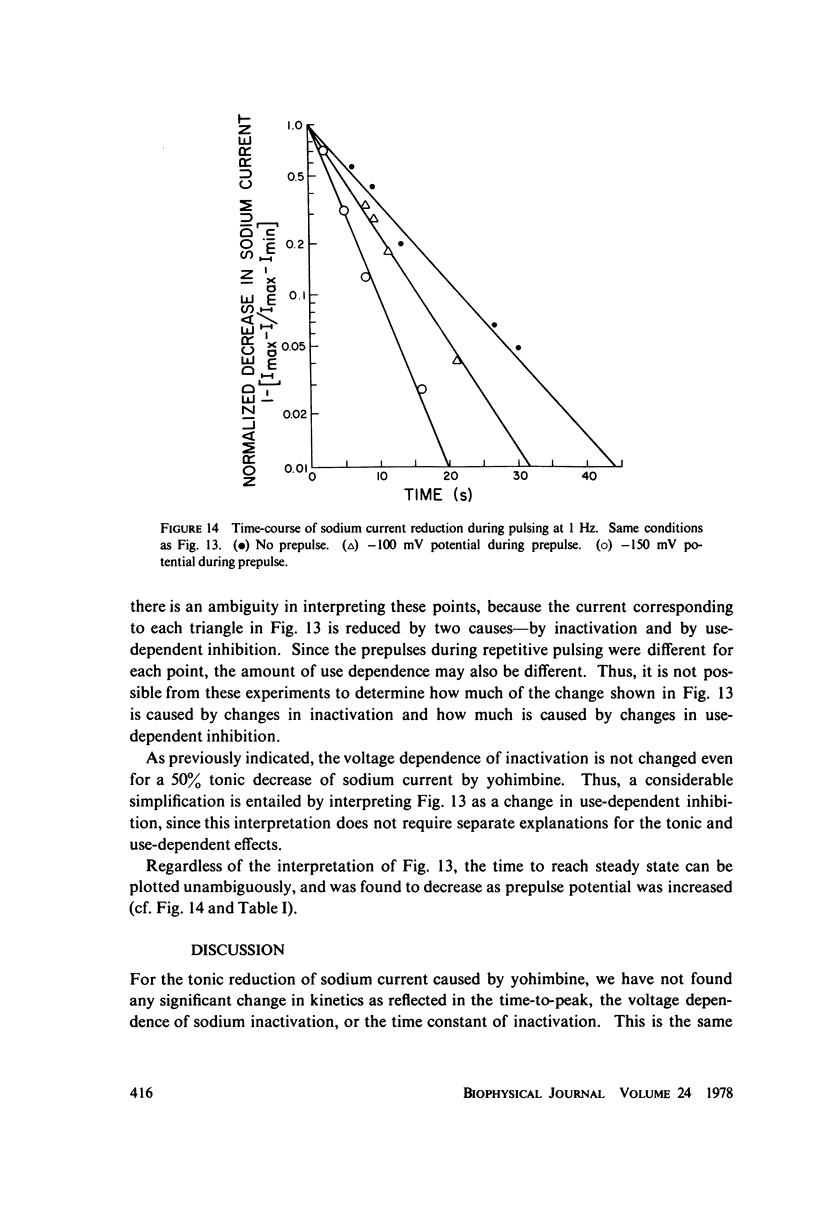
