Abstract
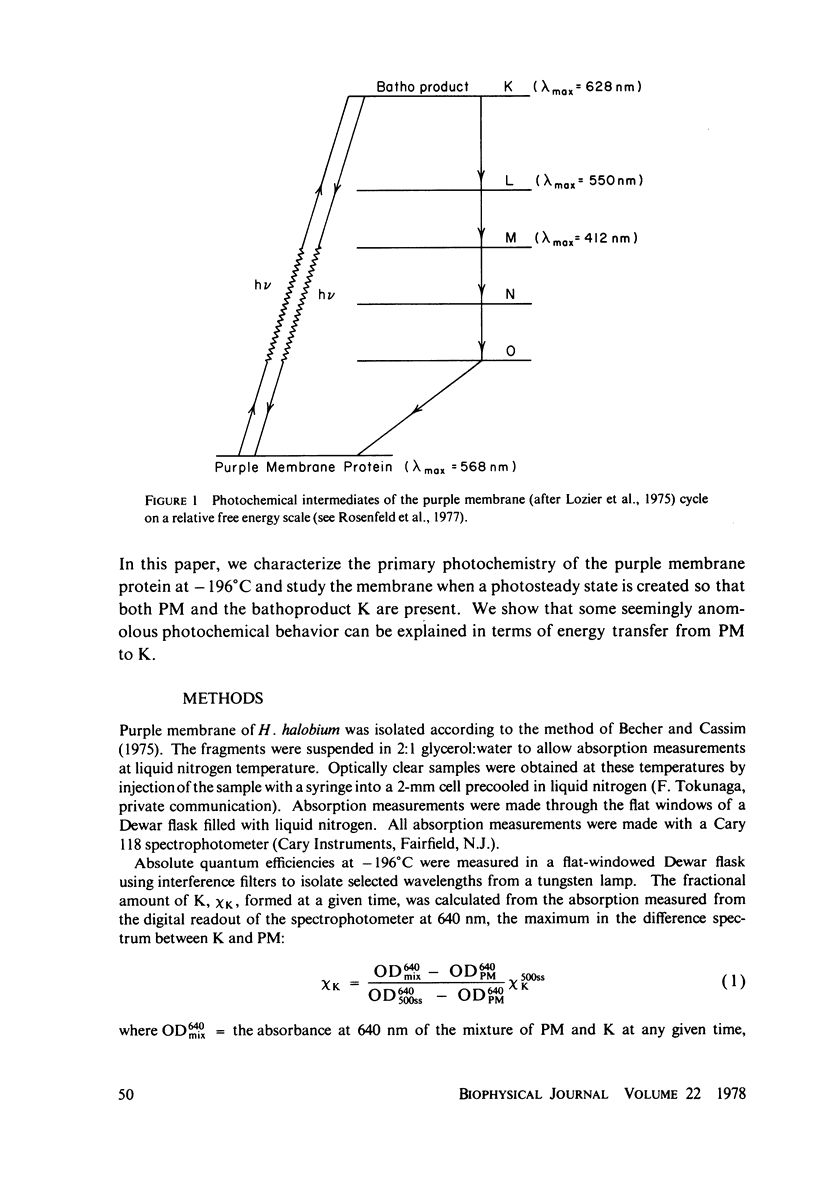
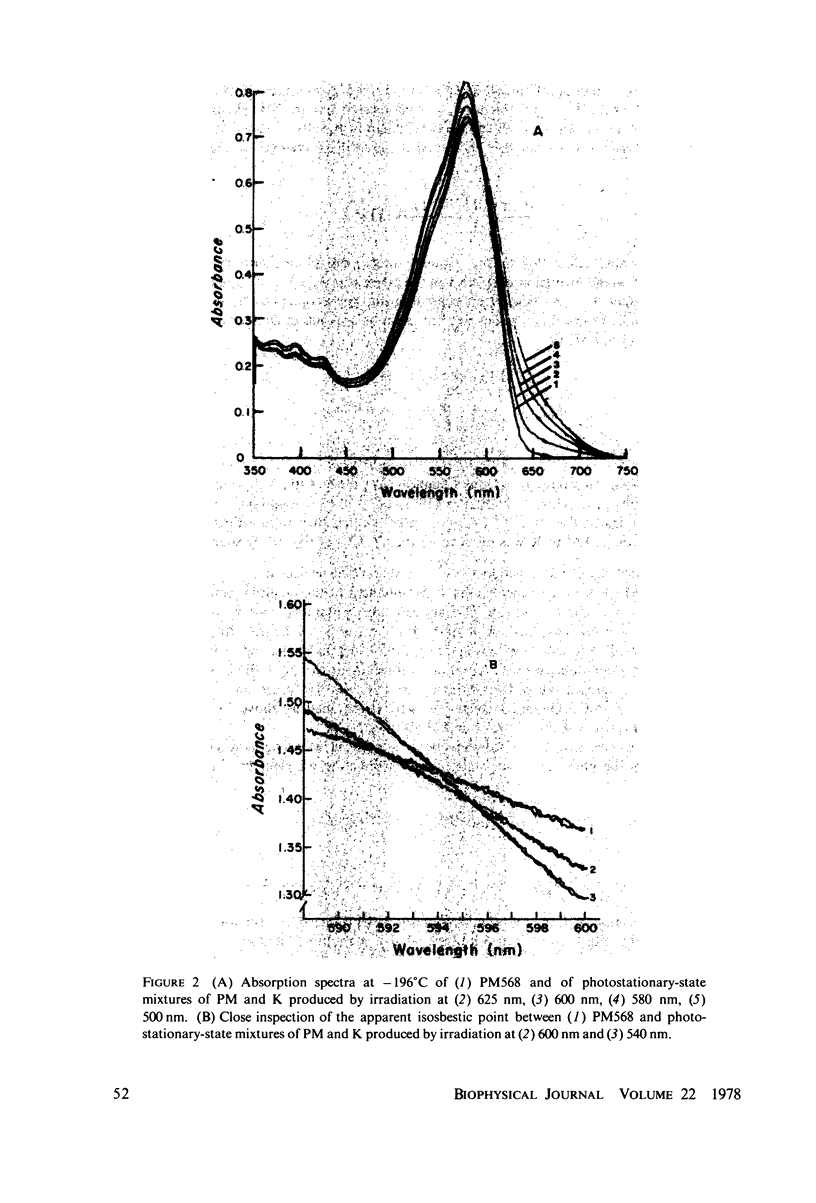
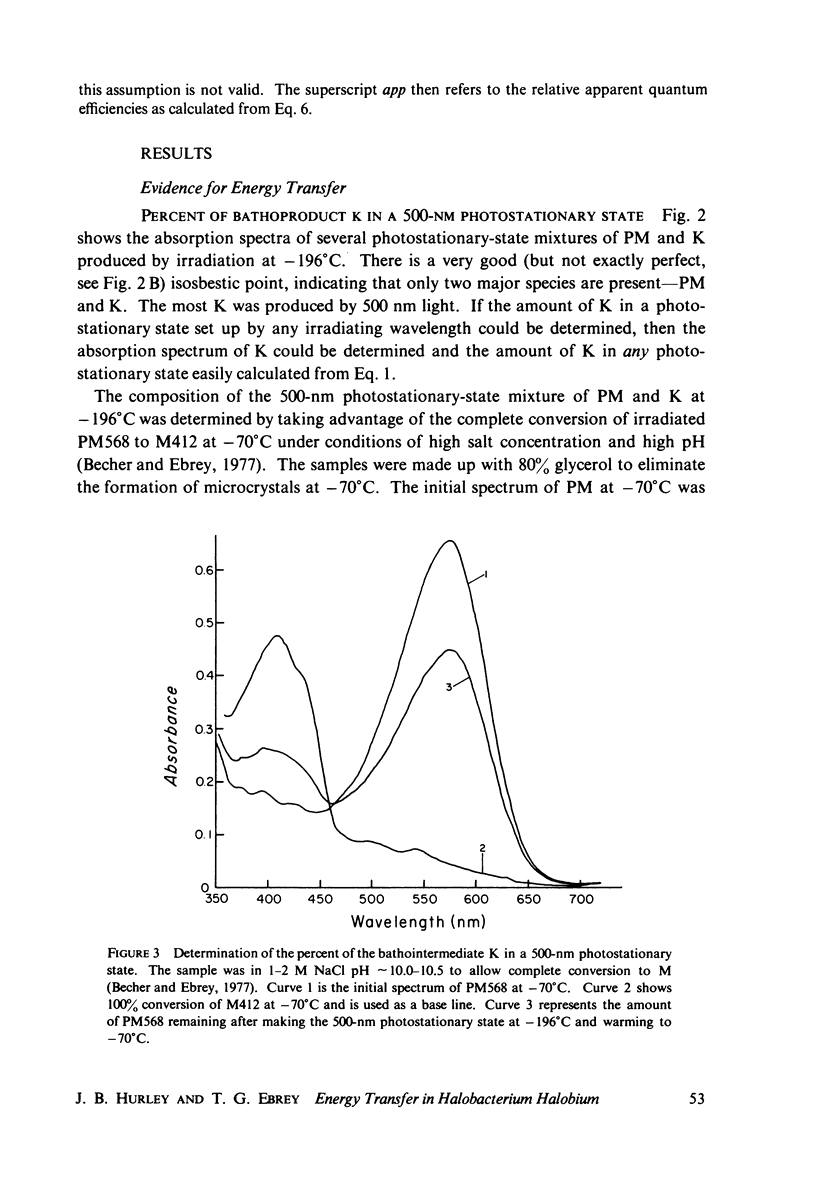
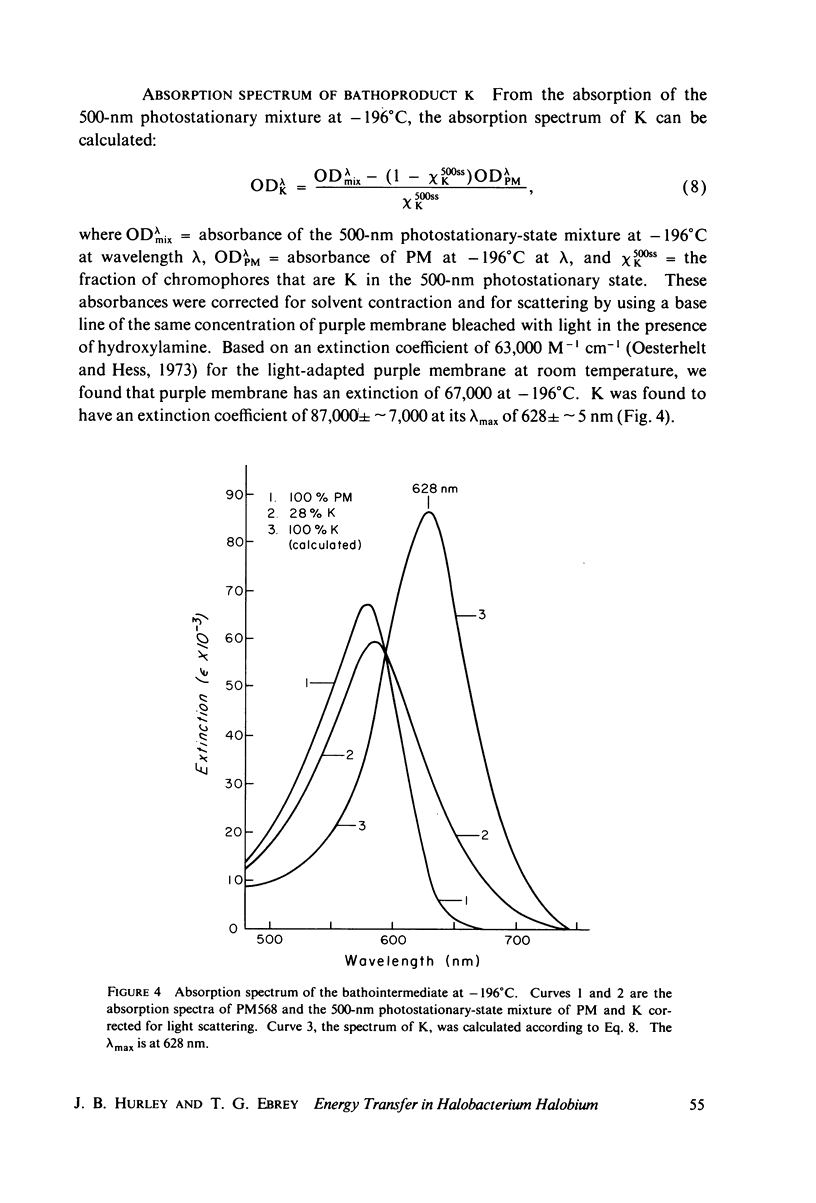
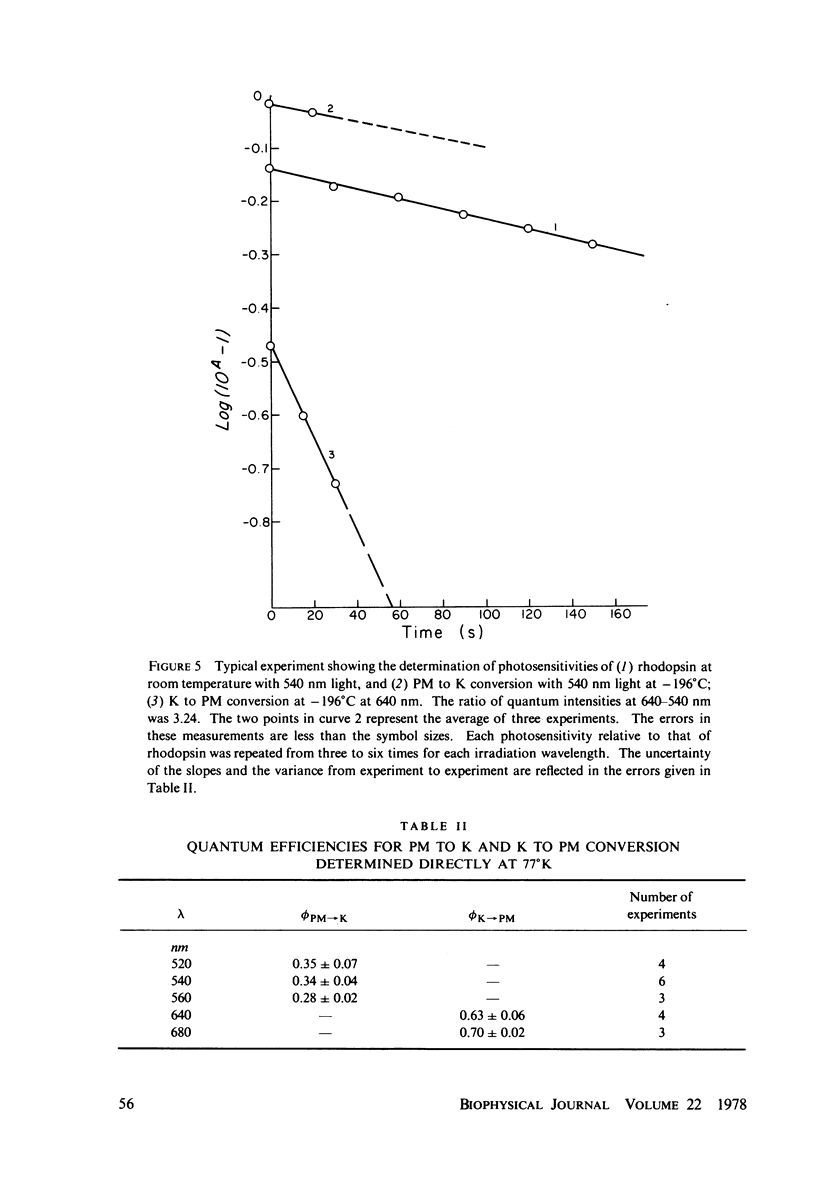
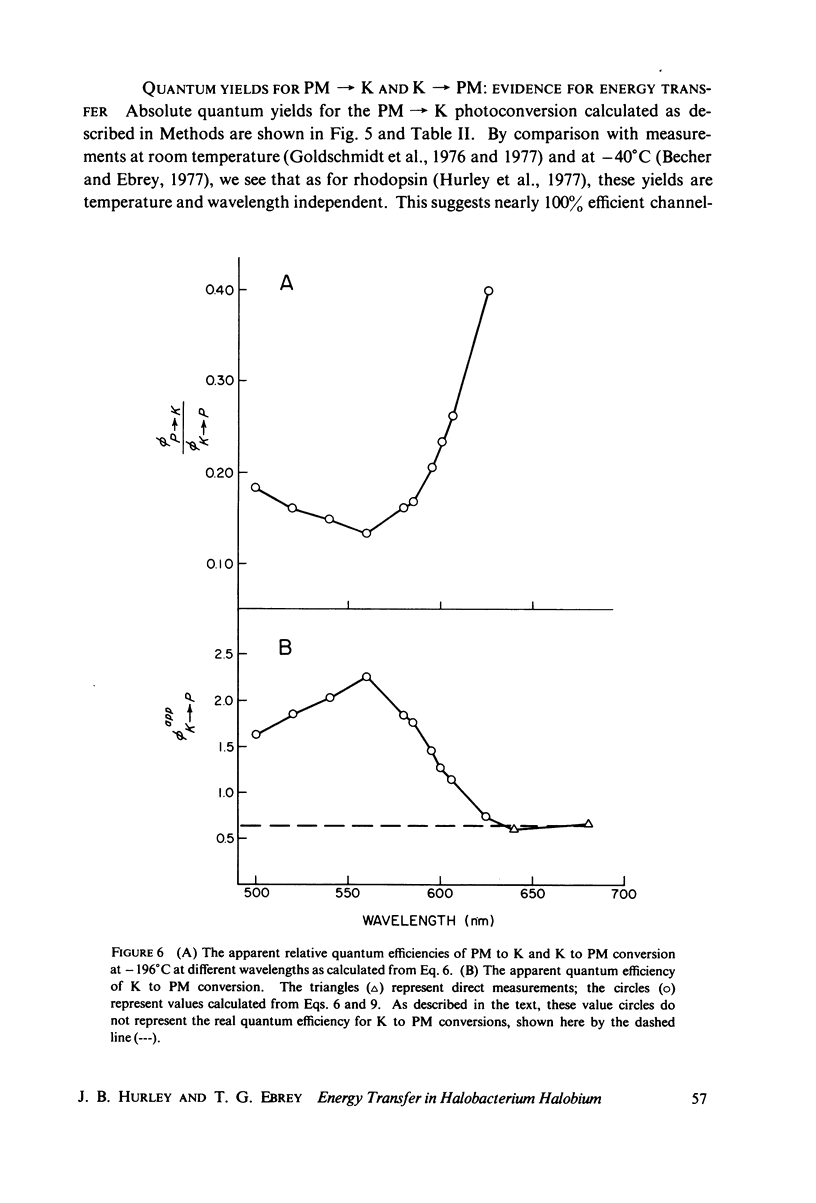
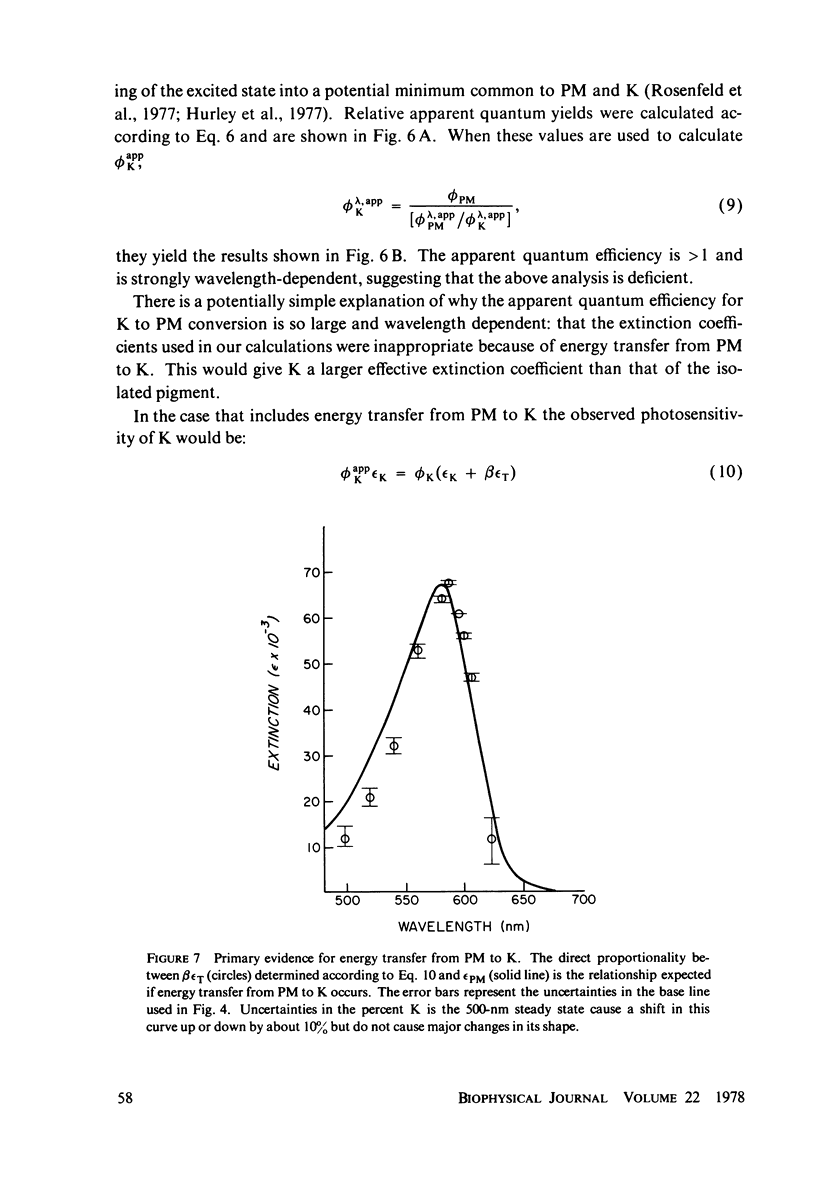
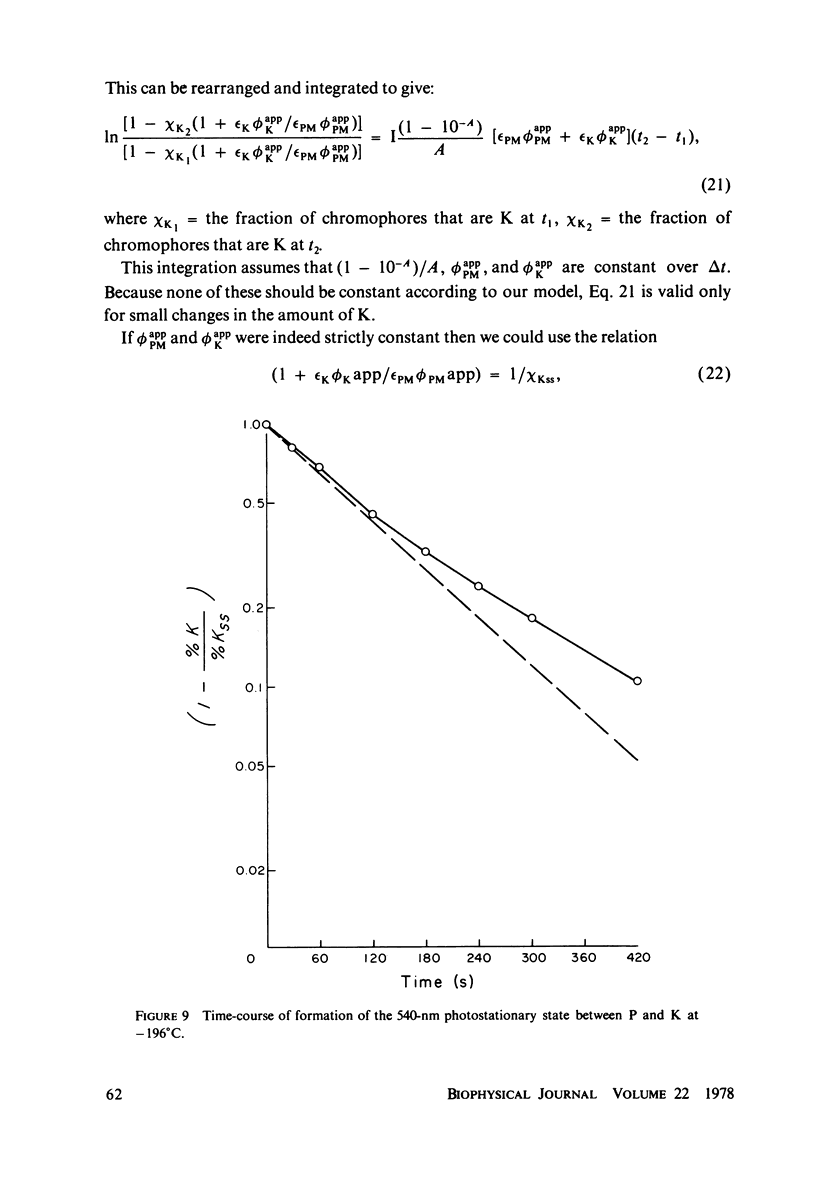
The absorption spectrum of the primary photoproduct (the bathoproduct, or K) of the purple membrane protein (PM) at-196 degrees C has a maximum at 628 nm and an extinction coefficient of 87,000. Knowing the absorption