Abstract
The inflammatory response is a key component of host defense. However, excessive or persistent inflammation can contribute to the pathogenesis of disease. Inflammation is regulated, in part, by cytokines, which are small, typically glycosylated proteins that interact with membrane receptors to regulate cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and secretion. During the past 10 years studies in humans and experimental animals have demonstrated that a cytokine called tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a key role in the initiation of inflammatory responses in the lung and other tissues, including inflammation resulting from inhalation of noxious particles. There is now compelling evidence that one of the pathways by which inhaled particles stimulate the recruitment and subsequent activation of inflammatory cells is through the activation of lung macrophages to release TNF-alpha. TNF-alpha then acts via paracrine and autocrine pathways to stimulate cells to release other cytokines known as chemokines, which are directly chemotactic to leukocytes and other cells that participate in inflammatory and wound healing responses. In addition to a TNF-alpha-mediated pathway, there is growing evidence that some particles such as quartz and crocidolite can directly activate lung epithelial cells to release chemokines such as macrophage inflammatory protein-2, cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant, and interleukin-8. A direct stimulatory effect of particles on lung epithelium may represent an additional or alternate pathway by which inhaled particles may elicit inflammation in the lung. Recent studies have suggested that oxidative stress may be a component of the mechanism by which particles activate cytokine production in cells such as macrophages and epithelial cells. The contribution of oxidative stress to particle-induced cytokine gene expression appears to be mediated, at least in part, through activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B.
Full text
PDF

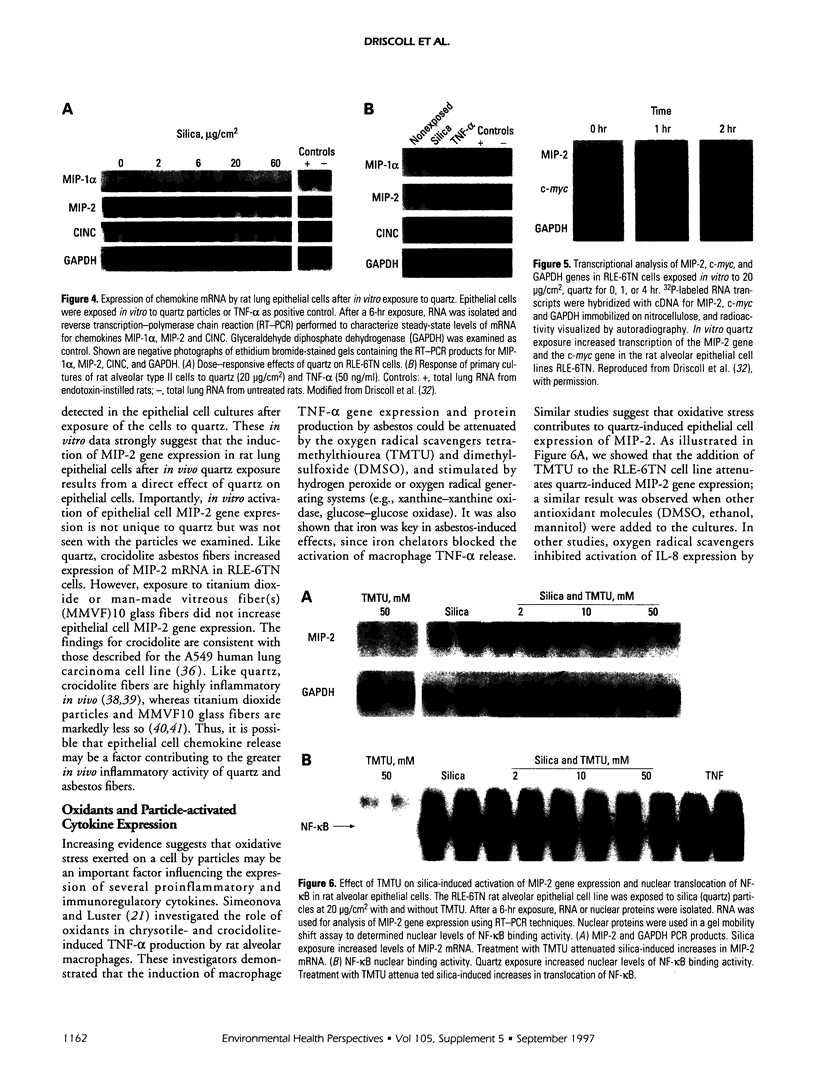


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anisowicz A., Messineo M., Lee S. W., Sager R. An NF-kappa B-like transcription factor mediates IL-1/TNF-alpha induction of gro in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):520–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzoni F., Beutler B. The tumor necrosis factor ligand and receptor families. N Engl J Med. 1996 Jun 27;334(26):1717–1725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199606273342607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanc P. D., Boushey H. A., Wong H., Wintermeyer S. F., Bernstein M. S. Cytokines in metal fume fever. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jan;147(1):134–138. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.1.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi F., DeVico A. L., Garzino-Demo A., Arya S. K., Gallo R. C., Lusso P. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. Science. 1995 Dec 15;270(5243):1811–1815. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5243.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C. A., Geiser T., Brunner T., von Tscharner V., Caput D., Ferrara P., Minty A., Baggiolini M. Monocyte chemotactic protein 3 is a most effective basophil- and eosinophil-activating chemokine. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):751–756. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das U. N., Padma M., Sagar P. S., Ramesh G., Koratkar R. Stimulation of free radical generation in human leukocytes by various agents including tumor necrosis factor is a calmodulin dependent process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1030–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90626-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Fantone J. C., Kenney J. S., Remick D. G. Oxygen radical scavengers selectively inhibit interleukin 8 production in human whole blood. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2123–2129. doi: 10.1172/JCI116097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Carter J. M., Howard B. W., Hassenbein D. G., Pepelko W., Baggs R. B., Oberdörster G. Pulmonary inflammatory, chemokine, and mutagenic responses in rats after subchronic inhalation of carbon black. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996 Feb;136(2):372–380. doi: 10.1006/taap.1996.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Carter J. M., Iype P. T., Kumari H. L., Crosby L. L., Aardema M. J., Isfort R. J., Cody D., Chestnut M. H., Burns J. L. Establishment of immortalized alveolar type II epithelial cell lines from adult rats. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1995 Jul-Aug;31(7):516–527. doi: 10.1007/BF02634029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
