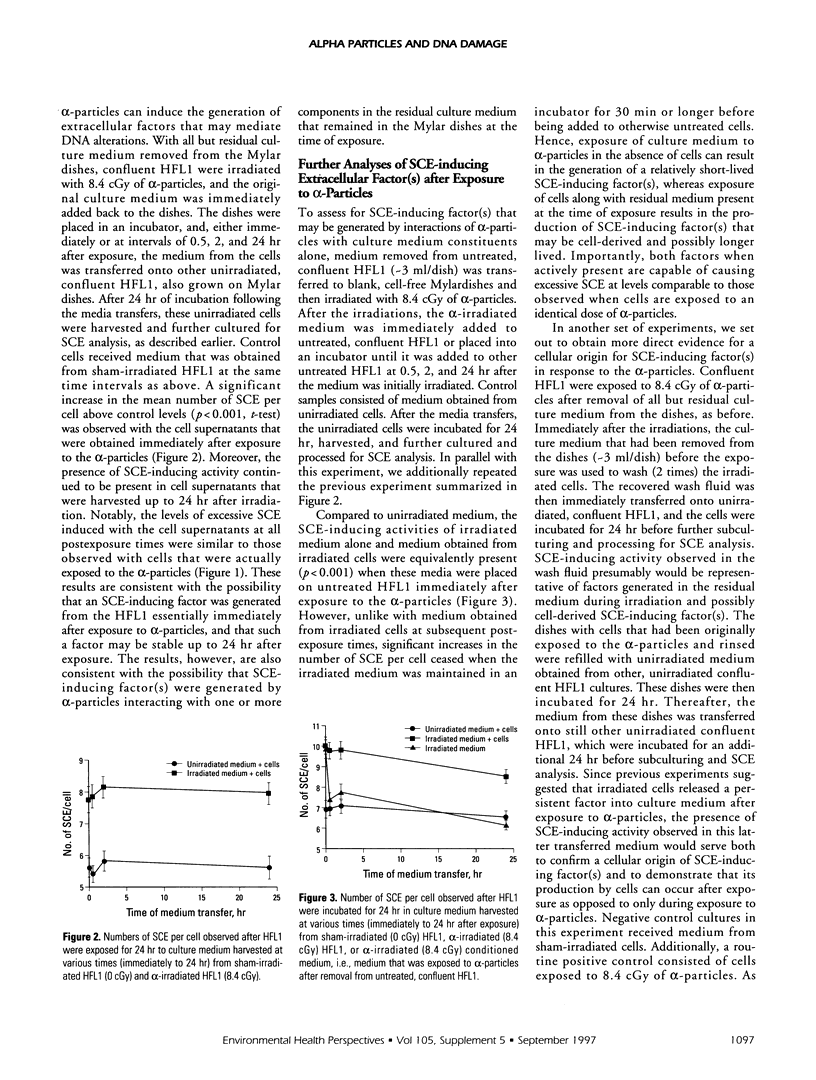
Abstract
The mechanism(s) by which alpha (alpha) particles like those emitted from inhaled radon and radon progeny cause their carcinogenic effects in the lung remains unclear. Although direct nuclear traversals by alpha-particles may be involved in mediating these outcomes, increasing evidence indicates that a particles can cause alterations in DNA in the absence of direct hits to cell nuclei. Using the occurrence of excessive sister chromatid exchanges (SCE) as an index of DNA damage in human lung fibroblasts, we investigated the hypothesis that alpha-particles may induce DNA damage through the generation of extracellular factors. We have found that a relatively low dose of alpha-particles can result in the generation of extracellular factors, which, upon transfer to unexposed normal human cells, can cause excessive SCE to an extent equivalent to that observed when the cells are directly irradiated with the same irradiation dose. A short-lived, SCE-inducing factor(s) is generated in alpha-irradiated culture medium containing serum in the absence of cells. A more persistent SCE-inducing factor(s), which can survive freeze-thaw and is heat labile is produced by fibroblasts after exposure to the alpha-particles. These results indicate that the initiating target for alpha-particle-induced genetic changes can be larger than a cell's nucleus or even a whole cell. How transmissible factors like those observed here in vitro may extend to the in vivo condition in the context of a-particle-induced carcinogenesis in the respiratory tract remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF

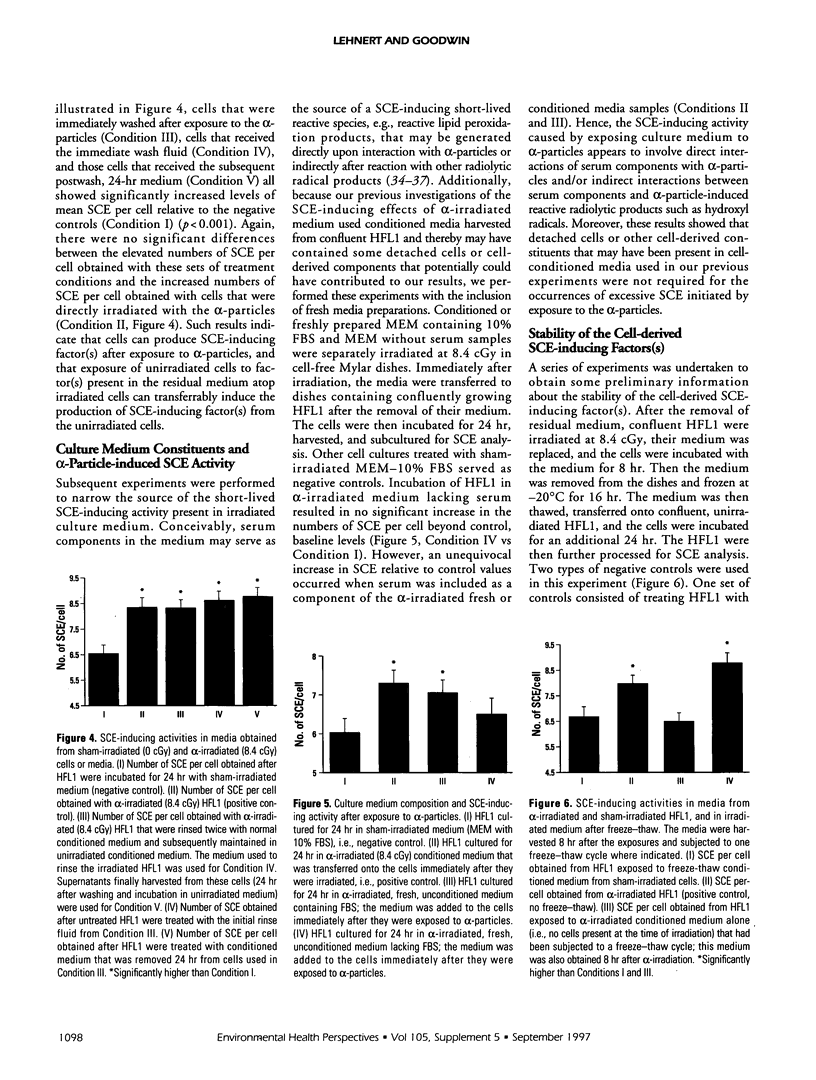


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghamohammadi S. Z., Goodhead D. T., Savage J. R. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges (SCE) in G0 lymphocytes by plutonium-238 alpha-particles. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1988 Jun;53(6):909–915. doi: 10.1080/09553008814551271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
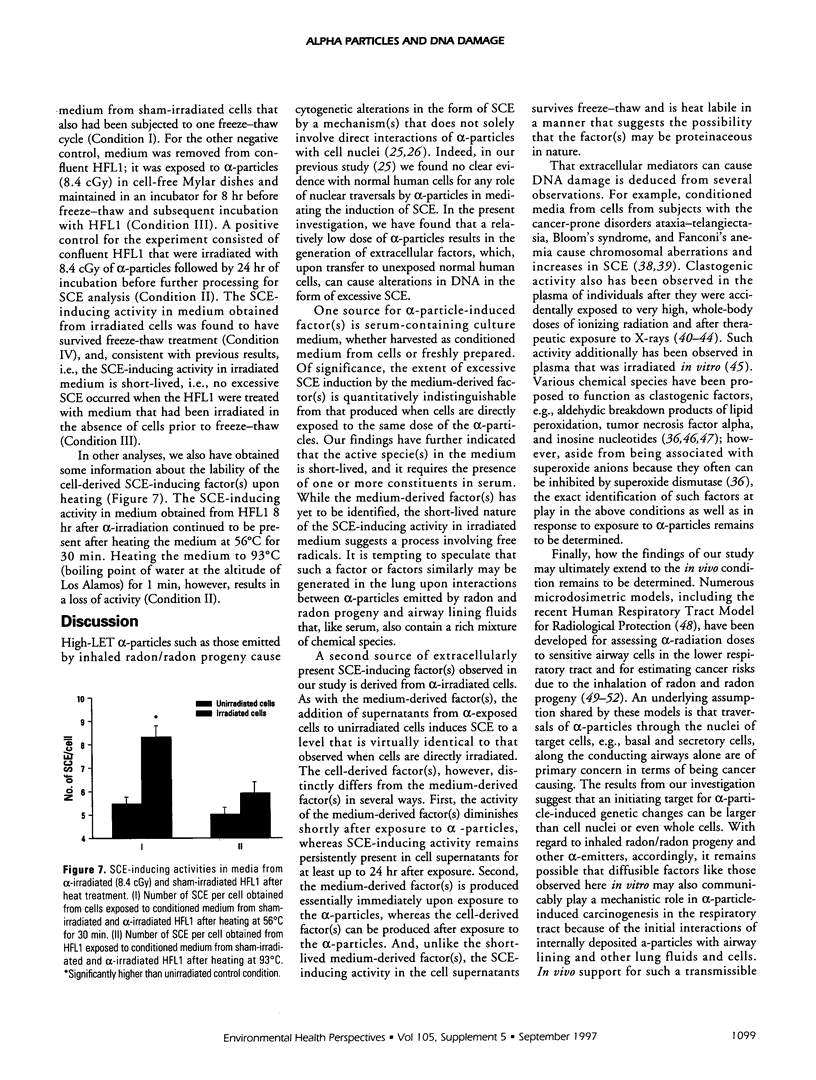
- Auclair C., Gouyette A., Levy A., Emerit I. Clastogenic inosine nucleotide as components of the chromosome breakage factor in scleroderma patients. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Apr;278(1):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90253-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. P., Rohrig N., Colvett R. D., Geard C. R., Marino S. A. Inactivation of synchronized Chinese Hamster V79 cells with charged-particle track segments. Radiat Res. 1980 May;82(2):277–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blöcher D. DNA double-strand break repair determines the RBE of alpha-particles. Int J Radiat Biol. 1988 Nov;54(5):761–771. doi: 10.1080/09553008814552201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. L., Newton G. J., Shyr L. J., Seiler F. A., Scott B. R. The combined effects of alpha-particles and X-rays on cell killing and micronuclei induction in lung epithelial cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Nov;58(5):799–811. doi: 10.1080/09553009014552181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornforth M. N., Goodwin E. H. The dose-dependent fragmentation of chromatin in human fibroblasts by 3.5-MeV alpha particles from 238Pu: experimental and theoretical considerations pertaining to single-track effects. Radiat Res. 1991 Jul;127(1):64–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande A., Goodwin E. H., Bailey S. M., Marrone B. L., Lehnert B. E. Alpha-particle-induced sister chromatid exchange in normal human lung fibroblasts: evidence for an extranuclear target. Radiat Res. 1996 Mar;145(3):260–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerit I., Arutyunyan R., Oganesian N., Levy A., Cernjavsky L., Sarkisian T., Pogossian A., Asrian K. Radiation-induced clastogenic factors: anticlastogenic effect of Ginkgo biloba extract. Free Radic Biol Med. 1995 Jun;18(6):985–991. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)00220-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerit I., Cerutti P. Clastogenic activity from Bloom syndrome fibroblast cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1868–1872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerit I. Reactive oxygen species, chromosome mutation, and cancer: possible role of clastogenic factors in carcinogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1994 Jan;16(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)90246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Eckl P., Ortner A. Possible mutagens derived from lipids and lipid precursors. Mutat Res. 1990 May;238(3):223–233. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(90)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. J. Radiation biology. Alpha-particle after effects. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):674–675. doi: 10.1038/355674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faguet G. B., Reichard S. M., Welter D. A. Radiation-induced clastogenic plasma factors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 May;12(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh K., Sumner H. Breaks in normal human chromosomes: are they induced by a transferable substance in the plasma of persons exposed to total-body irradiation? Radiat Res. 1968 Jul;35(1):171–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman A. W., Jaramillo R. J., Lechner J. F., Johnson N. F. Alpha-particle-induced p53 protein expression in a rat lung epithelial cell strain. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 15;54(22):5797–5800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollowell J. G., Jr, Littlefield L. G. Chromosome damage induced by plasma of x-rayed patients: an indirect effect of x-ray. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):240–244. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inkret W. C., Eisen Y., Harvey W. F., Koehler A. M., Raju M. R. Radiobiology of alpha particles. I. Exposure system and dosimetry. Radiat Res. 1990 Sep;123(3):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadhim M. A., Lorimore S. A., Hepburn M. D., Goodhead D. T., Buckle V. J., Wright E. G. Alpha-particle-induced chromosomal instability in human bone marrow cells. Lancet. 1994 Oct 8;344(8928):987–988. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91643-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadhim M. A., Macdonald D. A., Goodhead D. T., Lorimore S. A., Marsden S. J., Wright E. G. Transmission of chromosomal instability after plutonium alpha-particle irradiation. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):738–740. doi: 10.1038/355738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H. Spontaneous and induced sister chromatid exchanges as revealed by the BUdR-labeling method. Int Rev Cytol. 1977;49:55–97. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61947-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazutka J. R., Rudaitiene S. Modulation by novobiocin of sister-chromatid exchanges induced by tumor necrosis factor in human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1992 Aug;268(2):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(92)90227-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarkatti M., Nagarkatti P. S., Brooks A. Effect of radon on the immune system: alterations in the cellularity and functions of T cells in lymphoid organs of mouse. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1996 Apr 19;47(6):535–552. doi: 10.1080/009841096161528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Little J. B. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges by extremely low doses of alpha-particles. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6394–6396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Little J. B., Inkret W. C., Carpenter S., Raju M. R., Chen D. J., Strniste G. F. Response of X-ray-sensitive CHO mutant cells (xrs-6c) to radiation. II. Relationship between cell survival and the induction of chromosomal damage with low doses of alpha particles. Radiat Res. 1991 Jun;126(3):280–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Little J. B., Inkret W. C., Carpenter S., Thompson K., Raju M. R., Chen D. J., Strniste G. F. Cytogenetic effects of extremely low doses of plutonium-238 alpha-particle irradiation in CHO K-1 cells. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;244(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(90)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prise K. M. Use of radiation quality as a probe for DNA lesion complexity. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Jan;65(1):43–48. doi: 10.1080/09553009414550061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puskin J. S., Nelson C. B. EPA's perspective on risks from residential radon exposure. JAPCA. 1989 Jul;39(7):915–920. doi: 10.1080/08940630.1989.10466577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADFORD E. P., Jr, HUNT V. R. POLONIUM-210: A VOLATILE RADIOELEMENT IN CIGARETTES. Science. 1964 Jan 17;143(3603):247–249. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3603.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju M. R., Carpenter S. G., Chmielewski J. J., Schillaci M. E., Wilder M. E., Freyer J. P., Johnson N. F., Schor P. L., Sebring R. J., Goodhead D. T. Radiobiology of ultrasoft X rays. I. Cultured hamster cells (V79). Radiat Res. 1987 Jun;110(3):396–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju M. R., Eisen Y., Carpenter S., Inkret W. C. Radiobiology of alpha particles. III. Cell inactivation by alpha-particle traversals of the cell nucleus. Radiat Res. 1991 Nov;128(2):204–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley P. A. Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Jan;65(1):27–33. doi: 10.1080/09553009414550041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Goodhead D. T. The effect of 238Pu alpha-particles on the mouse fibroblast cell line C3H 10T1/2: characterization of source and RBE for cell survival. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1987 Dec;52(6):871–882. doi: 10.1080/09553008714552461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samet J. M., Marbury M. C., Spengler J. D. Health effects and sources of indoor air pollution. Part II. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jan;137(1):221–242. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaham M., Becker Y., Cohen M. M. A diffusable clastogenic factor in ataxia telangiectasia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(2-3):155–161. doi: 10.1159/000131476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen L. C., Cucinotta F. A., Atwell W., Nealy J. E. Temporal analysis of the October 1989 proton flare using computerized anatomical models. Radiat Res. 1993 Jan;133(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhäusler F., Hofmann W., Pohl E., Pohl-Rüling J. Radiation exposure of the respiratory tract and associated carcinogenic risk due to inhaled radon daughters. Health Phys. 1983 Aug;45(2):331–337. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198308000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd P., Wood J. C., Walker J. T., Weiss S. J. Lethal, potentially lethal, and nonlethal damage induction by heavy ions in cultured human cells. Radiat Res Suppl. 1985;8:S5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaca C. E., Wilhelm J., Harms-Ringdahl M. Interaction of lipid peroxidation products with DNA. A review. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;195(2):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(88)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore A. S., McMillan A. Lung cancer mortality among U.S. uranium miners: a reappraisal. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Sep;71(3):489–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S., Perry P. Differential Giemsa staining of sister chromatids and the study of chromatid exchanges without autoradiography. Chromosoma. 1974;48(4):341–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00290991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



