Abstract
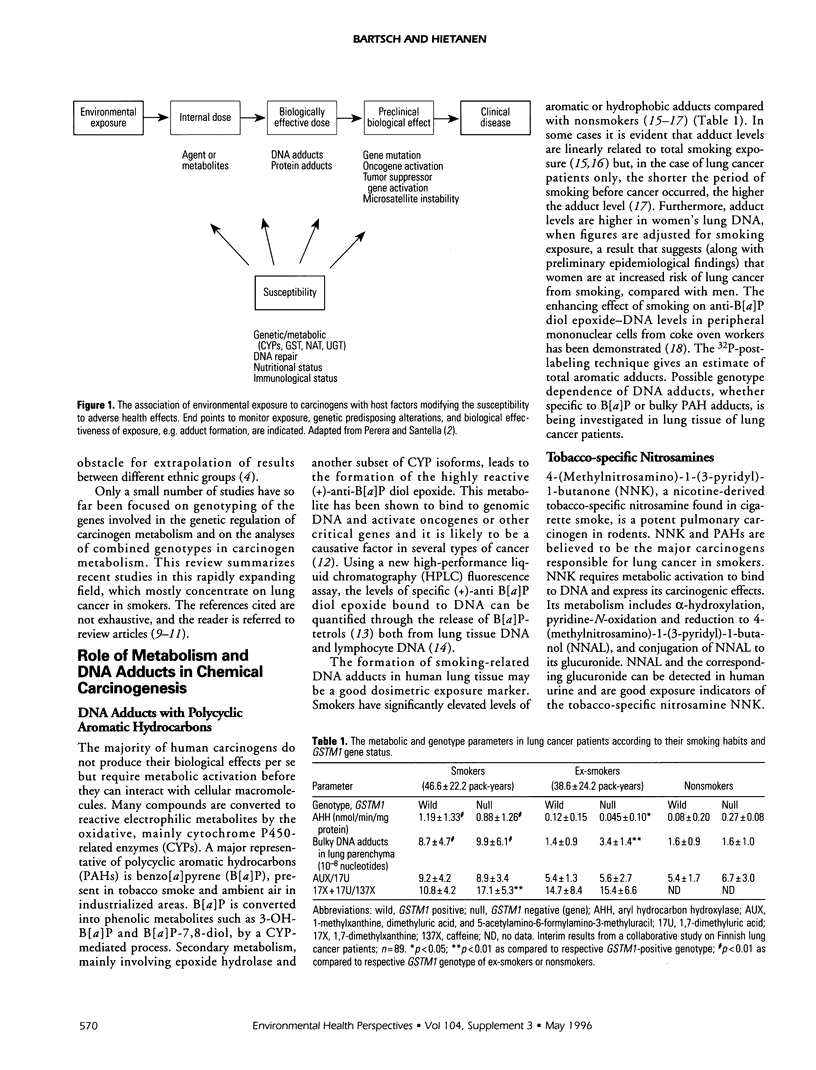
Individual susceptibility to cancer may result from host factors including differences n metabolism, DNA repair, altered expression of protooncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, and nutritional status. Since most carcinogens require metabolic activation before binding to DNA, variations in an individual's metabolic phenotype that have detected in enzymes involved in activation and detoxification should play an essential role in the development of environmental cancer. This phenotypic metabolic variation has now been related to genetic polymorphisms, and many genes encoding carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes have been identified and cloned. Consequently, allelic variants or genetic defects that give rise to the observed variation and new polymorphisms have been recognized. Development of simple polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assays has enabled identification of an individual's genotype for a variety of metabolic polymorphisms. Thus, recent knowledge of the genetic basis for individual metabolic variation has opened new possibilities of studies focusing on increased individual susceptibility to environmentally induced cancer, which are reviewed with special reference to smoking-induced lung cancer. Cancer susceptibility due to chemical exposure is likely to be determined by an individual's phenotype for a number of enzymes (both activating and detoxifying) relevant to that of a single carcinogen or mixtures of carcinogens. Given the number and variability in expression of carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes and the complexity of chemical exposures, assessment of a single polymorphic enzyme (genotype) may not be sufficient. Mutations in the p53 gene are among the most common genetic changes in human cancer. The frequency and type p53 mutations can act as a fingerprint of carcinogen exposure and may therefore provide information about external etiological agents, intensity of exposure, and host factors affecting the tumorigenesis process. In human lung cancer, p53 mutations (both the mutation pattern and frequency) have been linked with tobacco smoking; the type of mutation most frequently observed is G:C to T:A transversion, a mutation preferentially induced by benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide. An association between the presence of this transversion and the genotype deficient in glutathione S-transferase M1-mediated detoxification has been observed in lung cancer. Taken together, these findings suggest that determination of metabolic at risk genotypes in combination with levels of DNA adducts in target (surrogate) tissues and the p53 mutation pattern should allow the identification of susceptible individuals and subgroups in carcinogen-exposed populations.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltonen L. A., Peltomäki P., Leach F. S., Sistonen P., Pylkkänen L., Mecklin J. P., Järvinen H., Powell S. M., Jen J., Hamilton S. R. Clues to the pathogenesis of familial colorectal cancer. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):812–816. doi: 10.1126/science.8484121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov K., Rojas M., Geneste O., Castegnaro M., Camus A. M., Petruzzelli S., Giuntini C., Bartsch H. An improved fluorometric assay for dosimetry of benzo(a)pyrene diol-epoxide-DNA adducts in smokers' lung: comparisons with total bulky adducts and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6248–6253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anttila S., Vainio H., Hietanen E., Camus A. M., Malaveille C., Brun G., Husgafvel-Pursiainen K., Heikkilä L., Karjalainen A., Bartsch H. Immunohistochemical detection of pulmonary cytochrome P450IA and metabolic activities associated with P450IA1 and P450IA2 isozymes in lung cancer patients. Environ Health Perspect. 1992 Nov;98:179–182. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9298179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch H., Barbin A., Marion M. J., Nair J., Guichard Y. Formation, detection, and role in carcinogenesis of ethenobases in DNA. Drug Metab Rev. 1994;26(1-2):349–371. doi: 10.3109/03602539409029802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch H., Rojas M., Alexandrov K., Camus A. M., Castegnaro M., Malaveille C., Anttila S., Hirvonen K., Husgafvel-Pursiainen K., Hietanen E. Metabolic polymorphism affecting DNA binding and excretion of carcinogens in humans. Pharmacogenetics. 1995;5(Spec No):S84–S90. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199512001-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. A., Taylor J. A., Butler M. A., Stephens E. A., Wiest J., Brubaker L. H., Kadlubar F. F., Lucier G. W. Genotype/phenotype discordance for human arylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT2) reveals a new slow-acetylator allele common in African-Americans. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Aug;14(8):1689–1692. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.8.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. A., Thompson C. L., Taylor J., Miller C. R., Perera F., Hsieh L. L., Lucier G. W. Genetic monitoring of human polymorphic cancer susceptibility genes by polymerase chain reaction: application to glutathione transferase mu. Environ Health Perspect. 1992 Nov;98:113–117. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9298113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockmöller J., Kerb R., Drakoulis N., Nitz M., Roots I. Genotype and phenotype of glutathione S-transferase class mu isoenzymes mu and psi in lung cancer patients and controls. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 1;53(5):1004–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell B., Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Bock K. W., Iyanagi T., Jansen P. L., Lancet D., Mulder G. J., Chowdhury J. R., Siest G. The UDP glucuronosyltransferase gene superfamily: suggested nomenclature based on evolutionary divergence. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):487–494. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. A., Lang N. P., Young J. F., Caporaso N. E., Vineis P., Hayes R. B., Teitel C. H., Massengill J. P., Lawsen M. F., Kadlubar F. F. Determination of CYP1A2 and NAT2 phenotypes in human populations by analysis of caffeine urinary metabolites. Pharmacogenetics. 1992 Jun;2(3):116–127. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199206000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles B., Ketterer B. The role of glutathione and glutathione transferases in chemical carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(1):47–70. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofts F., Taioli E., Trachman J., Cosma G. N., Currie D., Toniolo P., Garte S. J. Functional significance of different human CYP1A1 genotypes. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Dec;15(12):2961–2963. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.12.2961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly A. K., Cholerton S., Gregory W., Idle J. R. Metabolic polymorphisms. Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Feb-Mar;57(2-3):129–160. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90053-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragani T. A., Manenti G., Pierotti M. A. Genetics of murine lung tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 1995;67:83–112. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60711-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Salguero P., Gonzalez F. J. The CYP2A gene subfamily: species differences, regulation, catalytic activities and role in chemical carcinogenesis. Pharmacogenetics. 1995;5(Spec No):S123–S128. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199512001-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R., Lescoe M. K., Rao M. R., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Garber J., Kane M., Kolodner R. The human mutator gene homolog MSH2 and its association with hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariboldi M., Manenti G., Canzian F., Falvella F. S., Radice M. T., Pierotti M. A., Della Porta G., Binelli G., Dragani T. A. A major susceptibility locus to murine lung carcinogenesis maps on chromosome 6. Nat Genet. 1993 Feb;3(2):132–136. doi: 10.1038/ng0293-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Samore M., McQuiddy P., Kasper C. B. Effects of 2-acetylaminofluorene and N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofluorene on the cellular levels of epoxide hydratase, cytochrome P-450b, and NADPH-cytochrome c (P-450) oxidoreductase messenger ribonucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11032–11036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallier E., Deutschmann S., Reichel C., Bolt H. M., Peter H. A comparative investigation of the metabolism of methyl bromide and methyl iodide in human erythrocytes. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1990;62(3):221–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00379437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. C., Hollstein M. Clinical implications of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. N Engl J Med. 1993 Oct 28;329(18):1318–1327. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199310283291807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. C. p53: at the crossroads of molecular carcinogenesis and risk assessment. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1980–1981. doi: 10.1126/science.8266092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett C., Aicher L., Sidhu J. S., Omiecinski C. J. Human microsomal epoxide hydrolase: genetic polymorphism and functional expression in vitro of amino acid variants. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;3(3):421–428. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Watanabe J., Kawajiri K. High susceptibility to lung cancer analyzed in terms of combined genotypes of P450IA1 and Mu-class glutathione S-transferase genes. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Aug;83(8):866–870. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01992.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Watanabe J., Nakachi K., Eguchi H., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K. Interindividual difference in expression of human Ah receptor and related P450 genes. Carcinogenesis. 1994 May;15(5):801–806. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Watanabe J., Nakachi K., Kawajiri K. Genetic linkage of lung cancer-associated MspI polymorphisms with amino acid replacement in the heme binding region of the human cytochrome P450IA1 gene. J Biochem. 1991 Sep;110(3):407–411. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirvonen A., Husgafvel-Pursiainen K., Anttila S., Vainio H. The GSTM1 null genotype as a potential risk modifier for squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Jul;14(7):1479–1481. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.7.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirvonen A., Husgafvel-Pursiainen K., Karjalainen A., Anttila S., Vainio H. Point-mutational MspI and Ile-Val polymorphisms closely linked in the CYP1A1 gene: lack of association with susceptibility to lung cancer in a Finnish study population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1992 Sep-Oct;1(6):485–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. C., Reyes H., Chu F. F., Sander F., Conley L. H., Brooks B. A., Hankinson O. Cloning of a factor required for activity of the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.1852076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiba M., Hagmar L., Rannug A., Högstedt B., Alexandrie A. K., Carstensen U., Hemminki K. Aromatic DNA adducts, micronuclei and genetic polymorphism for CYP1A1 and GST1 in chimney sweeps. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Jul;15(7):1347–1352. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.7.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingelman-Sundberg M., Johansson I., Persson I., Yue Q. Y., Dahl M. L., Bertilsson L., Sjöqvist F. Genetic polymorphism of cytochromes P450: interethnic differences and relationship to incidence of lung cancer. Pharmacogenetics. 1992 Dec;2(6):264–271. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199212000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionov Y., Peinado M. A., Malkhosyan S., Shibata D., Perucho M. Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):558–561. doi: 10.1038/363558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M. The 1982 Bernard B. brodie Award Lecture. Metabolism of Aromatic hydrocarbons by the cytochrome P-450 system and epoxide hydrolase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin C. J., Miners J. O., Burchell B., Mackenzie P. I. The glucuronidation of hydroxylated metabolites of benzo[a]pyrene and 2-acetylaminofluorene by cDNA-expressed human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Dec;14(12):2637–2639. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.12.2637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. S., Brooks B. A., Reyes H., Hoffman E. C., Hankinson O. An MspI RFLP in the human ARNT gene, encoding a subunit of the nuclear form of the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):351–351. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.5.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaderlik K. R., Kadlubar F. F. Metabolic polymorphisms and carcinogen-DNA adduct formation in human populations. Pharmacogenetics. 1995;5(Spec No):S108–S117. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199512001-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlubar F. F., Butler M. A., Kaderlik K. R., Chou H. C., Lang N. P. Polymorphisms for aromatic amine metabolism in humans: relevance for human carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect. 1992 Nov;98:69–74. doi: 10.1289/ehp.929869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalow W., Tang B. K. The use of caffeine for enzyme assays: a critical appraisal. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993 May;53(5):503–514. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1993.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Shields P. G., Caporaso N. E., Hoover R. N., Trump B. F., Sugimura H., Weston A., Harris C. C. Cytochrome P450IIE1 genetic polymorphisms, racial variation, and lung cancer risk. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 1;52(23):6712–6715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawajiri K., Nakachi K., Imai K., Yoshii A., Shinoda N., Watanabe J. Identification of genetically high risk individuals to lung cancer by DNA polymorphisms of the cytochrome P450IA1 gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80721-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer B., Harris J. M., Talaska G., Meyer D. J., Pemble S. E., Taylor J. B., Lang N. P., Kadlubar F. F. The human glutathione S-transferase supergene family, its polymorphism, and its effects on susceptibility to lung cancer. Environ Health Perspect. 