Abstract
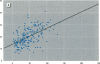
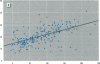
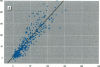
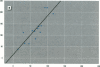
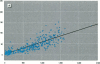
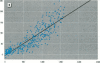
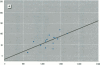
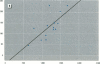
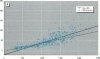
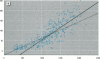
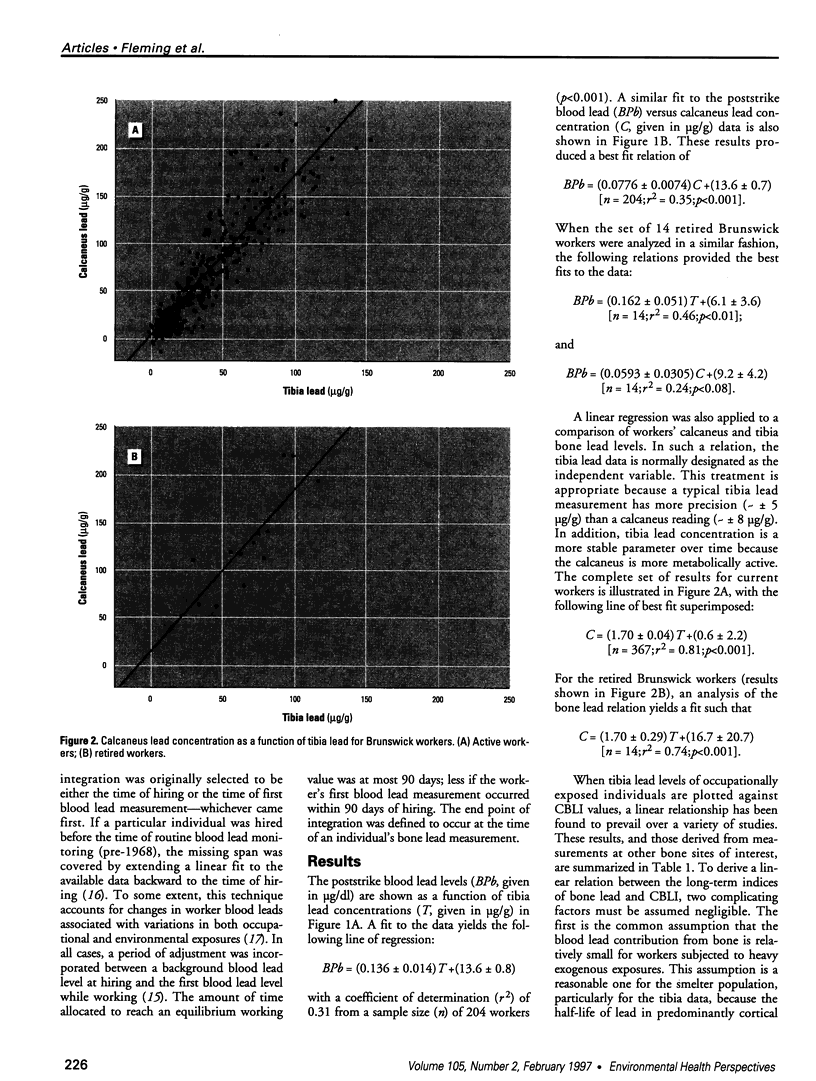
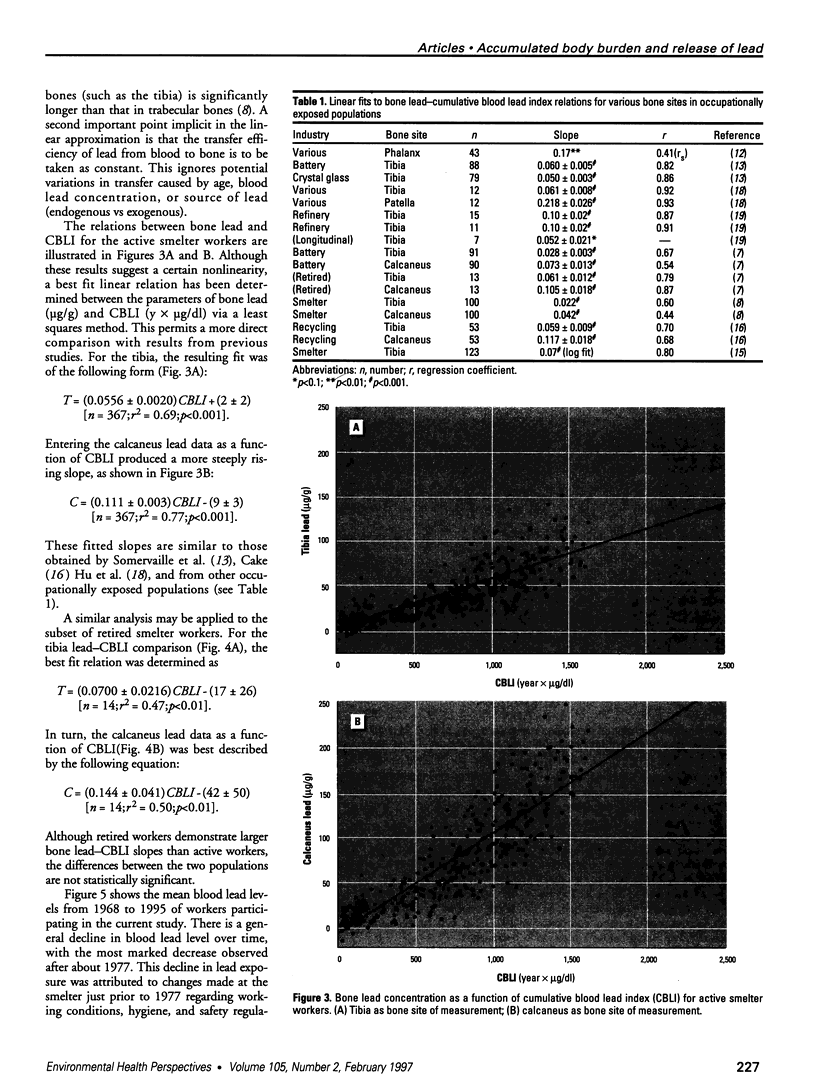
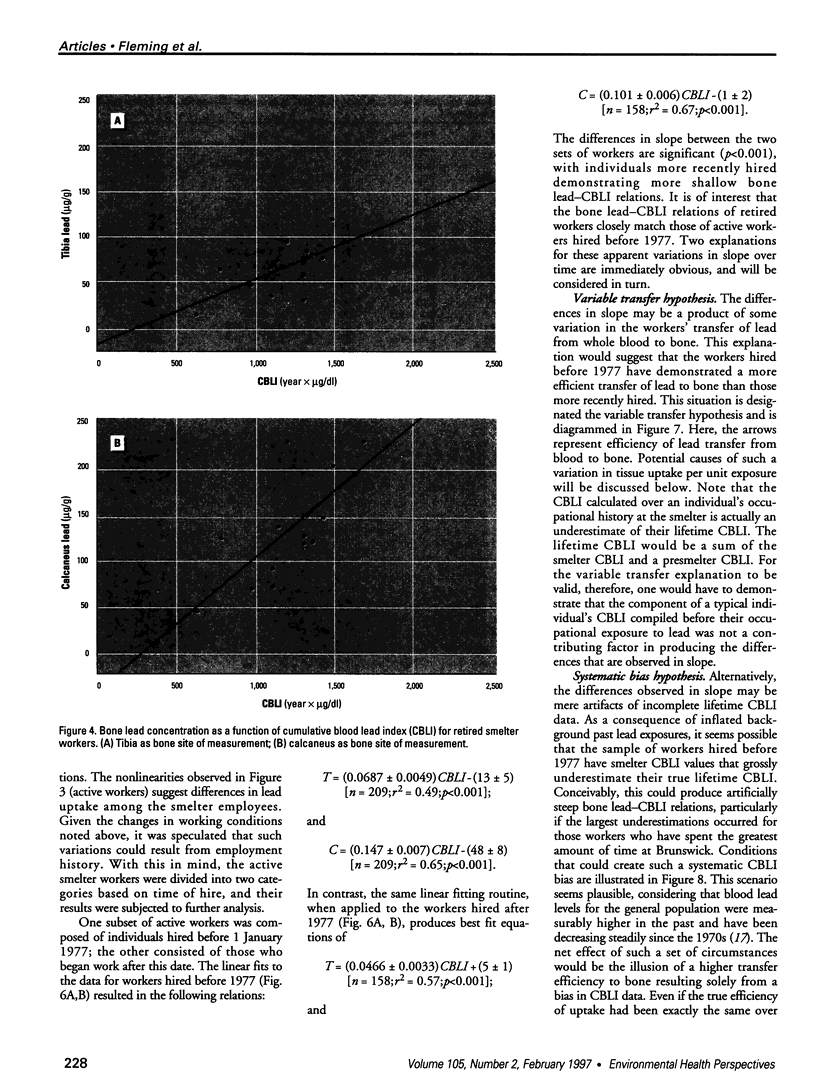
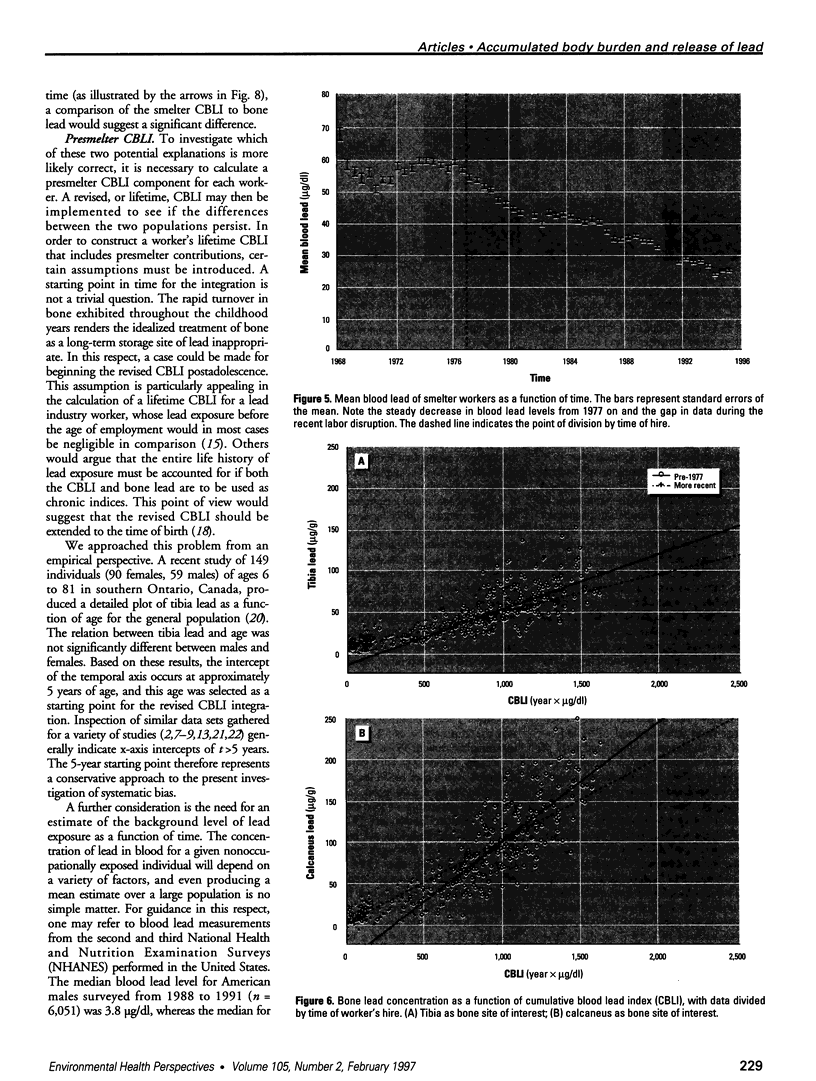
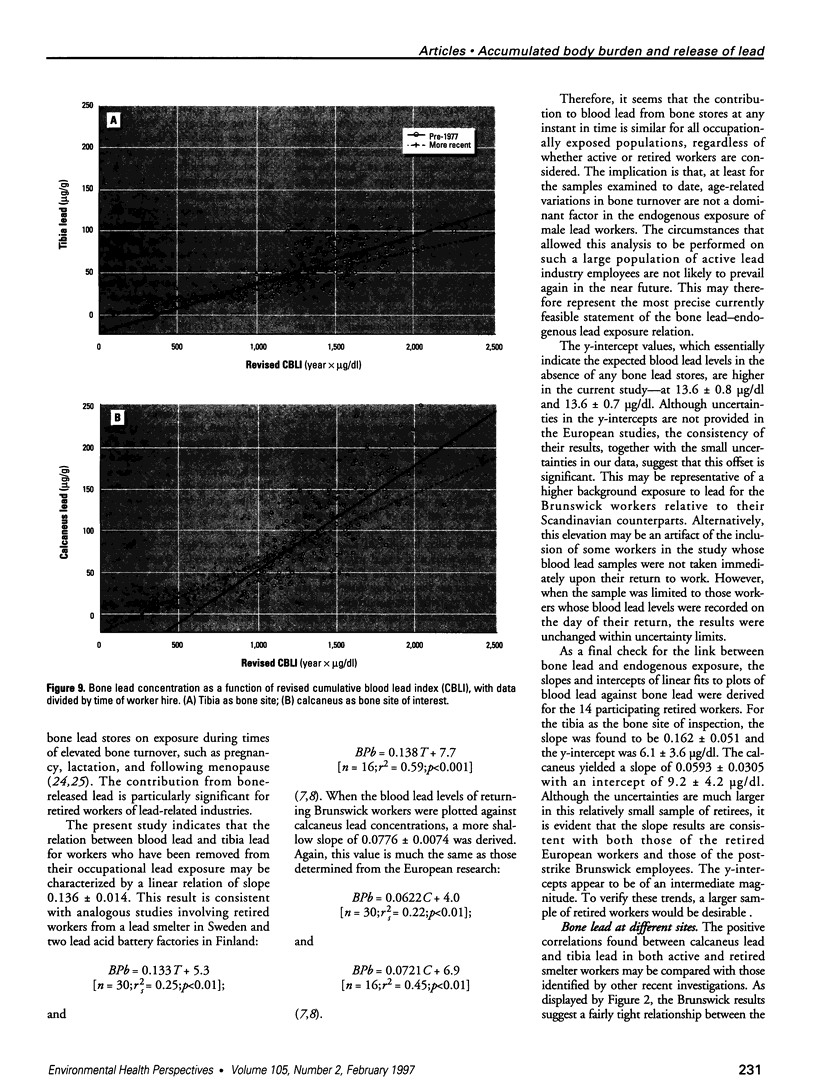
Bone lead levels for 367 active and 14 retired lead smelter workers were measured in vivo by X-ray fluorescence in May-June 1994. The bone sites of study were the tibia and calcaneus; magnitudes of concentration were used to gauge lead body burden. Whole blood lead readings from the workers generated a cumulative blood lead index (CBLI) that approximated the level of lead exposure over time. Blood lead values for 204 of the 381 workers were gathered from workers returning from a 10-month work interruption that ended in 1991; their blood level values were compared to their tibia and calcaneus lead levels. The resulting relations allowed constraints to be placed on the endogenous release of lead from bone in smelter works. Calcaneus lead levels were found to correlate strongly with those for tibia lead, and in a manner consistent with observations from other lead industry workers. Relations between bone lead concentration and CBLI demonstrated a distinctly nonlinear appearance. When the active population was divided by date of hire, a significant difference in the bone lead-CBLI slope emerged. After a correction to include the component of CBLI existing before the workers' employment at the smelter was made, this difference persisted. This implies that the transfer of lead from blood to bone in the workers has changed over time, possibly as a consequence of varying exposure conditions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annest J. L., Pirkle J. L., Makuc D., Neese J. W., Bayse D. D., Kovar M. G. Chronological trend in blood lead levels between 1976 and 1980. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 9;308(23):1373–1377. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306093082301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R., Chettle D. R., Scott M. C., Somervaille L. J., Pendlington M. Repeated measurements of tibia lead concentrations by in vivo x ray fluorescence in occupational exposure. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Jan;49(1):14–16. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry P. S. A comparison of concentrations of lead in human tissues. Br J Ind Med. 1975 May;32(2):119–139. doi: 10.1136/oem.32.2.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cake K. M., Bowins R. J., Vaillancourt C., Gordon C. L., McNutt R. H., Laporte R., Webber C. E., Chettle D. R. Partition of circulating lead between serum and red cells is different for internal and external sources of lead. Am J Ind Med. 1996 May;29(5):440–445. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0274(199605)29:5<440::AID-AJIM2>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chettle D. R., Scott M. C., Somervaille L. J. Lead in bone: sampling and quantitation using K X-rays excited by 109Cd. Environ Health Perspect. 1991 Feb;91:49–55. doi: 10.1289/ehp.919149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christoffersson J. O., Schütz A., Ahlgren L., Haeger-Aronsen B., Mattsson S., Skerfving S. Lead in finger-bone analysed in vivo in active and retired lead workers. Am J Ind Med. 1984;6(6):447–457. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700060608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erkkilä J., Armstrong R., Riihimäki V., Chettle D. R., Paakkari A., Scott M., Somervaille L., Starck J., Kock B., Aitio A. In vivo measurements of lead in bone at four anatomical sites: long term occupational and consequent endogenous exposure. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Sep;49(9):631–644. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.9.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardsson L., Attewell R., Chettle D. R., Englyst V., Lundström N. G., Nordberg G. F., Nyhlin H., Scott M. C., Todd A. C. In vivo measurements of lead in bone in long-term exposed lead smelter workers. Arch Environ Health. 1993 May-Jun;48(3):147–156. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1993.9940813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C. L., Chettle D. R., Webber C. E. An improved instrument for the in vivo detection of lead in bone. Br J Ind Med. 1993 Jul;50(7):637–641. doi: 10.1136/oem.50.7.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu H., Pepper L., Goldman R. Effect of repeated occupational exposure to lead, cessation of exposure, and chelation on levels of lead in bone. Am J Ind Med. 1991;20(6):723–735. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700200603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosnett M. J., Becker C. E., Osterloh J. D., Kelly T. J., Pasta D. J. Factors influencing bone lead concentration in a suburban community assessed by noninvasive K x-ray fluorescence. JAMA. 1994 Jan 19;271(3):197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett R. W. An age-specific kinetic model of lead metabolism in humans. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Dec;101(7):598–616. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manton W. I., Cook J. D. High accuracy (stable isotope dilution) measurements of lead in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Br J Ind Med. 1984 Aug;41(3):313–319. doi: 10.1136/oem.41.3.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manton W. I., Malloy C. R. Distribution of lead in body fluids after ingestion of soft solder. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Feb;40(1):51–57. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manton W. I. Total contribution of airborne lead to blood lead. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Mar;42(3):168–172. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.3.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. H. Multicompartment kinetic model for lead. III. Lead in blood plasma and erythrocytes. Environ Res. 1985 Apr;36(2):473–489. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(85)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Ryde S. J., Jones S. J., Wyatt R. M., Hainsworth I. R., Cobbold S. S., Evans C. J., Braithwaite R. A. In vivo measurements of cadmium and lead in occupationally-exposed workers and an urban population. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1990 Jul-Dec;26-27:407–414. doi: 10.1007/BF02992695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty E. J. Physiologically based models for bone-seeking elements. IV. Kinetics of lead disposition in humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;118(1):16–29. doi: 10.1006/taap.1993.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle J. L., Brody D. J., Gunter E. W., Kramer R. A., Paschal D. C., Flegal K. M., Matte T. D. The decline in blood lead levels in the United States. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) JAMA. 1994 Jul 27;272(4):284–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz M. B. Toxicokinetics of bone lead. Environ Health Perspect. 1991 Feb;91:33–37. doi: 10.1289/ehp.919133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roels H., Konings J., Green S., Bradley D., Chettle D., Lauwerys R. Time-integrated blood lead concentration is a valid surrogate for estimating the cumulative lead dose assessed by tibial lead measurement. Environ Res. 1995 May;69(2):75–82. doi: 10.1006/enrs.1995.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbergeld E. K., Schwartz J., Mahaffey K. Lead and osteoporosis: mobilization of lead from bone in postmenopausal women. Environ Res. 1988 Oct;47(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(88)80023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somervaille L. J., Chettle D. R., Scott M. C. In vivo measurement of lead in bone using x-ray fluorescence. Phys Med Biol. 1985 Sep;30(9):929–943. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/30/9/005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somervaille L. J., Chettle D. R., Scott M. C., Tennant D. R., McKiernan M. J., Skilbeck A., Trethowan W. N. In vivo tibia lead measurements as an index of cumulative exposure in occupationally exposed subjects. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Mar;45(3):174–181. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.3.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somervaille L. J., Nilsson U., Chettle D. R., Tell I., Scott M. C., Schütz A., Mattsson S., Skerfving S. In vivo measurements of bone lead--a comparison of two x-ray fluorescence techniques used at three different bone sites. Phys Med Biol. 1989 Dec;34(12):1833–1845. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/34/12/007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd A. C., Chettle D. R. In vivo X-ray fluorescence of lead in bone: review and current issues. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Feb;102(2):172–177. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd A. C., McNeill F. E., Palethorpe J. E., Peach D. E., Chettle D. R., Tobin M. J., Strosko S. J., Rosen J. C. In vivo X-ray fluorescence of lead in bone using K X-ray excitation with 109Cd sources: radiation dosimetry studies. Environ Res. 1992 Apr;57(2):117–132. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(05)80073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmers L. E., Jr, Aufderheide A. C., Wallgren J., Rapp G., Jr, Alich A. Lead in bone. IV. Distribution of lead in the human skeleton. Arch Environ Health. 1988 Nov-Dec;43(6):381–391. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1988.9935855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deSilva P. E. Determination of lead in plasma and studies on its relationship to lead in erythrocytes. Br J Ind Med. 1981 Aug;38(3):209–217. doi: 10.1136/oem.38.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]