Abstract
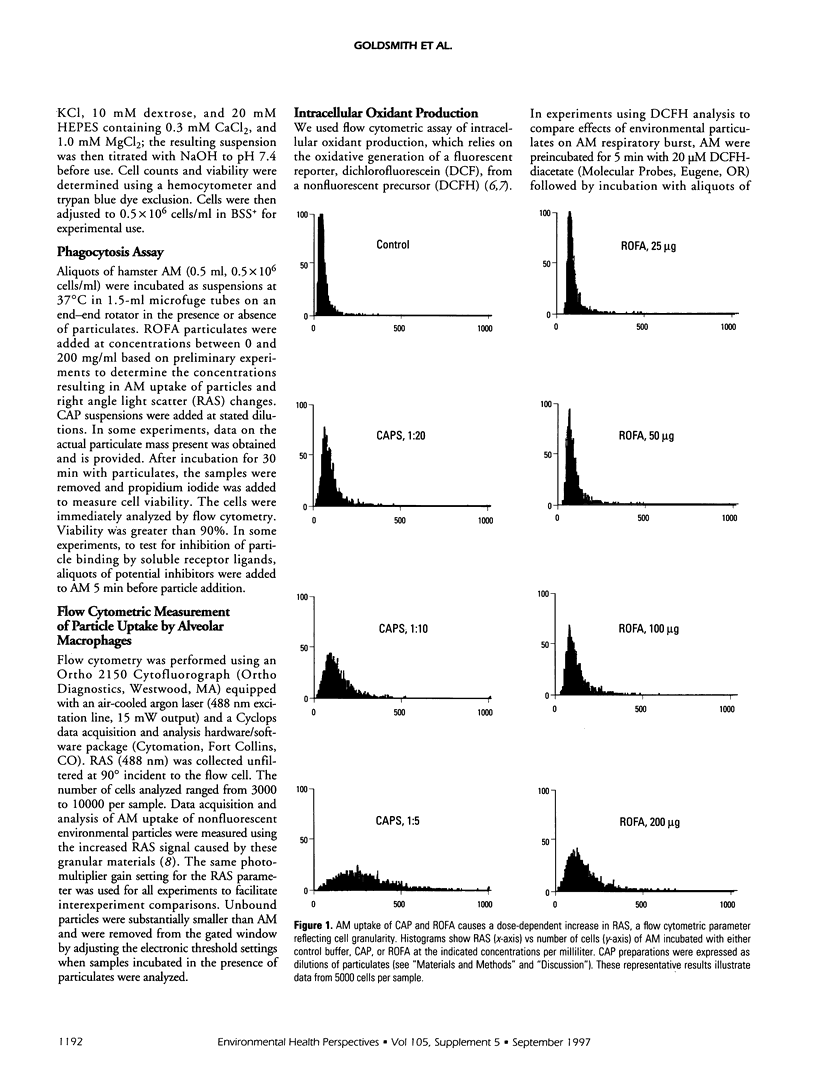
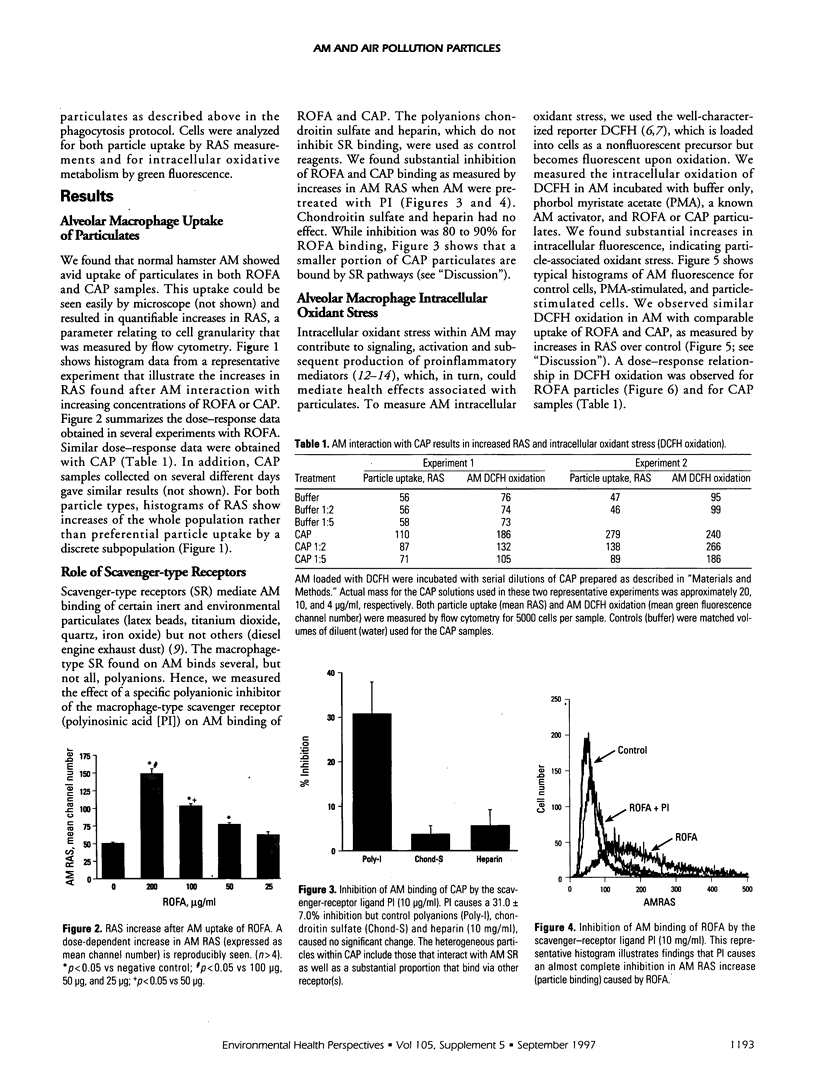
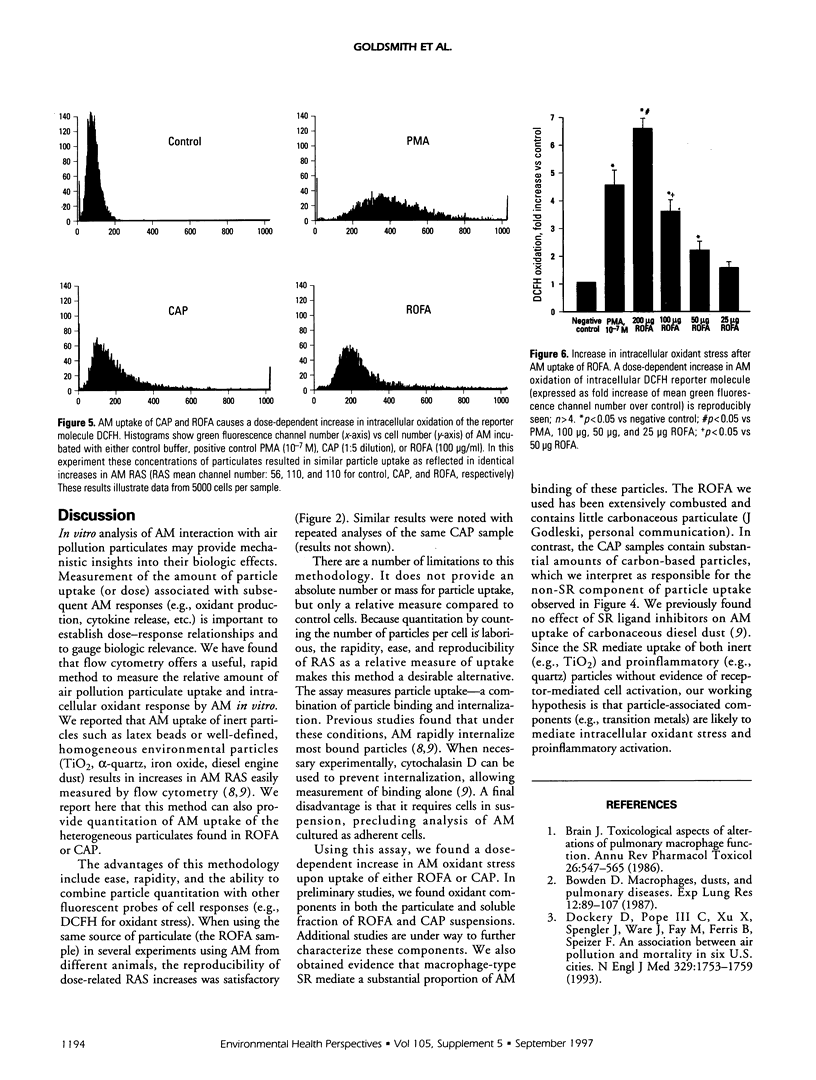
We applied flow cytometric analysis to characterize the in vitro response of alveolar macrophages (AM) to air pollution particulates. Normal hamster AM were incubated with varying concentrations of residual oil fly ash (ROFA) or concentrated ambient air particulates (CAP). We found a dose-dependent increase in AM-associated right angle light scatter (RAS) after uptake of ROFA (e.g., mean channel number 149.4 +/- 6.5, 102.5 +/- 4.1, 75.8 +/- 3.5, and 61.0 +/- 4.6 at 200, 100, 50, and 25 mg/ml, respectively) or CAP. A role for scavenger-type receptors (SR) in AM uptake of components of ROFA and CAP was identified by marked inhibition of RAS increases in AM pretreated with the specific SR inhibitor polyinosinic acid. We combined measurement of particle uptake (RAS) with flow cytometric analysis of intracellular oxidation of dichlorofluorescin. Both ROFA and CAP caused a dose-related intracellular oxidant stress within AM, comparable to that seen with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) (e.g., fold increase over control, 6.6 +/- 0.4, 3.6 +/- 0.4, 4.6 +/- 0.5, 200 mg/ml ROFA, 100 mg/ml ROFA, and 10(-7) M PMA, respectively). We conclude that flow cytometry of RAS increases provides a useful relative measurement of AM uptake of complex particulates within ROFA and CAP. Both ROFA and CAP cause substantial intracellular oxidant stress within AM, which may contribute to subsequent cell activation and production of proinflammatory mediators.