Abstract
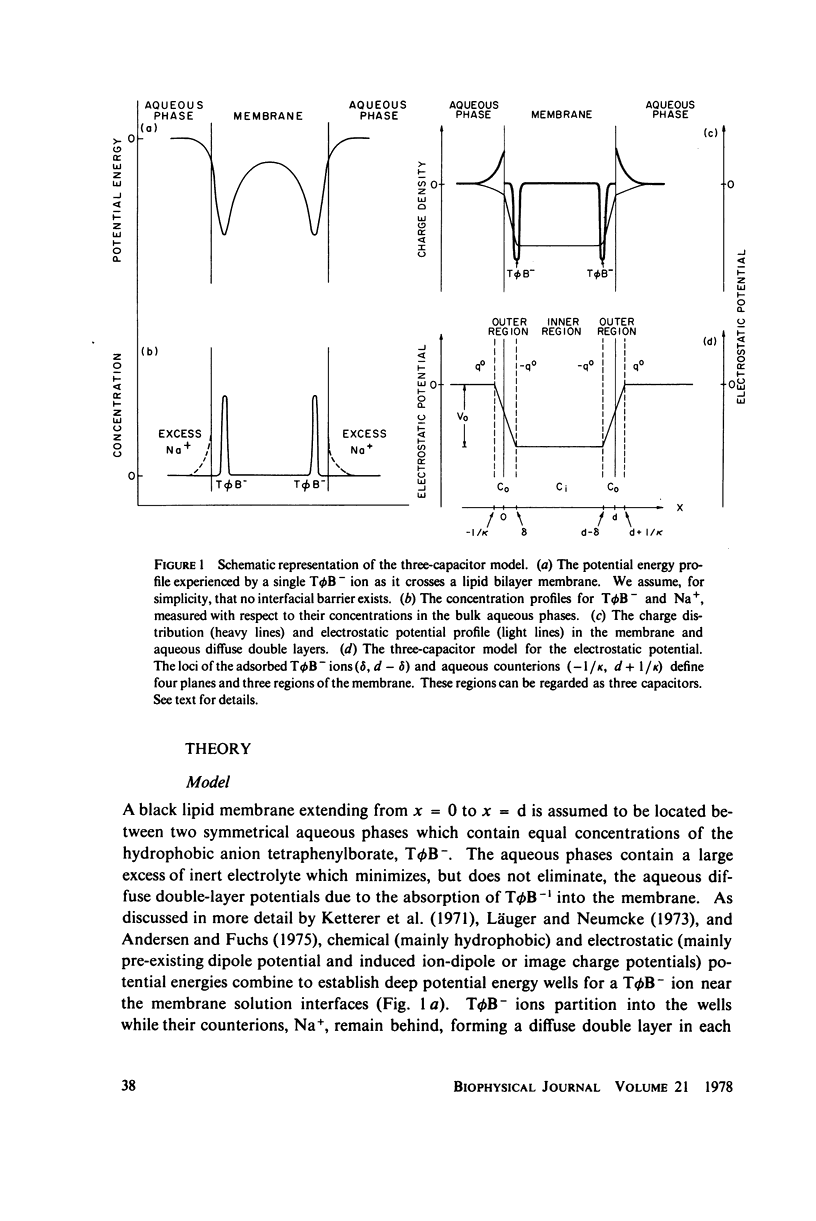
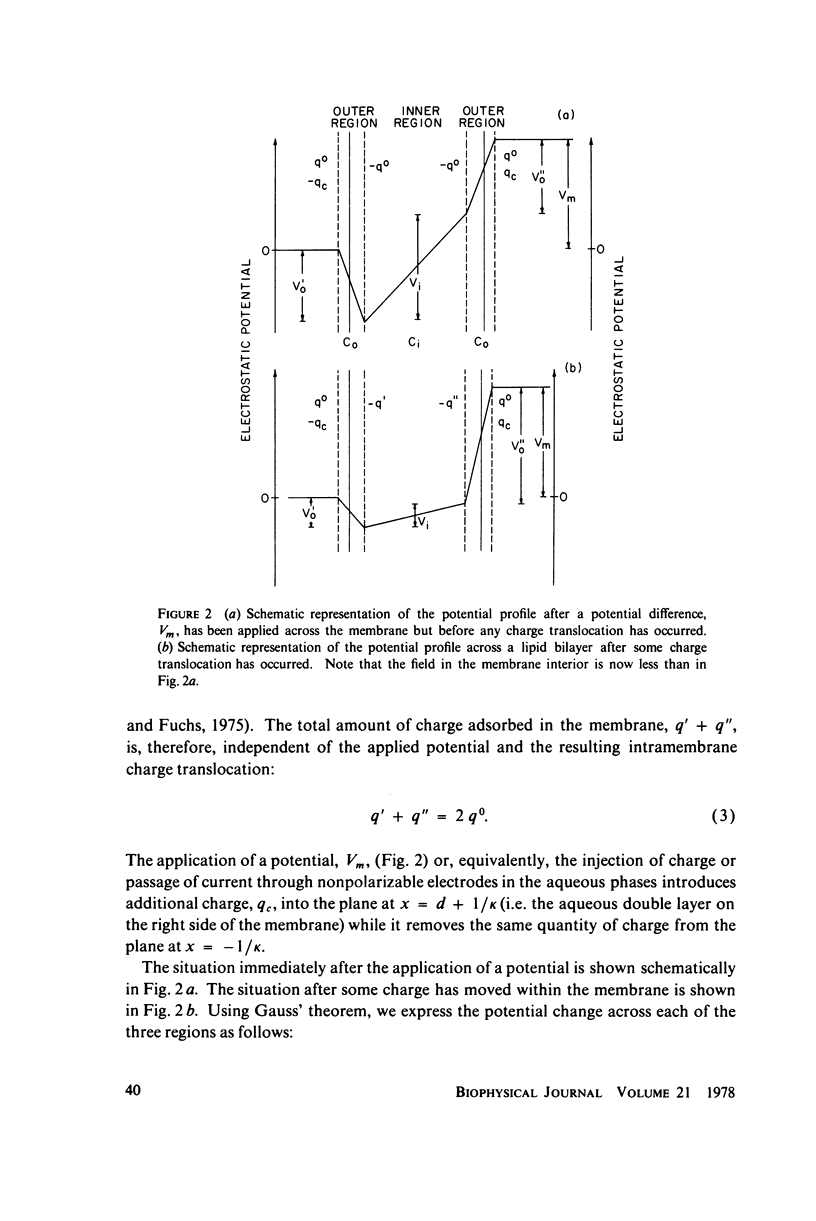
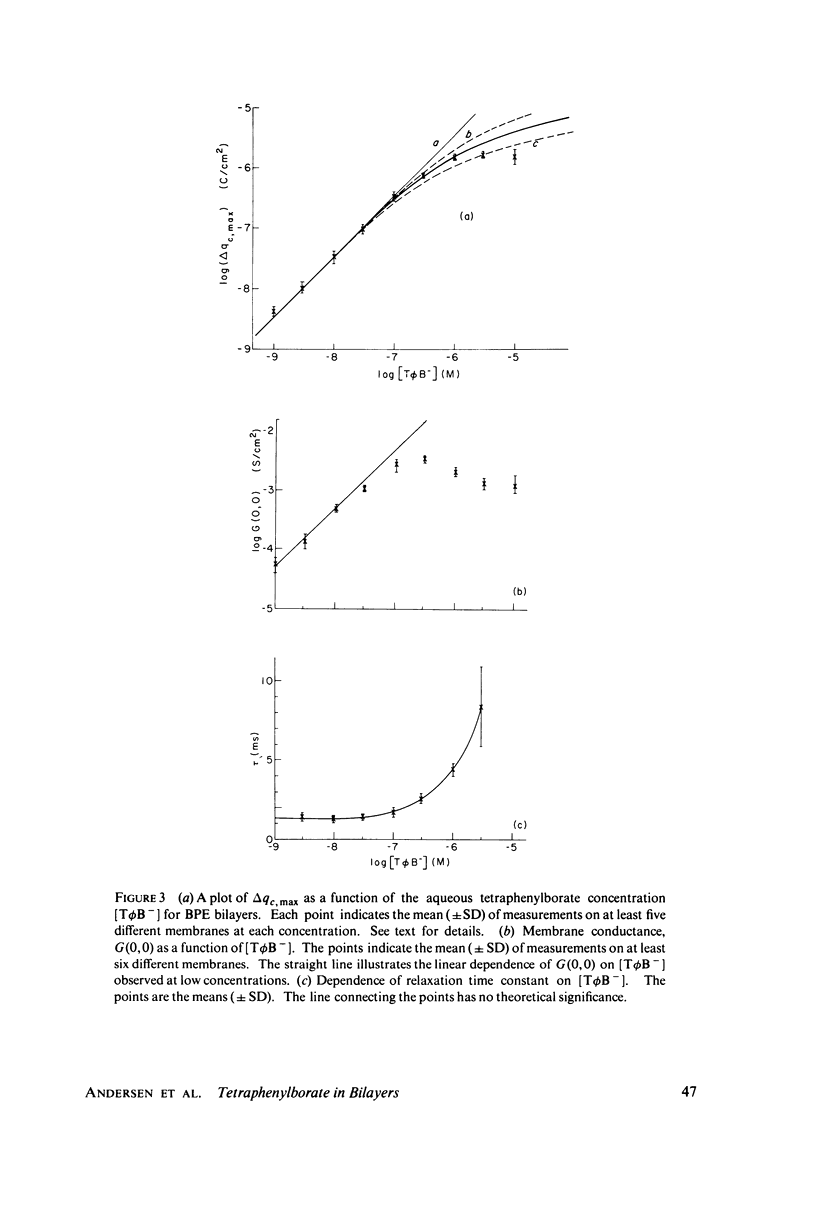
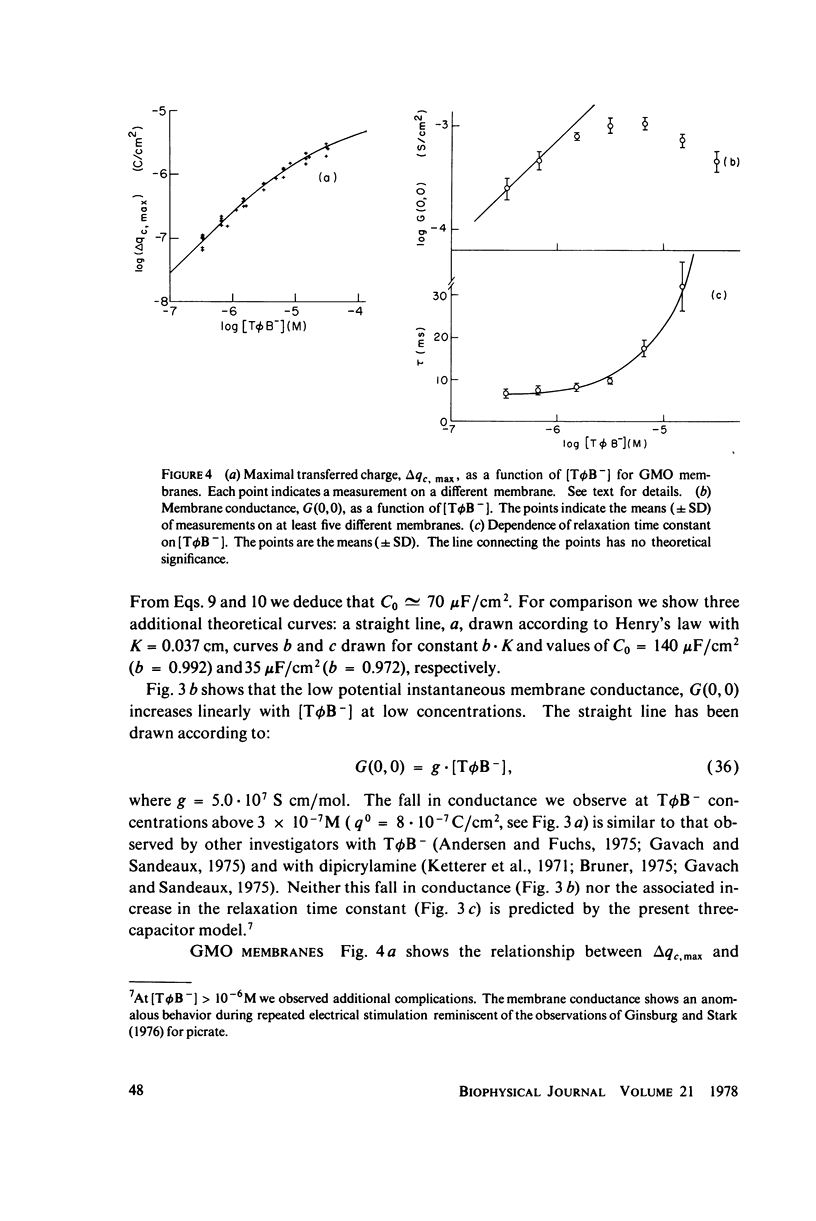
We have shown that the absorption of tetraphenylborate into black lipid membranes formed from either bacterial phosphatidylethanolamine or glycerolmonooleate produces concentration-dependent changes in the electrostatic potential between the membrane interior and the bulk aqueous phases. These potential changes were studied by a variety of techniques: voltage clamp, charge pulse, and "probe" measurements on black lipid membranes; electrophroetic mobility measurements on phospholipid vesicles; and surface potential measurements on phospholipid monolayers. The magnitude of the potential changes indicates that tetraphenylborate absorbs into a region of the membrane with a low dielectric constant, where it produces substantial boundary potentials, as first suggested by Markin et al. (1971). Many features of our data can be explained by a simple three-capacitor model, which we develop in a self-consistent manner. Some discrepancies between our data and the simple model suggest that discrete charge phenomena may be important within these thin membranes.
Full text
PDF


























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altendorf K., Hirata H., Harold F. M. Accumulation of lipid-soluble ions and of rubidium as indicators of the electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1405–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Finkelstein A., Katz I., Cass A. Effect of phloretin on the permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):749–771. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Fuchs M. Potential energy barriers to ion transport within lipid bilayers. Studies with tetraphenylborate. Biophys J. 1975 Aug;15(8):795–830. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85856-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Currents associated with the ionic gating structures in nerve membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:265–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babakov A. V., Miagkov I. V., Sotnikov P. S., Terekhov O. P. Issledovanie skachka élektricheskogo potentsiala dlia fosfolipidnykh monosloev na granitse vodavozdukh i fiziko-khimicheskie svoistva fosfolipidnykh membran. Biofizika. 1972 Mar-Apr;17(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakeeva L. E., Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A., Kuliene V. V., Levitsky D. O., Liberman E. A., Severina I. I., Skulachev V. P. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. II. Intact mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Läuger P., Janko K. Transport kinetics of hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Charge-pulse relaxation studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):701–720. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Läuger P. Transport kinetics of dipicrylamine through lipid bilayer membranes. Effects of membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 14;468(2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner L. J. The interaction of hydrophobic ions with lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1975;22(2):125–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01868167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciani S. Influence of molecular variations of ionophore and lipid on the selective ion permeability of membranes: II. A theoretical model. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 25;30(1):45–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01869659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg S. W., Delgado A. B. Inner voltage clamping. A method for studying interactions among hydrophobic ions in a lipid bilayer. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):71–86. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85508-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg S. W., Kissel G. Charge pulse studies of transport phenomena in bilayer membranes. I. Steady-state measurements of actin- and valinomycin-mediated transport in glycerol monooleate bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1975;20(3-4):269–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01870639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg S. W., Nakadomari H. Charge ulse studies of transport phenomena in bilayer membranes. II. Detailed theory of steady-state behavior and application to valinomycin-mediated potassium transport. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):81–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01869400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAME D. C. The electrical double layer and the theory of electrocapillarity. Chem Rev. 1947 Dec;41(3):441–501. doi: 10.1021/cr60130a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavach C., Sandeaux R. Non-mediated zero voltage conductance of hydrophobic ions through bilayer lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 17;413(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Stark G. Facilitated transport of di- and trinitrophenolate ions across lipid membranes by valinomycin and nonactin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):685–700. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigor'ev P. A., Ermishkin L. N., Markin V. S. Priamoe prokhozhdenie ionov cherez lipidnye membrany. II. Eksperimental'naia chast. Biofizika. 1972 Sep-Oct;17(5):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Rüppel H. Fast photoelectric effects and the properties of vertebrate photoreceptors as electric cables. Fed Proc. 1971 Jan-Feb;30(1):64–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Hladky S. B. Ion transport across thin lipid membranes: a critical discussion of mechanisms in selected systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1972 May;5(2):187–282. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Myers V. B. Surface charge, surface dipoles and membrane conductance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 25;307(3):429–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. A model system for mitochondrial ion transport and respiratory control. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1375–1381. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90539-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B. The energy barriers to ion transport by nonactin across thin lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 30;352(1):71–85. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong F. T. Charge transfer across pigmented bilayer lipid membrane and its interfaces. Photochem Photobiol. 1976 Aug;24(2):155–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1976.tb06809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E. The temporal and steady-state relationships between activation of the sodium conductance and movement of the gating particles in the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(1):157–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E. A., Margulis D. M. Pronitsaemost', prostranstvennyi i granichnye zariady bimolekuliarnykh fosfolipidnykh membran. I. Koéffitsient raspredeleniia. Biofizika. 1974 May-Jun;19(3):450–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E. A., Topaly V. P. Perenos ionov cherez bimolekuliarnye membrany i klassifikatsiia pazobshchitelei okislitel'nogo fosforilirovaniia. Biofizika. 1968 Nov-Dec;13(6):1025–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E. A., Topaly V. P. Pronitsaemost' bimolekuliarnykh fosfolipidnykh membran dlia zhirorastvorimykh ionov. Biofizika. 1969 May-Jun;14(3):452–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markin V. S., Grigor'ev P. A., Ermishkin L. N. Priamoe prokhozhdenie ionov cherez lipidnye membrany. I. Matematicheskaia model. Biofizika. 1971 Nov-Dec;16(6):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Szabo G., Eisenman G., Ciani S. M. Surface charge and the conductance of phospholipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1268–1275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Szabo G., Eisenman G. Divalent ions and the surface potential of charged phospholipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):667–687. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Harary H. The hydrophobic adsorption of charged molecules to bilayer membranes: a test of the applicability of the stern equation. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1941–1948. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. Salicylates and phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1973 May 25;243(5404):234–236. doi: 10.1038/243234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Development of K+-Na+ discrimination in experimental bimolecular lipid membranes by macrocyclic antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 21;26(4):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90559-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Nonner W., Stämpfli R. Asymmetrical displacement current and its relation with the activation of sodium current in the membrane of frog myelinated nerve. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Jun 22;363(3):193–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00594601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paltauf F., Hauser H., Phillips M. C. Monolayer characteristics of some 1,2-diacyl, I-alkyl-2-acyl and 1,2-dialkyl phospholipids at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent D. F. An apparatus for the measurement of very small membrane relaxation currents. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):100–109. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G., Eisenman G., McLaughlin S. G., Krasne S. Ionic probes of membrane structures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:273–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl H. W., Darszon A., Montal M. Rhodopsin in model membranes: charge displacements in interfacial layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):207–210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf J., Benz R., Pohl W. G. Properties of bilayer membranes in the presence of dipicrylamine. A comparative study by optical absorption and electrical relaxation measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):429–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90262-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



