Abstract
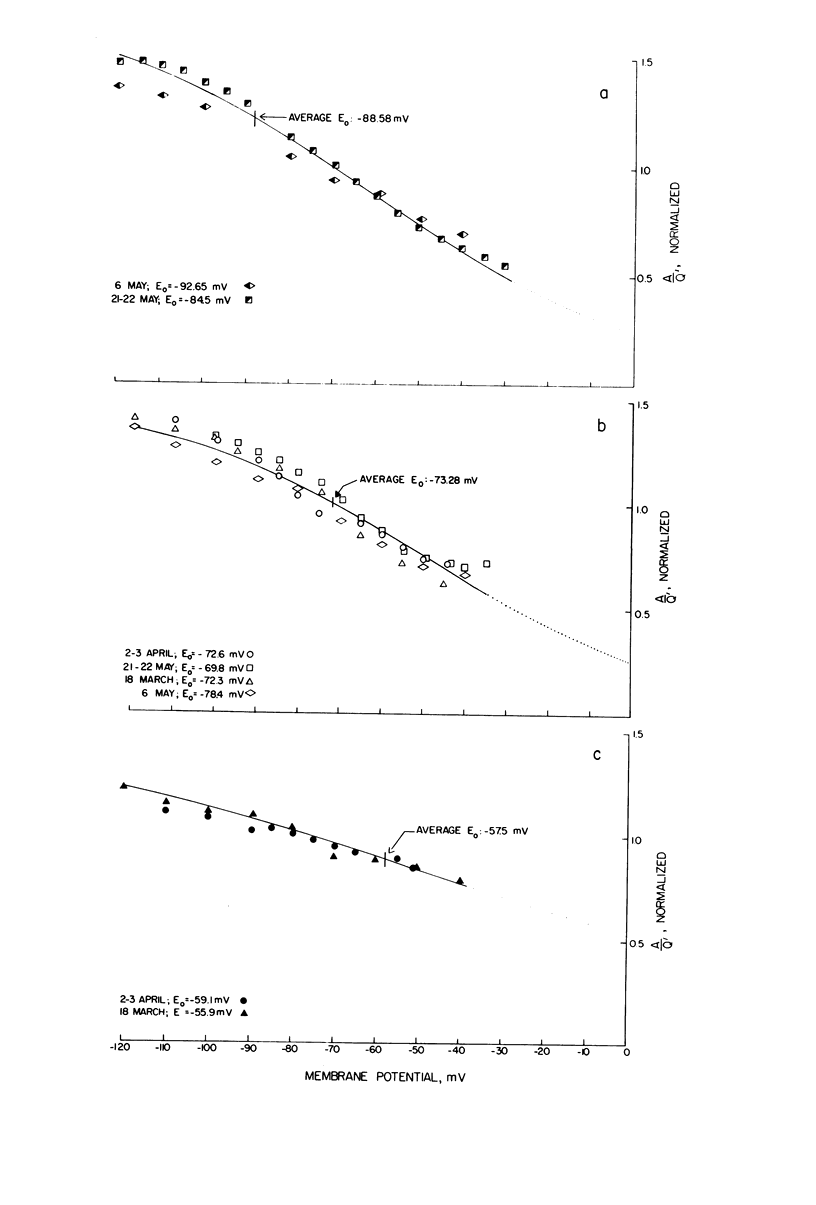
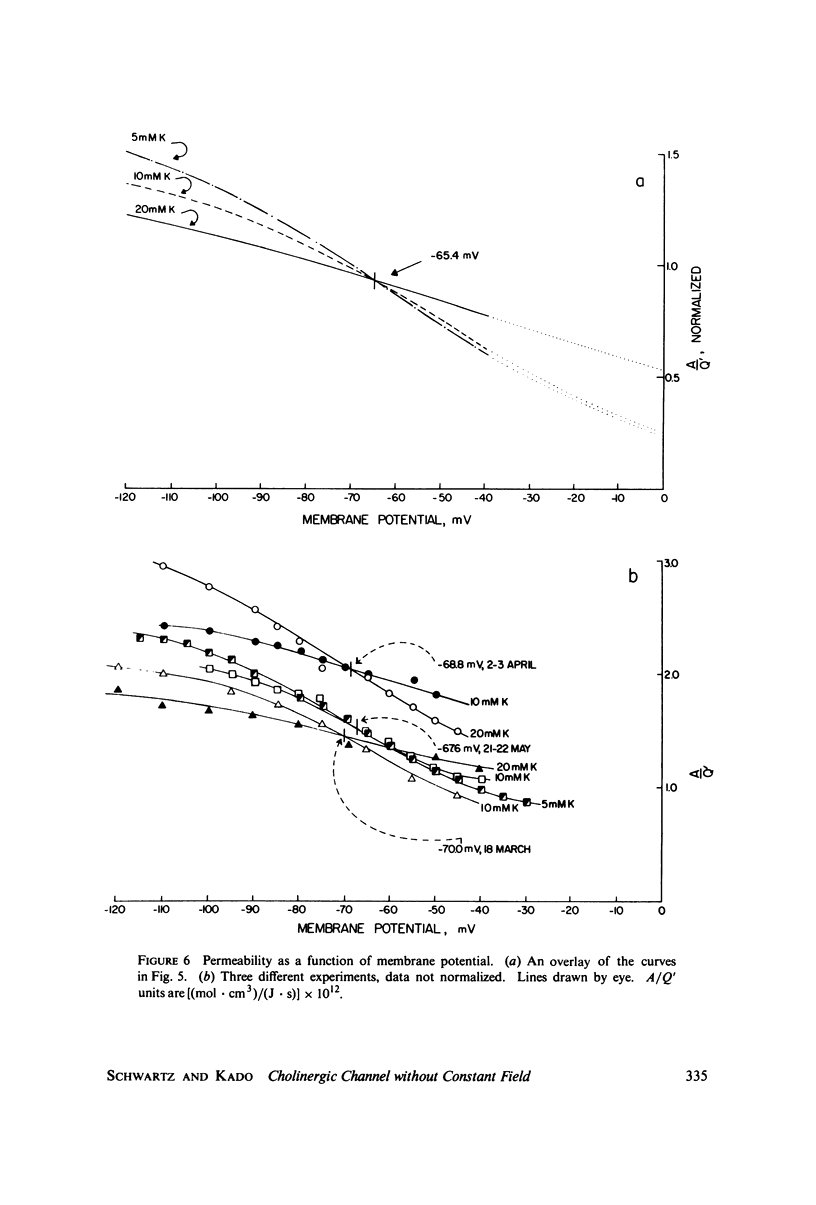
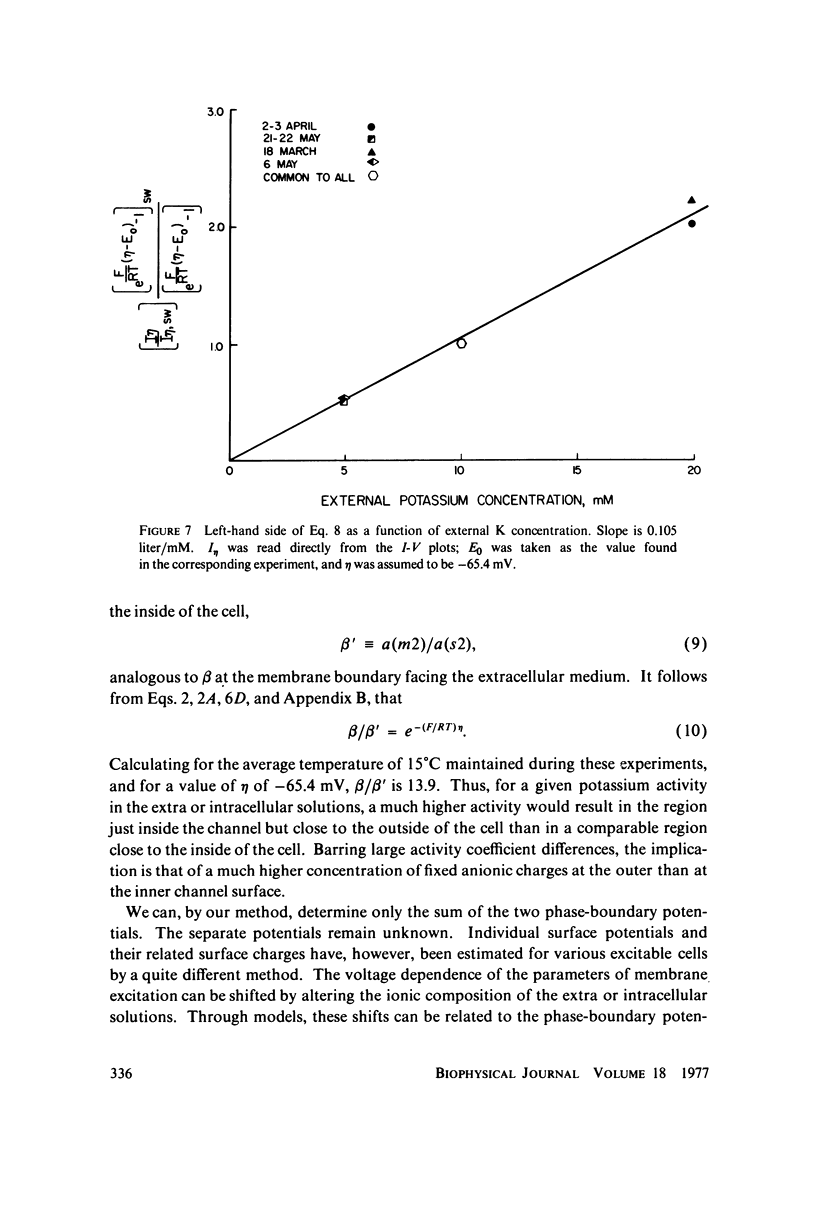
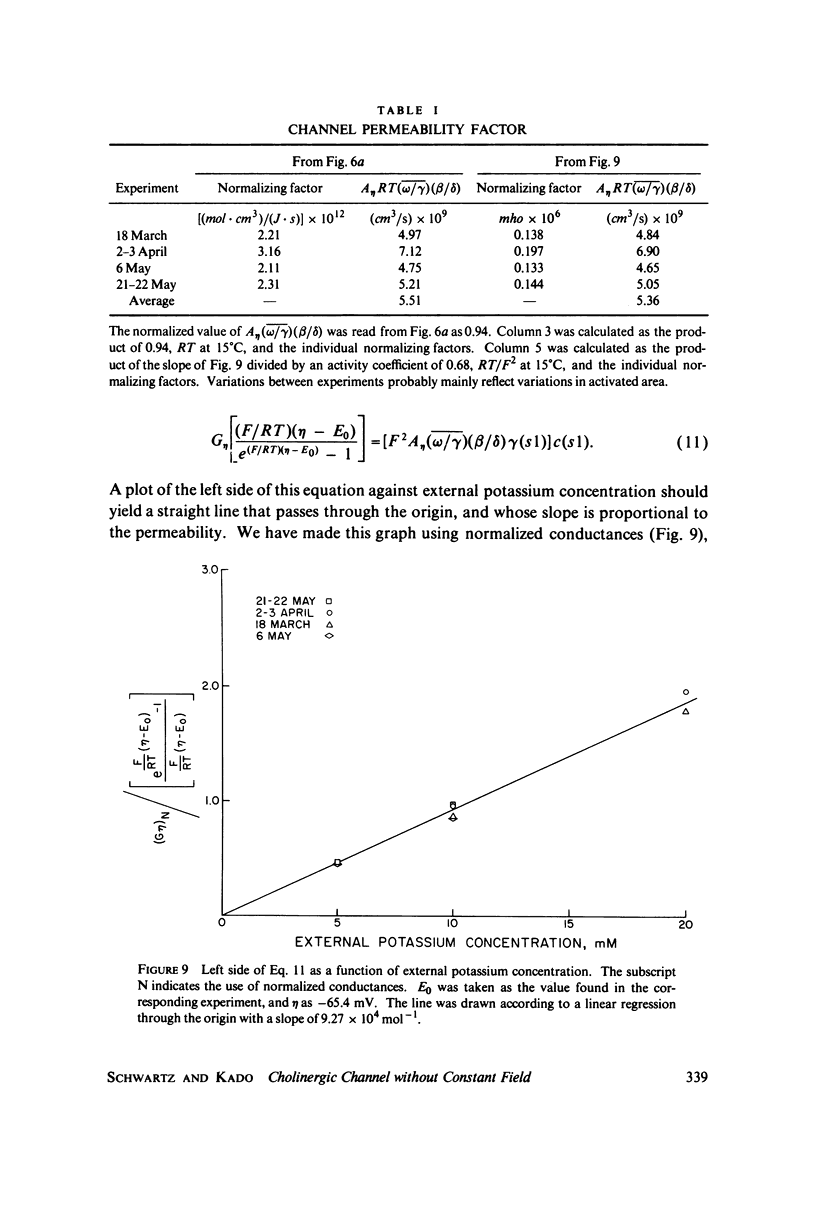
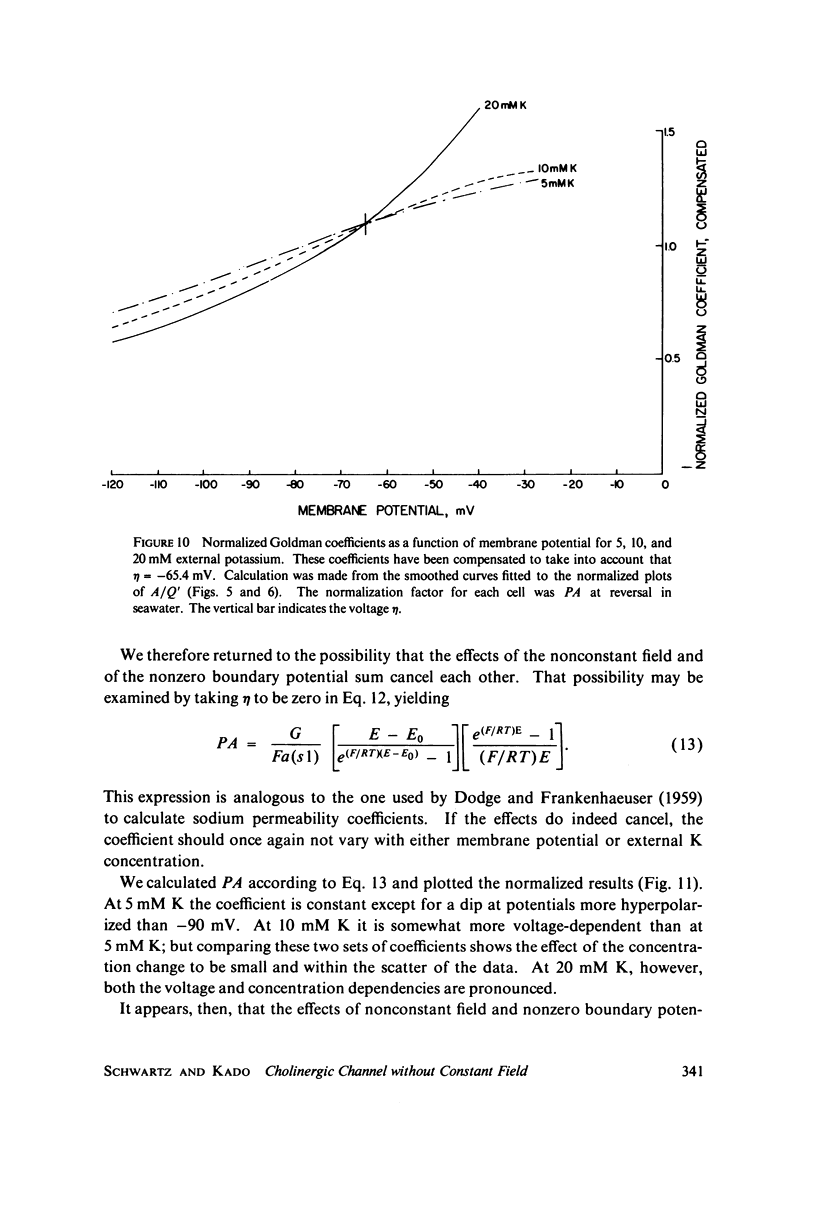
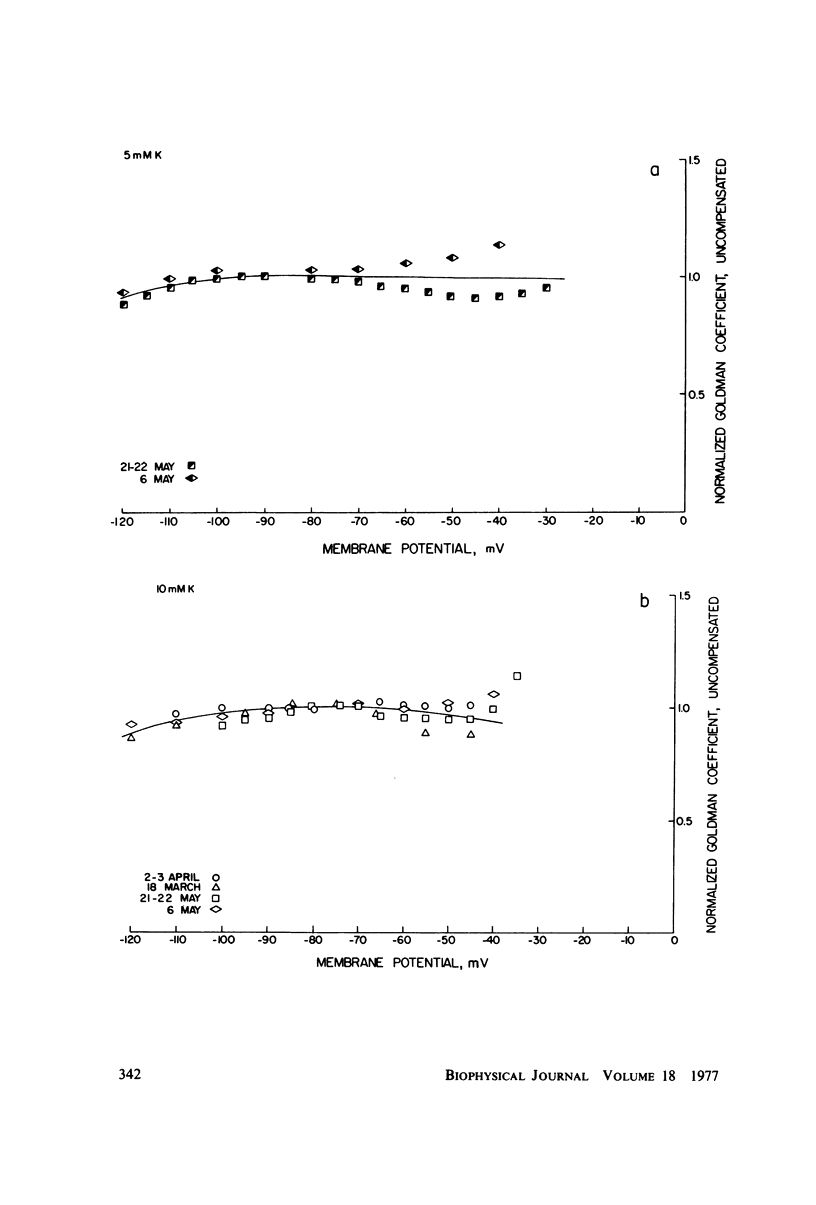
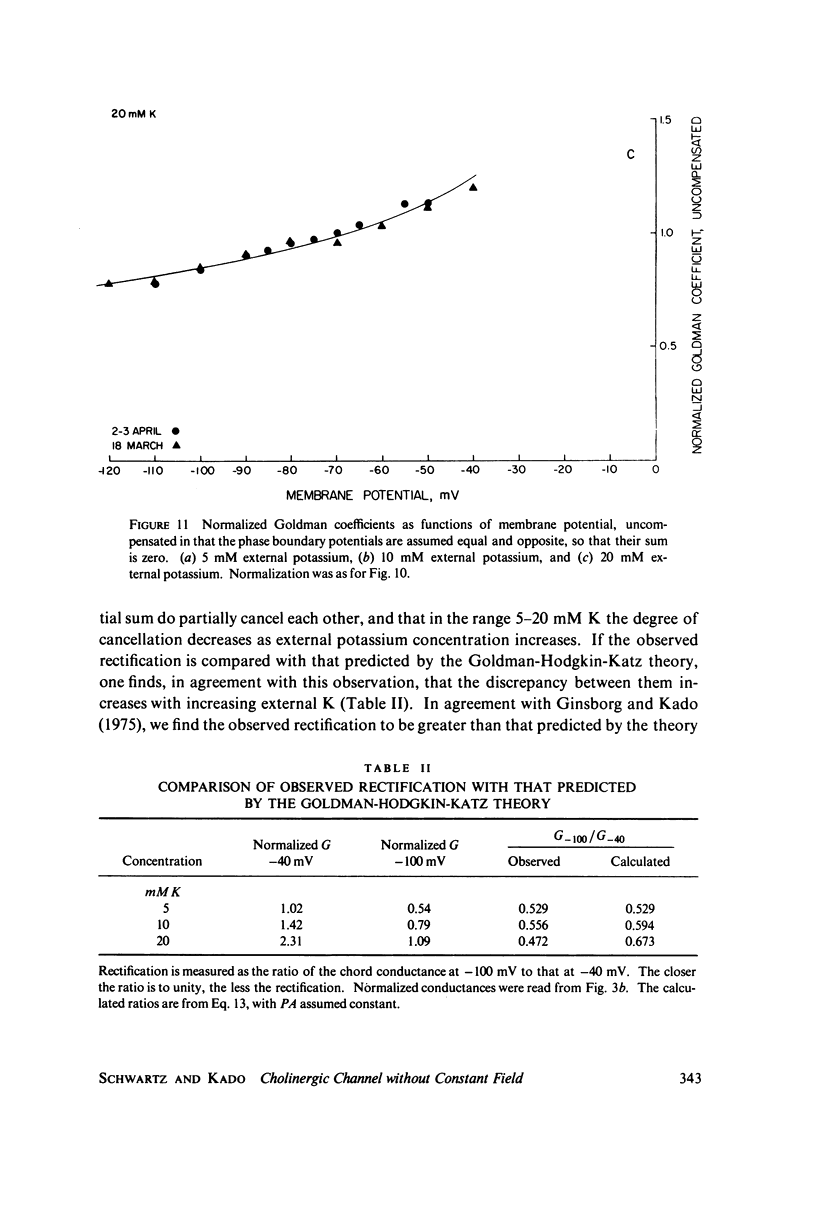
A potassium-selective, chemically excitable channel, whose characteristics cannot be accurately described by constant-field theory, is studied by a new approach based on diffusion theory but with no need for the classical assumptions of constant field, homogeneous membrane, and equal phase-boundary potentials at both interfaces. Permeability is defined, free of these constraints, and the Goldman coefficient is demonstrated to be a special case useful only when the constraints apply. Permeability can be evaluated directly from current-voltage data, and it is found not to be a parameter in this channel, but rather a function of both the voltage and the concentration of the permeant ion. However, it becomes concentration-independent when the membrane voltage is equal to the sum of the phase-boundary potentials. That sum can therefore be determined from these data, and it is -65 mV in this channel. The permeability at that potential is a channel parameter, and equal to 8.66 X 10(-6) cm/s for this channel. A constant field is shown not to exist in this channel and the Goldman coefficient not to be a parameter but a function of potential and concentration. Although errors introduced into this coefficient by nonconstant field and unequal surface potentials partially cancel each other, the coefficient is nevertheless not a correct measure of permeability.