spectrum allowed us to calculate the quantum efficiencies for PM to K and K to PM conversion at -196 degrees C. Direct measurements of these quantum yeilds at -196 degrees C gave 0.33 +/- 0.05 and 0.67 +/- 0.04, respectively. Determination of relative quantum efficiencies for PM to K and K to PM conversion by analysis of the absorption spectra of several photostationary-state mixtures of PM and K at -196 degrees C, however, gave wavelength-dependent quantum efficiencies that appear to be greater than 1. These anomolous results can be readily explained in terms of energy transfer from PM to K within the trimer clusters of pigment molecules which exist in the purple membrane. A model for such a transfer predicts an efficiency of energy transfer from PM to K of about 43%.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aton B., Doukas A. G., Callender R. H., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. Resonance Raman studies of the purple membrane. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2995–2999. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B. M., Cassim J. Y. Improved isolation procedures for the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):161–178. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B., Ebrey T. G. The quantum efficiency for the photochemical conversion of the purple membrane protein. Biophys J. 1977 Feb;17(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85636-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrey T. G., Becher B., Mao B., Kilbride P., Honig B. Exciton interactions and chromophore orientation in the purple membrane. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):377–397. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt C. R., Kalisky O., Rosenfeld T., Ottolenghi M. The quantum efficiency of the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biophys J. 1977 Feb;17(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85635-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt C. R., Ottolenghi M., Korenstein R. On the primary quantum yields in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):839–843. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85732-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjee R., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. The fluorescence from the chromophore of the purple membrane protein. Biophys J. 1978 Apr;22(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85471-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Ebrey T. G., Honig B., Ottolenghi M. Temperature and wavelength effects on the photochemistry of rhodopsin, isorhodopsin, bacteriorhodopsin and their photoproducts. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):540–542. doi: 10.1038/270540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W. The photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1805–1809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Hess B. Reversible photolysis of the purple complex in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 17;37(2):316–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettei M. J., Yudd A. P., Nakanishi K., Henselman R., Stoeckenius W. Identification of retinal isomers isolated from bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1955–1959. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