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowden D. H. Macrophages, dust, and pulmonary diseases. Exp Lung Res. 1987;12(2):89–107. doi: 10.3109/01902148709062834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain J. D. Toxicological aspects of alterations of pulmonary macrophage function. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:547–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.002555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Preston A. M., Takeuchi E., Kenney J., Boxer L. A., Remick D. G. Regulation of interleukin 8 gene expression by oxidant stress. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25568–25576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockery D. W., Pope C. A., 3rd, Xu X., Spengler J. D., Ware J. H., Fay M. E., Ferris B. G., Jr, Speizer F. E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 9;329(24):1753–1759. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312093292401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghio A. J., Kennedy T. P., Whorton A. R., Crumbliss A. L., Hatch G. E., Hoidal J. R. Role of surface complexed iron in oxidant generation and lung inflammation induced by silicates. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):L511–L518. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.5.L511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser R., Elreedy S., Hoppin J. A., Christiani D. C. Airway obstruction in boilermakers exposed to fuel oil ash. A prospective investigation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Nov;152(5 Pt 1):1478–1484. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.152.5.7582280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobzik L., Godleski J. J., Brain J. D. Oxidative metabolism in the alveolar macrophage: analysis by flow cytometry. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Apr;47(4):295–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobzik L., Godleski J. J., Brain J. D. Selective down-regulation of alveolar macrophage oxidative response to opsonin-independent phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4312–4319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobzik L., Huang S., Paulauskis J. D., Godleski J. J. Particle opsonization and lung macrophage cytokine response. In vitro and in vivo analysis. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2753–2759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobzik L. Lung macrophage uptake of unopsonized environmental particulates. Role of scavenger-type receptors. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 1;155(1):367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. Air pollution and daily mortality: a review and meta analysis. Environ Res. 1994 Jan;64(1):36–52. doi: 10.1006/enrs.1994.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. What are people dying of on high air pollution days? Environ Res. 1994 Jan;64(1):26–35. doi: 10.1006/enrs.1994.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer B., Imrich A., Kobzik L. Flow cytometric assay of lung macrophage uptake of environmental particulates. Cytometry. 1995 May 1;20(1):23–32. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