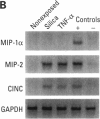
- Driscoll K. E., Hassenbein D. G., Carter J. M., Kunkel S. L., Quinlan T. R., Mossman B. T. TNF alpha and increased chemokine expression in rat lung after particle exposure. Toxicol Lett. 1995 Dec;82-83:483–489. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(95)03578-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Hassenbein D. G., Carter J., Poynter J., Asquith T. N., Grant R. A., Whitten J., Purdon M. P., Takigiku R. Macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 and 2: expression by rat alveolar macrophages, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells and in rat lung after mineral dust exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;8(3):311–318. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Hassenbein D. G., Carter J., Poynter J., Asquith T. N., Grant R. A., Whitten J., Purdon M. P., Takigiku R. Macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 and 2: expression by rat alveolar macrophages, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells and in rat lung after mineral dust exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;8(3):311–318. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
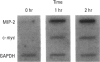
- Driscoll K. E., Howard B. W., Carter J. M., Asquith T., Johnston C., Detilleux P., Kunkel S. L., Isfort R. J. Alpha-quartz-induced chemokine expression by rat lung epithelial cells: effects of in vivo and in vitro particle exposure. Am J Pathol. 1996 Nov;149(5):1627–1637. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Lindenschmidt R. C., Maurer J. K., Higgins J. M., Ridder G. Pulmonary response to silica or titanium dioxide: inflammatory cells, alveolar macrophage-derived cytokines, and histopathology. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):381–390. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E. Macrophage inflammatory proteins: biology and role in pulmonary inflammation. Exp Lung Res. 1994 Nov-Dec;20(6):473–490. doi: 10.3109/01902149409031733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois C. M., Bissonnette E., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Asbestos fibers and silica particles stimulate rat alveolar macrophages to release tumor necrosis factor. Autoregulatory role of leukotriene B4. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 May;139(5):1257–1264. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.5.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubravec D. B., Spriggs D. R., Mannick J. A., Rodrick M. L. Circulating human peripheral blood granulocytes synthesize and secrete tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6758–6761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosset P., Lassalle P., Vanhée D., Wallaert B., Aerts C., Voisin C., Tonnel A. B. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 by human alveolar macrophages exposed in vitro to coal mine dust. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Nov;5(5):431–436. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.5.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Machleidt T., Alkalay I., Krönke M., Ben-Neriah Y., Baeuerle P. A. Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):182–185. doi: 10.1038/365182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg T. W., Miiller W. C., McConnell E. E., Chevalier J., Hadley J. G., Bernstein D. M., Thevenaz P., Anderson R. Chronic inhalation toxicity of size-separated glass fibers in Fischer 344 rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1993 May;20(4):464–476. doi: 10.1006/faat.1993.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman M., Weinberg J. B. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces increased hydrogen peroxide production and Fc receptor expression, but not increased Ia antigen expression by peritoneal macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Dec;42(6):704–707. doi: 10.1002/jlb.42.6.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen Y. M., Barchowsky A., Treadwell M., Driscoll K. E., Mossman B. T. Asbestos induces nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) DNA-binding activity and NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression in tracheal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8458–8462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen Y. M., Marsh J. P., Absher M. P., Hemenway D., Vacek P. M., Leslie K. O., Borm P. J., Mossman B. T. Expression of antioxidant enzymes in rat lungs after inhalation of asbestos or silica. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10625–10630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmenout A., Fransen L., Tavernier J., Van der Heyden J., Tizard R., Kawashima E., Shaw A., Johnson M. J., Semon D., Müller R. Molecular cloning and expression of human tumor necrosis factor and comparison with mouse tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):515–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. D., Krangel M. S. Biology and biochemistry of the chemokines: a family of chemotactic and inflammatory cytokines. Crit Rev Immunol. 1992;12(1-2):17–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Vassallo C., Luhowskyj S., Chi-Rosso G., Lobb R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Lapierre L. A., Mendrick D. L., Fiers W., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1893–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan T. R., Marsh J. P., Janssen Y. M., Leslie K. O., Hemenway D., Vacek P., Mossman B. T. Dose-responsive increases in pulmonary fibrosis after inhalation of asbestos. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Jul;150(1):200–206. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.1.8025751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich E. A., Panuska J. R., Wallis R. S., Wolf C. B., Leonard M. L., Ellner J. J. Dyscoordinate expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by human blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Apr;139(4):1010–1016. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.4.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J., Andersson T., Olsson I. Effect of tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutrophil degranulation. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3199–3205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal G. J., Germolec D. R., Blazka M. E., Corsini E., Simeonova P., Pollock P., Kong L. Y., Kwon J., Luster M. I. Asbestos stimulates IL-8 production from human lung epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1994 Oct 1;153(7):3237–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Albermann K., Baeuerle P. A. Nuclear factor kappa B: an oxidative stress-responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic Res Commun. 1992;17(4):221–237. doi: 10.3109/10715769209079515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeonova P. P., Luster M. I. Iron and reactive oxygen species in the asbestos-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha response from alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995 Jun;12(6):676–683. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.12.6.7539275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Baglioni C. The active form of tumor necrosis factor is a trimer. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6951–6954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L., Basha M. A., Chensue S. W., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Toews G. B., Westwick J., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 gene expression by a pulmonary epithelial cell line. A model for cytokine networks in the lung. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI114928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L., Phan S. H., Rollins B. J., Strieter R. M. Alveolar macrophage-derived cytokines induce monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression from human pulmonary type II-like epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9912–9918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis W. J., Beatty P. G., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. Human monocyte adherence to cultured vascular endothelium: monoclonal antibody-defined mechanisms. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2323–2330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner S. J., Libby P. Human vascular smooth muscle cells. Target for and source of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):100–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer U., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Sherry B. Genomic cloning and promoter analysis of macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-2, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta, members of the chemokine superfamily of proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):4996–5012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Liu C. C., Butler G., Cohn Z. A., Galli S. J. Identification, purification, and characterization of a mast cell-associated cytolytic factor related to tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9175–9179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Lee T. C., Guillemin B., Yu M. C., Rom W. N. Enhanced IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha release and messenger RNA expression in macrophages from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or after asbestos exposure. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):4188–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]