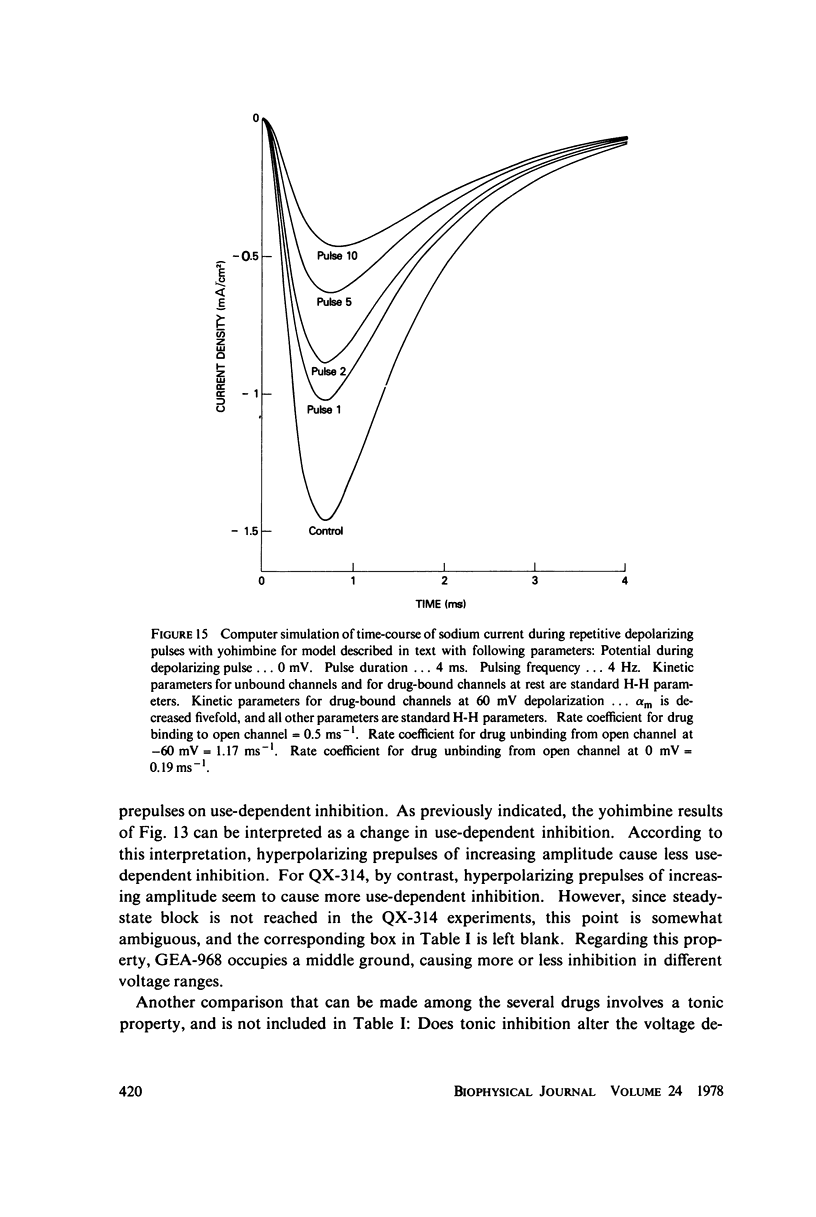
Abstract