Full text
PDF


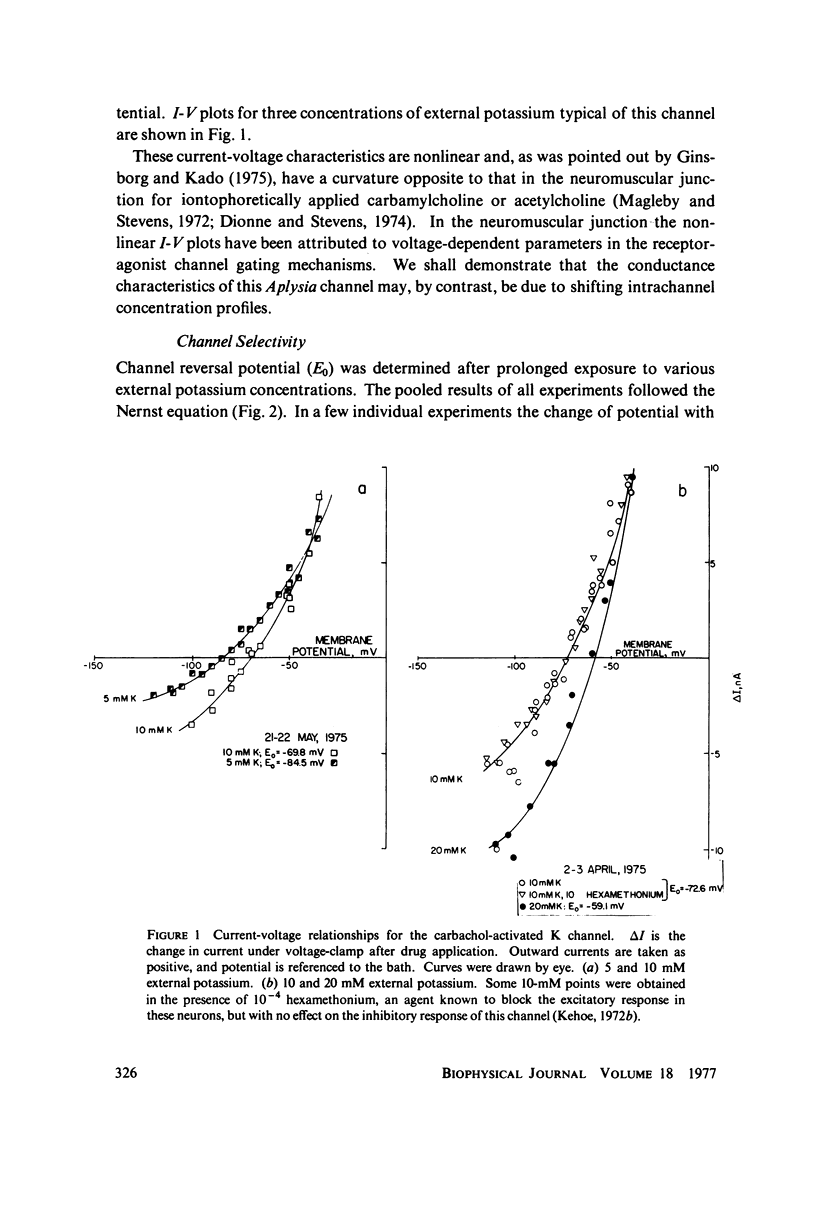
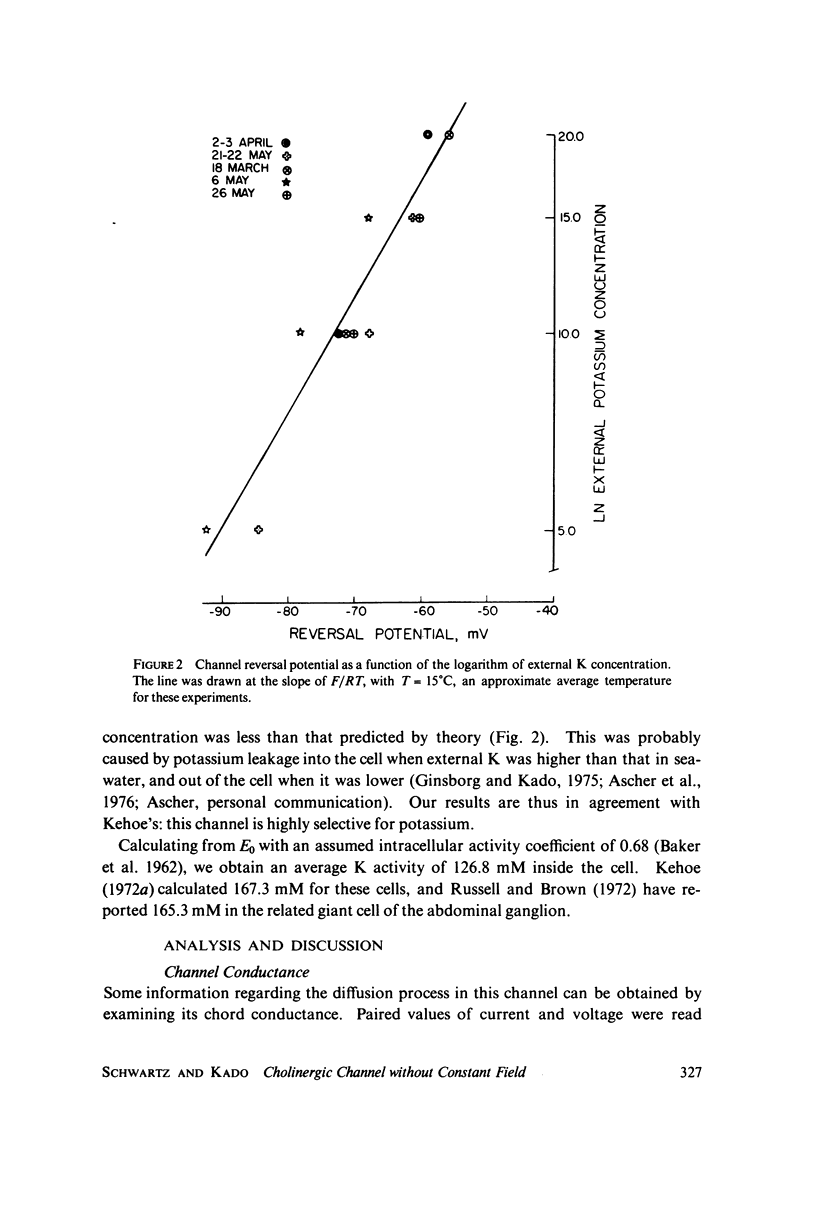

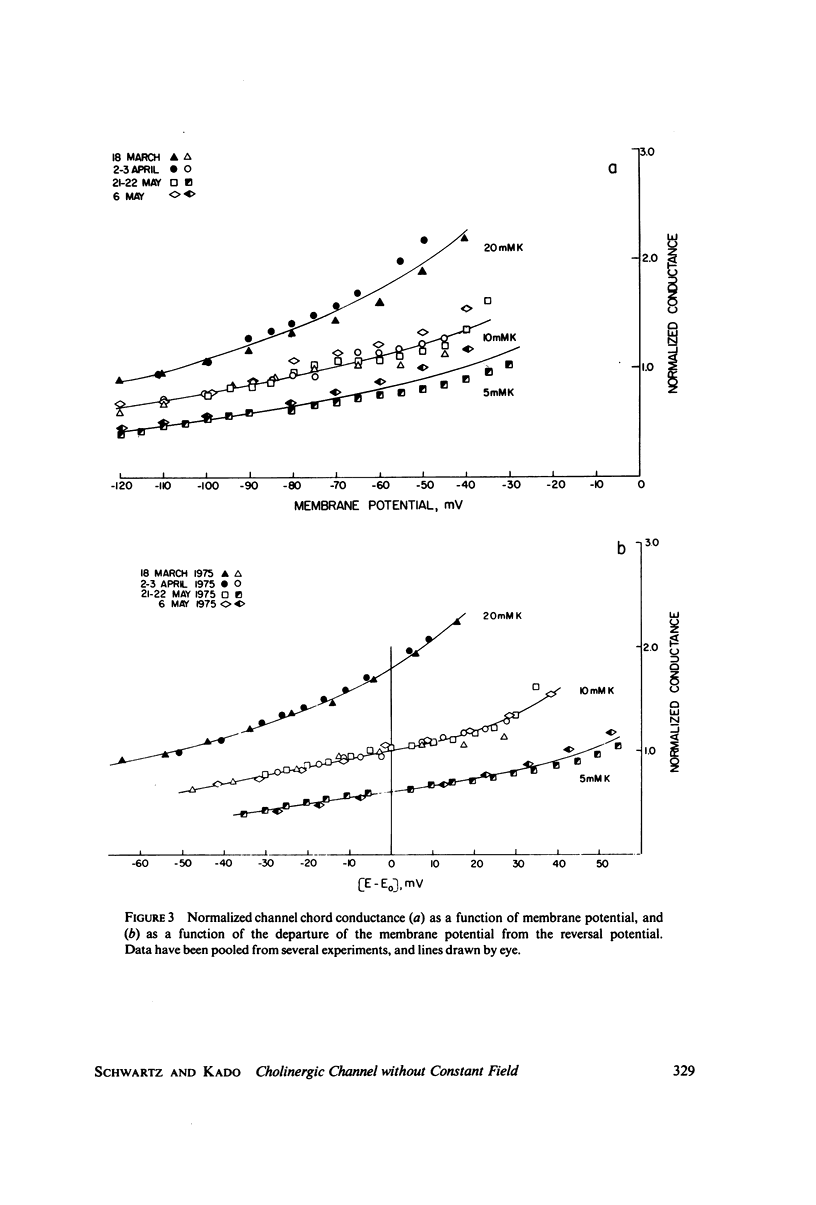
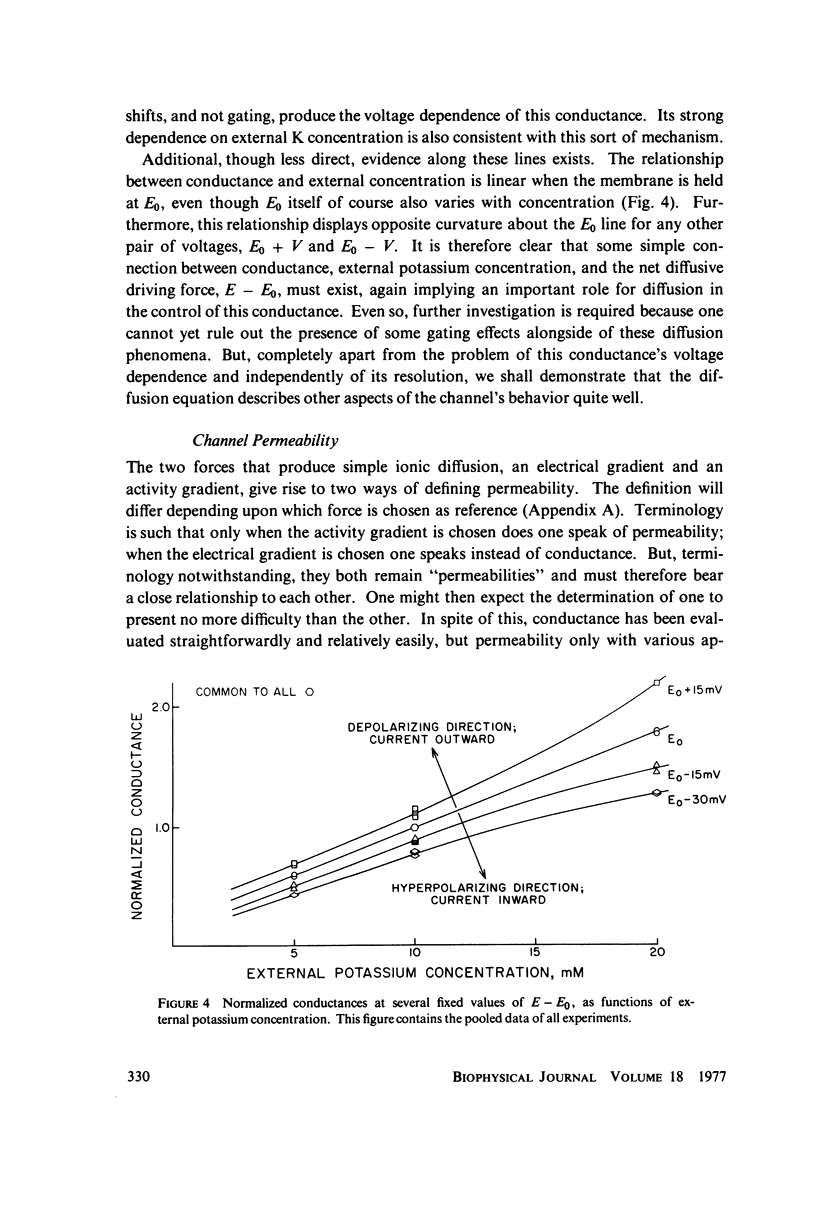












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher P., Kunze D., Neild T. O. Chloride distribution in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):441–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. Replacement of the axoplasm of giant nerve fibres with artificial solutions. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:330–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Effects of ionic concentration on permeability properties of nodal membrane in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Potential clamp experiments. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Apr;87(4):474–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M., Begenisich T. Sodium channel selectivity. Dependence on internal permeant ion concentration. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Aug;68(2):111–125. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.2.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L., Meves H. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):821–836. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Stevens C. F. Voltage dependence of agonist effectiveness at the frog neuromuscular junction: resolution of a paradox. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):245–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin H., Neumcke B. Specific and unspecific charges at the sodium channels of the nerve membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):207–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00586919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Mauro A. Equivalent Circuits as Related to Ionic Systems. Biophys J. 1963 May;3(3):215–237. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86817-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. L., Ehrenstein G. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: determination of surface charge. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):447–463. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86396-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., Kado R. T. Voltage-current relationship of a carbachol-induced potassium-ion pathway in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):713–725. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in sodium channels. A four-barrier model. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Nov;66(5):535–560. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.5.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F. The interpretation of voltage-concentration relations. J Theor Biol. 1974 Nov;48(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(74)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimizuka H., Koketsu K. Ion transport through cell membrane. J Theor Biol. 1964 Mar;6(2):290–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(64)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozhayeva G. N., Naumov A. P. Effect of surface charge on the steady-state potassium conductance of nodal membrane. Nature. 1970 Oct 10;228(5267):164–165. doi: 10.1038/228164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M., Brown A. M. Active transport of potassium by the giant neuron of the aplysia abdominal ganglion. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):519–533. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. L. Direct effects on the membrane potential due to "pumps" that transfer no net charge. Biophys J. 1971 Nov;11(11):944–960. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86265-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


