Abstract
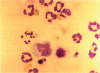
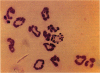
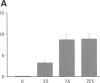
Silica is a toxicant that can stimulate cells to produce various cellular products such as free radicals, cytokines, and growth factors. Silica and its induced substances may induce apoptosis to regulate the evolution of silica-induced inflammation and fibrosis. To examine this hypothesis, groups of Wistar male rats were intratracheally instilled with different doses of Min-U-Sil 5 silica (Silica, Berkeley Springs, WV). Ten days after the instillation, we obtained cells by bronchoalveolar lavage and placed them on slides by cytospin preparation. The slides were stained with Diff-Quik (Lab Aids, Sydney, NSW, Australia) and examined under oil immersion. A substantial number of cells with apoptotic features were identified in all silica-instilled rats and the apoptosis was confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The number of apoptotic cells was clearly related to silica dosage. Engulfment of apoptotic cells by macrophages was also noted. Neutrophil influx in silica-instilled rats could be saturated with the increase of silica dosage and the number of macrophages in different dose groups changed in parallel with the proportion of apoptotic cells. Fifty-six days after instillation, morphologically apoptotic cells could be identified in granulomatous cells of lung tissue from silica-instilled rats. We conclude that intratracheal instillation of silica could induce apoptosis in both alveolar and granulomatous cells, and the apoptotic change and subsequent engulfment by macrophages might play a role in the evolution of silica-induced effects.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absher M., Sjöstrand M., Baldor L. C., Hemenway D. R., Kelley J. Patterns of secretion of transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-alpha) in experimental silicosis. Acute and subacute effects of cristobalite exposure in the rat. Reg Immunol. 1993 May-Aug;5(3-4):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackford J. A., Jr, Antonini J. M., Castranova V., Dey R. D. Intratracheal instillation of silica up-regulates inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression and increases nitric oxide production in alveolar macrophages and neutrophils. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 Oct;11(4):426–431. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.11.4.7522485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Oberhammer F., Jirtle R. L., Askari M., Sedivy R., Grasl-Kraupp B., Purchio A. F., Schulte-Hermann R. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 as a signal for induction of cell death by apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 1993 Mar;67(3):531–536. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G., Crossley J., Xing Z. Macrophage engulfment of apoptotic neutrophils contributes to the resolution of acute pulmonary inflammation in vivo. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995 Feb;12(2):232–237. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.12.2.7865221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Jiang H. X., Mochimaru H., Yoneyama H., Kudoh S., Ohkuni H., Ooami H., Ferrans V. J. Alveolar fibrosis and capillary alteration in experimental pulmonary silicosis in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Jun;151(6):1946–1955. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.6.7767544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. L., Henson J. E., Henson P. M. Phagocytosis of senescent neutrophils by human monocyte-derived macrophages and rabbit inflammatory macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):430–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. B., Parchment R. E., Lewellyn A. L. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of programmed cell death in the blastocyst. Differentiation. 1991 Apr;46(3):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1991.tb00880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Collart M. A., Grau G. E., Sappino A. P., Vassalli P. Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):245–247. doi: 10.1038/344245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom W. N. Relationship of inflammatory cell cytokines to disease severity in individuals with occupational inorganic dust exposure. Am J Ind Med. 1991;19(1):15–27. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700190104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffiotti U., Daniel L. N., Mao Y., Shi X., Williams A. O., Kaighn M. E. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis by crystalline silica in relation to oxygen radicals. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Dec;102 (Suppl 10):159–163. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s10159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin A., Conan-Cibotti M., Henkart P. A. Cytotoxic effect of TNF and lymphotoxin on T lymphoblasts. J Immunol. 1995 Oct 15;155(8):3716–3718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J. S., Wyllie A. H., Henson J. E., Walport M. J., Henson P. M., Haslett C. Macrophage phagocytosis of aging neutrophils in inflammation. Programmed cell death in the neutrophil leads to its recognition by macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):865–875. doi: 10.1172/JCI113970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Hermann R., Bursch W., Kraupp-Grasl B., Oberhammer F., Wagner A., Jirtle R. Cell proliferation and apoptosis in normal liver and preneoplastic foci. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Dec;101 (Suppl 5):87–90. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101s587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki J., Kawanami O., Yoneyama H., Hara F. [Analysis of cells in bronchoalveolar lavage and ultrastructure of lung tissues in experimental silicosis]. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1993 Jun;31(6):686–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida H., Takeda Y., Takei H., Shinzawa H., Takahashi T., Sendo F. In vivo regulation of rat neutrophil apoptosis occurring spontaneously or induced with TNF-alpha or cycloheximide. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 1;154(5):2403–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. O., Flanders K. C., Saffiotti U. Immunohistochemical localization of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in rats with experimental silicosis, alveolar type II hyperplasia, and lung cancer. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1831–1840. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama H., Kawanami O., Usuki J., Furuta T., Ohkuni H., Todome Y., Ooami H. [Adhesion ultrastructures of mononuclear cells in experimentally-induced silicotic granuloma]. Arerugi. 1993 Aug;42(8):955–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]