawa M., Tsuboi M., Ito Y., Sugiura M. Comparative study of human intestinal and hepatic esterases as related to enzymatic properties and hydrolizing activity for ester-type drugs. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;30(4):529–535. doi: 10.1254/jjp.30.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving C. C. Influence of the aryl group on the reaction of glucuronides of N-arylacethydroxamic acids with polynucleotides. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):524–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki M., Iwama M., Miyata N., Iitoi Y., Kanke Y. Effects of vitamin E deficiency on hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450 and phase II enzymes in male and female rats. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1994;64(2):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyanagi T., Haniu M., Sogawa K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Watanabe S., Shively J. E., Anan K. F. Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding 3-methylcholanthrene inducible rat mRNA for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15607–15614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. R., McCarthy L. R., Harding D., Wilson S., Coughtrie M. W., Burchell B. Cloning of a human liver microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferase cDNA. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):581–588. doi: 10.1042/bj2420581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jezequel S. G. Fluconazole: interspecies scaling and allometric relationships of pharmacokinetic properties. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;46(3):196–199. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1994.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen H., Odden E., Lie O., Johnsen B. A., Fonnum F. Metabolism of T-2 toxin by rat liver carboxylesterase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 May 1;35(9):1469–1473. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlubar F. F., Miller J. A., Miller E. C. Hepatic microsomal N-glucuronidation and nucleic acid binding of N-hydroxy arylamines in relation to urinary bladder carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1977 Mar;37(3):805–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata S., Hayasaka M., Hayashi H., Sakata M., Hatakeyama Y., Ogura N. Phenthoate metabolites in human poisoning. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1994;32(1):49–60. doi: 10.3109/15563659409000430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krijgsheld K. R., Koster H. J., Scholtens E., Mulder G. J. Cholestatic effect of harmol glucuronide in the rat. Prevention of harmol-induced cholestasis by increased formation of harmol sulfate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jun;221(3):731–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuykendall J. R., Taylor M. L., Bogdanffy M. S. Cytotoxicity and DNA-protein crosslink formation in rat nasal tissues exposed to vinyl acetate are carboxylesterase-mediated. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;123(2):283–292. doi: 10.1006/taap.1993.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Molecular cloning of the human esterase D gene, a genetic marker of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6337–6341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Wheatley W., Benedict W. F., Huang C. M., Lee E. Y. Purification, biochemical characterization, and biological function of human esterase D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6790–6794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. L., Nikula K. J., Novak R., Dahl A. R. Comparative localization of carboxylesterase in F344 rat, beagle dog, and human nasal tissue. Anat Rec. 1994 May;239(1):55–64. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092390107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K., Guengerich F. P., Yang S. K. Enantioselective hydrolysis of lorazepam 3-acetate by esterases in human and rat liver microsomes and rat brain S9 fraction. Drug Metab Dispos. 1991 May-Jun;19(3):609–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentzen R. J., Ts'o P. O. Benzo[a]yrenedione/benzo[a]pyrenediol oxidation-reduction couples and the generation of reactive reduced molecular oxygen. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1467–1473. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell W. E., Castle M. C. Species differences in the hydrolysis of meperidine and its inhibition by organophosphate compounds. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Aug;11(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhaeva G. F., Iankovskaia V. L., Odoeva G. A., Shestakova N. N., Khovanskikh A. E. Rol' ésteraz v proiavlenii toksicheskikh svoistv tiofosfororganicheskikh insektoakaritsidov, soderzhashchikh fragment merkaptouksusnoi kisloty. Bioorg Khim. 1985 Jul;11(7):957–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhaeva G. F., Veselova V. L., Mastriukova T. A., Shipov A. E., Zhdanova G. V. Vzaimodeistvie nekotorykh ditio- i tiofosfatov, soderzhashchikh fragmenty amino kislot, s karboksilésterazoi iz pecheni krysy. Bioorg Khim. 1983 Jul;9(7):920–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattes P. M., Mattes W. B. alpha-Naphthyl butyrate carboxylesterase activity in human and rat nasal tissue. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1992 May;114(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(92)90098-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell D. M., Brecht K. M., O'Neill B. L. The effect of carboxylesterase inhibition on interspecies differences in soman toxicity. Toxicol Lett. 1987 Nov;39(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(87)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken N. W., Blain P. G., Williams F. M. Human xenobiotic metabolizing esterases in liver and blood. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 5;46(7):1125–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90459-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Searches for ultimate chemical carcinogens and their reactions with cellular macromolecules. Cancer. 1981 May 15;47(10):2327–2345. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810515)47:10<2327::aid-cncr2820471003>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Miller E. C. Electrophilic sulfuric acid ester metabolites as ultimate carcinogens. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;197:583–595. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5134-4_55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda C. L., Chung W., Reed R. E., Zhao X., Henderson M. C., Wang J. L., Williams D. E., Buhler D. R. Flavin-containing monooxygenase: a major detoxifying enzyme for the pyrrolizidine alkaloid senecionine in guinea pig tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):546–552. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90142-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirsalis J. C., Hamilton C. M., Schindler J. E., Green C. E., Dabbs J. E. Effects of soya bean flakes and liquorice root extract on enzyme induction and toxicity in B6C3F1 mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 1993 May;31(5):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(93)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mommsen S., Aagaard J. Tobacco as a risk factor in bladder cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4(3):335–338. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.3.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordenti J., Chen S. A., Moore J. A., Ferraiolo B. L., Green J. D. Interspecies scaling of clearance and volume of distribution data for five therapeutic proteins. Pharm Res. 1991 Nov;8(11):1351–1359. doi: 10.1023/a:1015836720294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordenti J. Man versus beast: pharmacokinetic scaling in mammals. J Pharm Sci. 1986 Nov;75(11):1028–1040. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600751104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munger J. S., Shi G. P., Mark E. A., Chin D. T., Gerard C., Chapman H. A. A serine esterase released by human alveolar macrophages is closely related to liver microsomal carboxylesterases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18832–18838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka S., Terayama K., Kawashima C., Kawasaki T. A novel glucuronyltransferase in nervous system presumably associated with the biosynthesis of HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope on glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22711–22714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Wakabayashi K. Purification and characterization of esterases D-1 and D-2 from human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 15;263(1):130–136. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90621-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey A., Hassen A. M., Benedict D. R., Fitzpatrick D. W. Effect of UDP-glucuronyltransferase induction on zearalenone metabolism. Toxicol Lett. 1990 Apr;51(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(90)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang K. S., Mulder G. J. The effect of hepatic blood flow on formation of metabolites. Drug Metab Dispos. 1990 May-Jun;18(3):270–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang K. S., Rowland M. Hepatic clearance of drugs. I. Theoretical considerations of a "well-stirred" model and a "parallel tube" model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding, and the hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1977 Dec;5(6):625–653. doi: 10.1007/BF01059688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. B., Jacob P., 3rd, Benowitz N. L., Cashman J. R. Stereoselective metabolism of (S)-(-)-nicotine in humans: formation of trans-(S)-(-)-nicotine N-1'-oxide. Chem Res Toxicol. 1993 Nov-Dec;6(6):880–888. doi: 10.1021/tx00036a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupko J. M., Hearn W. L., Radomski J. L. N-Glucuronidation of N-hydroxy aromatic amines: a mechanism for their transport and bladder-specific carcinogenicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 30;50(3):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston E. J., English J. J., Dooner H. K. Sequence of three bronze alleles of maize and correlation with the genetic fine structure. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):185–197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. J., Jagadeesan V. Effect of long term iron deficiency on the activities of hepatic and extra-hepatic drug metabolising enzymes in Fischer rats. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 1995 Jan;110(1):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(94)00109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner E., Pavković E., Radić Z., Simeon V. Differentiation of esterases reacting with organophosphorus compounds. Chem Biol Interact. 1993 Jun;87(1-3):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(93)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz R. H., Fox T. R., Quast J. F., Hermann E. A., Watanabe P. G. Molecular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of orthophenylphenol and its sodium salt. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Jan;43(1):99–119. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddles P. W., Richards L. J., Bowles M. R., Pond S. M. Cloning and analysis of a cDNA encoding a human liver carboxylesterase. Gene. 1991 Dec 15;108(2):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90448-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saboori A. M., Lang D. M., Newcombe D. S. Structural requirements for the inhibition of human monocyte carboxylesterase by organophosphorus compounds. Chem Biol Interact. 1991;80(3):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(91)90092-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammett D., Lee E. W., Kocsis J. J., Snyder R. Partial hepatectomy reduces both metabolism and toxicity of benzene. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1979 Sep;5(5):785–792. doi: 10.1080/15287397909529789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepkovic D. W., Haley N. J., Axelrad C. M., Shigematsu A., LaVoie E. J. Short-term studies on the in vivo metabolism of N-oxides of nicotine in rats. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1986;18(2):205–214. doi: 10.1080/15287398609530861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata F., Takagi Y., Kitajima M., Kuroda T., Omura T. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human carboxylesterase gene. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):76–82. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen A., Eckerson H. W., Gan K. N., Hailat N., La Du B. N. Characteristics of the genetically determined allozymic forms of human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1991 Jan-Feb;19(1):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson R. C., Primo-Parmo S. L., Kuo C. L., Adkins S., Lockridge O., La Du B. N. Reconsideration of the catalytic center and mechanism of mammalian paraoxonase/arylesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7187–7191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C., Wilson M. G., Towner J. W., Benedict W., Murphree A. L., Yunis J. J. Regional assignment of genes for human esterase D and retinoblastoma to chromosome band 13q14. Science. 1980 May 30;208(4447):1042–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.7375916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire J., Dryja T. P., Dunn J., Goddard A., Hofmann T., Musarella M., Willard H. F., Becker A. J., Gallie B. L., Phillips R. A. Cloning of the esterase D gene: a polymorphic gene probe closely linked to the retinoblastoma locus on chromosome 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6573–6577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott W. T., McKenna M. J. Hydrolysis of several glycol ether acetates and acrylate esters by nasal mucosal carboxylesterase in vitro. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985 Apr;5(2):399–404. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(85)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultatos L. G., Shao M., Murphy S. D. The role of hepatic biotransformation in mediating the acute toxicity of the phosphorothionate insecticide chlorpyrifos. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 30;73(1):60–68. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A., Muchmore E., Diaz S. A sialic acid-specific O-acetylesterase in human erythrocytes: possible identity with esterase D, the genetic marker of retinoblastomas and Wilson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):882–886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viani A., Temellini A., Tusini G., Pacifici G. M. Human brain sulphotransferase and glucuronyltransferase. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1990 Mar;9(2):65–69. doi: 10.1177/096032719000900201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser T. J., Kaptein E., van Raaij J. A., Joe C. T., Ebner T., Burchell B. Multiple UDP-glucuronyltransferases for the glucuronidation of thyroid hormone with preference for 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3). FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 2;315(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81134-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitarius J. A., Sultatos L. G. The role of calcium in the hydrolysis of the organophosphate paraoxon by human serum A-esterase. Life Sci. 1995;56(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00422-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlländer A., Szinicz L. Detoxification of soman in the perfused rat liver: quantitative uptake and stereoisomer metabolism. Arch Toxicol. 1990;64(7):586–589. doi: 10.1007/BF01971839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall K. L., Gao W. S., te Koppele J. M., Kwei G. Y., Kauffman F. C., Thurman R. G. The liver plays a central role in the mechanism of chemical carcinogenesis due to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Carcinogenesis. 1991 May;12(5):783–786. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.5.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P., Packman S., Loughman W., Sparkes M., Sparkes R., McMahon A., Gregory T., Ablin A. Location of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene(s) and the human esterase D locus. J Med Genet. 1984 Apr;21(2):92–95. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R. D., Chu F. S. Modification of in vitro metabolism of T-2 toxin by esterase inhibitors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.115-119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. M. Clinical significance of esterases in man. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1985 Sep-Oct;10(5):392–403. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198510050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. J., Lee E. Y., To H. A., Bookstein R., Shew J. Y., Donoso L. A., Sery T., Giblin M., Shields J. A., Lee W. H. Human esterase D gene: complete cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and application in the genetic diagnosis of human retinoblastoma. Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;79(2):137–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00280552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Ramsay N. Retinoblastoma and subband deletion of chromosome 13. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Feb;132(2):161–163. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120270059012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. M., Ansher S. S., Nagata T., Kadlubar F. F., Jakoby W. B. N-methylation: potential mechanism for metabolic activation of carcinogenic primary arylamines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2514–2517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