1992 Nov;98:87–94. doi: 10.1289/ehp.929887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivistö K. T., Griese E. U., Fritz P., Linder A., Hakkola J., Raunio H., Beaune P., Kroemer H. K. Expression of cytochrome P 450 3A enzymes in human lung: a combined RT-PCR and immunohistochemical analysis of normal tissue and lung tumours. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;353(2):207–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00168759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G. All in the (cancer) family. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):103–104. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G. Antioncogenes and human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10914–10921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Schork N. J. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2037–2048. doi: 10.1126/science.8091226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. P., Bunce N. J. The Ah receptor and the mechanism of dioxin toxicity. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):273–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2760273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landi M. T., Bertazzi P. A., Shields P. G., Clark G., Lucier G. W., Garte S. J., Cosma G., Caporaso N. E. Association between CYP1A1 genotype, mRNA expression and enzymatic activity in humans. Pharmacogenetics. 1994 Oct;4(5):242–246. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199410000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Han C. Y., Lin B. K., Hardy S. Slow acetylator mutations in the human polymorphic N-acetyltransferase gene in 786 Asians, blacks, Hispanics, and whites: application to metabolic epidemiology. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):827–834. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Nicolaides N. C., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Parsons R. E., Jen J., Papadopolous N., Peltomäki P., de la Chapelle A., Hamilton S. R. Mismatch repair gene defects in sporadic colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):48–55. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkinson A. M. The genetic basis of susceptibility to lung tumors in mice. Toxicology. 1989 Mar;54(3):241–271. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(89)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlo A., Mabry M., Gabrielson E., Vollmer R., Baylin S. B., Sidransky D. Frequent microsatellite instability in primary small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 15;54(8):2098–2101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair J., Barbin A., Guichard Y., Bartsch H. 1,N6-ethenodeoxyadenosine and 3,N4-ethenodeoxycytine in liver DNA from humans and untreated rodents detected by immunoaffinity/32P-postlabeling. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Mar;16(3):613–617. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.3.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakachi K., Imai K., Hayashi S., Kawajiri K. Polymorphisms of the CYP1A1 and glutathione S-transferase genes associated with susceptibility to lung cancer in relation to cigarette dose in a Japanese population. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 1;53(13):2994–2999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Elovaara E., Anttila S., Hirvonen A., Camus A. M., Hayes J. D., Ketterer B., Vainio H. Expression and polymorphism of glutathione S-transferase in human lungs: risk factors in smoking-related lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Apr;16(4):707–711. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norppa H., Hirvonen A., Järventaus H., Uusküla M., Tasa G., Ojajärvi A., Sorsa M. Role of GSTT1 and GSTM1 genotypes in determining individual sensitivity to sister chromatid exchange induction by diepoxybutane in cultured human lymphocytes. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Jun;16(6):1261–1264. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.6.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens I. S., Ritter J. K. The novel bilirubin/phenol UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT1 gene locus: implications for multiple nonhemolytic familial hyperbilirubinemia phenotypes. Pharmacogenetics. 1992 Jun;2(3):93–108. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199206000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen O., Nebert D. W. Metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: etiologic role in carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1982 Jun;34(2):189–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemble S., Schroeder K. R., Spencer S. R., Meyer D. J., Hallier E., Bolt H. M., Ketterer B., Taylor J. B. Human glutathione S-transferase theta (GSTT1): cDNA cloning and the characterization of a genetic polymorphism. Biochem J. 1994 May 15;300(Pt 1):271–276. doi: 10.1042/bj3000271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson I., Johansson I., Bergling H., Dahl M. L., Seidegård J., Rylander R., Rannug A., Högberg J., Sundberg M. I. Genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P4502E1 in a Swedish population. Relationship to incidence of lung cancer. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 22;319(3):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter H., Deutschmann S., Reichel C., Hallier E. Metabolism of methyl chloride by human erythrocytes. Arch Toxicol. 1989;63(5):351–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00303122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen D. D., McKinney C. E., Ikeya K., Smith H. H., Bale A. E., McBride O. W., Nebert D. W. Human CYP1A1 gene: cosegregation of the enzyme inducibility phenotype and an RFLP. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;48(4):720–725. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyronneau M. A., Renaud J. P., Jaouen M., Urban P., Cullin C., Pompon D., Mansuy D. Expression in yeast of three allelic cDNAs coding for human liver P-450 3A4. Different stabilities, binding properties and catalytic activities of the yeast-produced enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Dec 1;218(2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. H., Hewer A., Martin C. N., Garner R. C., King M. M. Correlation of DNA adduct levels in human lung with cigarette smoking. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):790–792. doi: 10.1038/336790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. H., Schoket B., Hewer A., Bailey E., Kostic S., Vincze I. Influence of cigarette smoking on the levels of DNA adducts in human bronchial epithelium and white blood cells. Int J Cancer. 1990 Oct 15;46(4):569–575. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannug A., Alexandrie A. K., Persson I., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Genetic polymorphism of cytochromes P450 1A1, 2D6 and 2E1: regulation and toxicological significance. J Occup Environ Med. 1995 Jan;37(1):25–36. doi: 10.1097/00043764-199501000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redford-Ellis M., Gowenlock A. H. Studies on the reaction of chloromethane with human blood. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1971;30(1):36–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1971.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas M., Alexandrov K., Auburtin G., Wastiaux-Denamur A., Mayer L., Mahieu B., Sebastien P., Bartsch H. Anti-benzo[a]pyrene diolepoxide--DNA adduct levels in peripheral mononuclear cells from coke oven workers and the enhancing effect of smoking. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Jun;16(6):1373–1376. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.6.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas M., Alexandrov K., van Schooten F. J., Hillebrand M., Kriek E., Bartsch H. Validation of a new fluorometric assay for benzo[a]pyrene diolepoxide-DNA adducts in human white blood cells: comparisons with 32P-postlabeling and ELISA. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Mar;15(3):557–560. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.3.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryberg D., Hewer A., Phillips D. H., Haugen A. Different susceptibility to smoking-induced DNA damage among male and female lung cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 15;54(22):5801–5803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryberg D., Kure E., Lystad S., Skaug V., Stangeland L., Mercy I., Børresen A. L., Haugen A. p53 mutations in lung tumors: relationship to putative susceptibility markers for cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 15;54(6):1551–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., DePierre J. W. Microsomal epoxide hydrolase. Properties, regulation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 29;695(3-4):251–270. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(83)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Pero R. W., Markowitz M. M., Roush G., Miller D. G., Beattie E. J. Isoenzyme(s) of glutathione transferase (class Mu) as a marker for the susceptibility to lung cancer: a follow up study. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jan;11(1):33–36. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Pero R. W., Miller D. G., Beattie E. J. A glutathione transferase in human leukocytes as a marker for the susceptibility to lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1986 May;7(5):751–753. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Vorachek W. R., Pero R. W., Pearson W. R. Hereditary differences in the expression of the human glutathione transferase active on trans-stilbene oxide are due to a gene deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7293–7297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields P. G., Sugimura H., Caporaso N. E., Petruzzelli S. F., Bowman E. D., Trump B. F., Weston A., Harris C. C. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts and the CYP1A1 restriction fragment length polymorphism. Environ Health Perspect. 1992 Nov;98:191–194. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9298191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shridhar V., Siegfried J., Hunt J., del Mar Alonso M., Smith D. I. Genetic instability of microsatellite sequences in many non-small cell lung carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 15;54(8):2084–2087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodum R. S., Chung F. L. 1,N2-ethenodeoxyguanosine as a potential marker for DNA adduct formation by trans-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Cancer Res. 1988 Jan 15;48(2):320–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Takahashi T., Kuroishi T., Suyama M., Ariyoshi Y., Takahashi T., Ueda R. p53 mutations in non-small cell lung cancer in Japan: association between mutations and smoking. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):734–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tefre T., Ryberg D., Haugen A., Nebert D. W., Skaug V., Brøgger A., Børresen A. L. Human CYP1A1 (cytochrome P(1)450) gene: lack of association between the Msp I restriction fragment length polymorphism and incidence of lung cancer in a Norwegian population. Pharmacogenetics. 1991 Oct;1(1):20–25. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199110000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thier R., Foest U., Deutschmann S., Schroeder K. R., Westphal G., Hallier E., Peter H. Distribution of methylene chloride in human blood. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1991;14:254–258. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74936-0_53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thier R., Taylor J. B., Pemble S. E., Humphreys W. G., Persmark M., Ketterer B., Guengerich F. P. Expression of mammalian glutathione S-transferase 5-5 in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535 leads to base-pair mutations upon exposure to dihalomethanes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8576–8580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiano H. F., Wang R. L., Hosokawa M., Crespi C., Tindall K. R., Langenbach R. Human CYP2A6 activation of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK): mutational specificity in the gpt gene of AS52 cells. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Dec;15(12):2859–2866. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.12.2859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu F., Kikuchi H., Motomiya M., Abe T., Sagami I., Ohmachi T., Wakui A., Kanamaru R., Watanabe M. Association between restriction fragment length polymorphism of the human cytochrome P450IIE1 gene and susceptibility to lung cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Mar;82(3):254–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedlund P. J., Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. 1462V mutation in the human CYP1A1 gene: lack of correlation with either the Msp I 1.9 kb (M2) allele or CYP1A1 inducibility in a three-generation family of east Mediterranean descent. Pharmacogenetics. 1994 Feb;4(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiencke J. K., Pemble S., Ketterer B., Kelsey K. T. Gene deletion of glutathione S-transferase theta: correlation with induced genetic damage and potential role in endogenous mutagenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1995 Apr-May;4(3):253–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Chang R. L., Levin W., Yagi H., Thakker D. R., van Bladeren P. J., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Mutagenicity of the enantiomers of the diastereomeric bay-region benz(a)anthracene 3,4-diol-1,2-epoxides in bacterial and mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Dec;43(12 Pt 1):5821–5825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooster R., Cleton-Jansen A. M., Collins N., Mangion J., Cornelis R. S., Cooper C. S., Gusterson B. A., Ponder B. A., von Deimling A., Wiestler O. D. Instability of short tandem repeats (microsatellites) in human cancers. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):152–156. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong S., Howie A. F., Ketterer B., Taylor J., Hayes J. D., Beckett G. J., Wathen C. G., Wolf C. R., Spurr N. K. Glutathione S-transferase mu locus: use of genotyping and phenotyping assays to assess association with lung cancer susceptibility. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Sep;12(9):1533–1537. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.9.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Ghissassi F., Barbin A., Nair J., Bartsch H. Formation of 1,N6-ethenoadenine and 3,N4-ethenocytosine by lipid peroxidation products and nucleic acid bases. Chem Res Toxicol. 1995 Mar;8(2):278–283. doi: 10.1021/tx00044a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