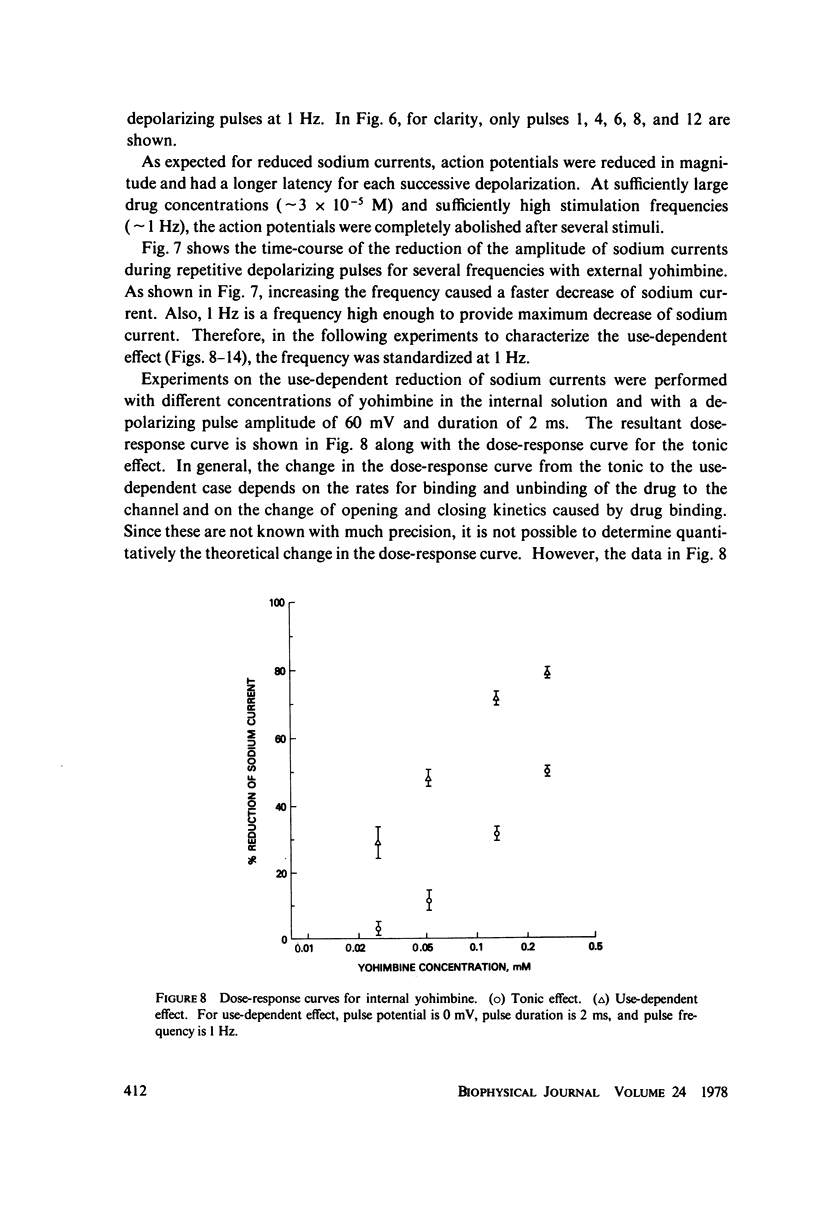
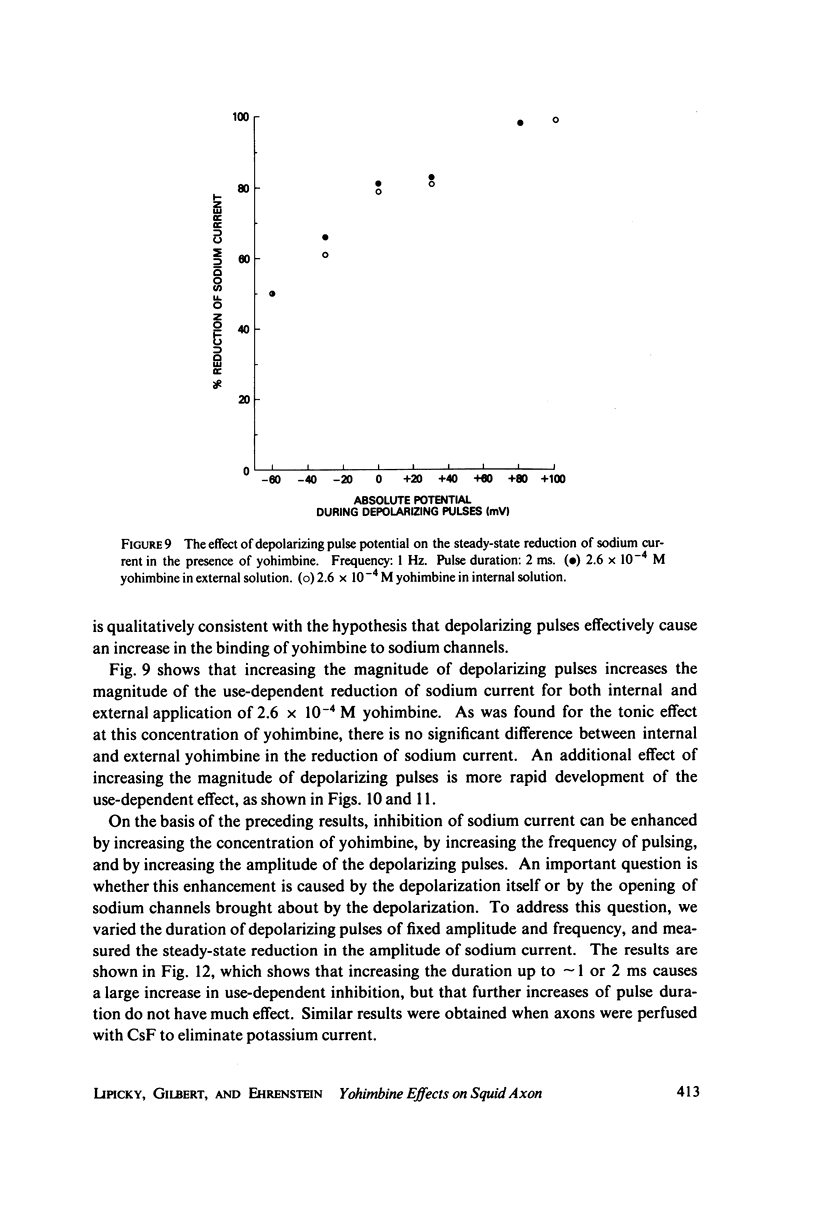
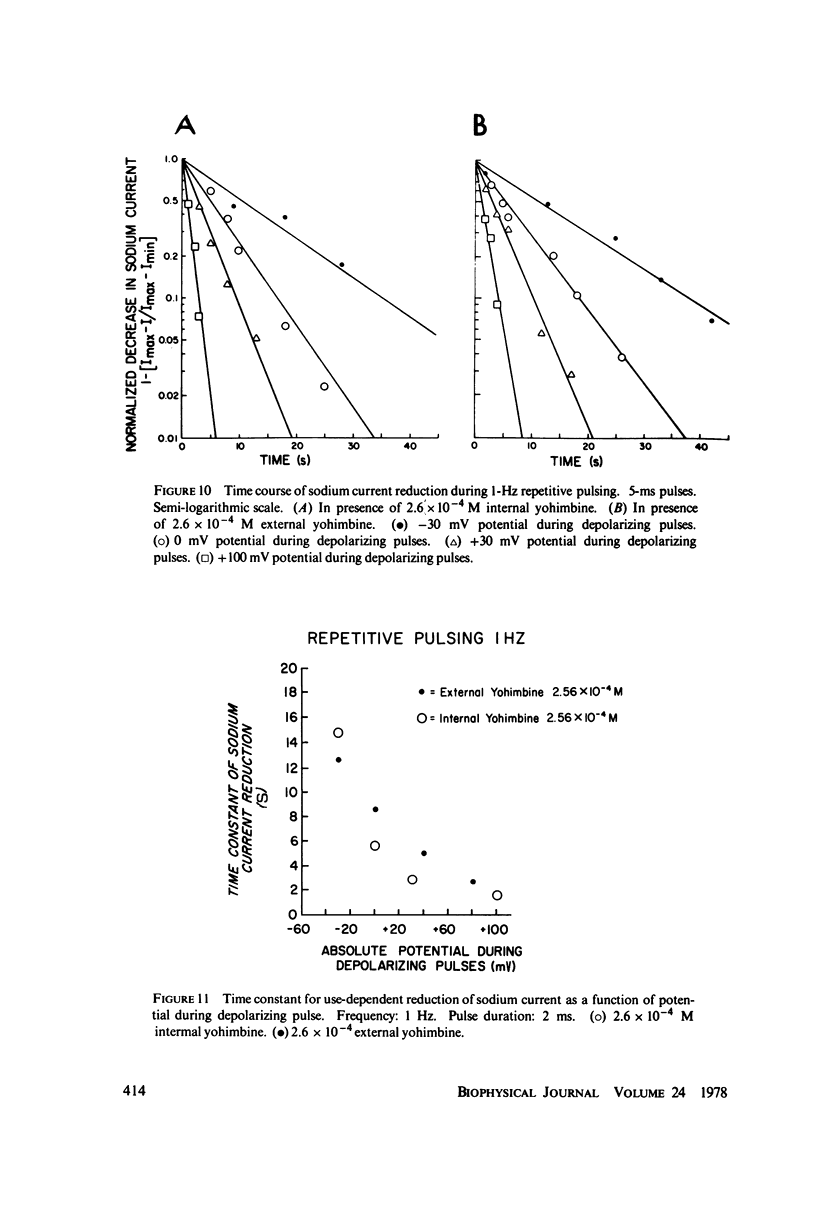
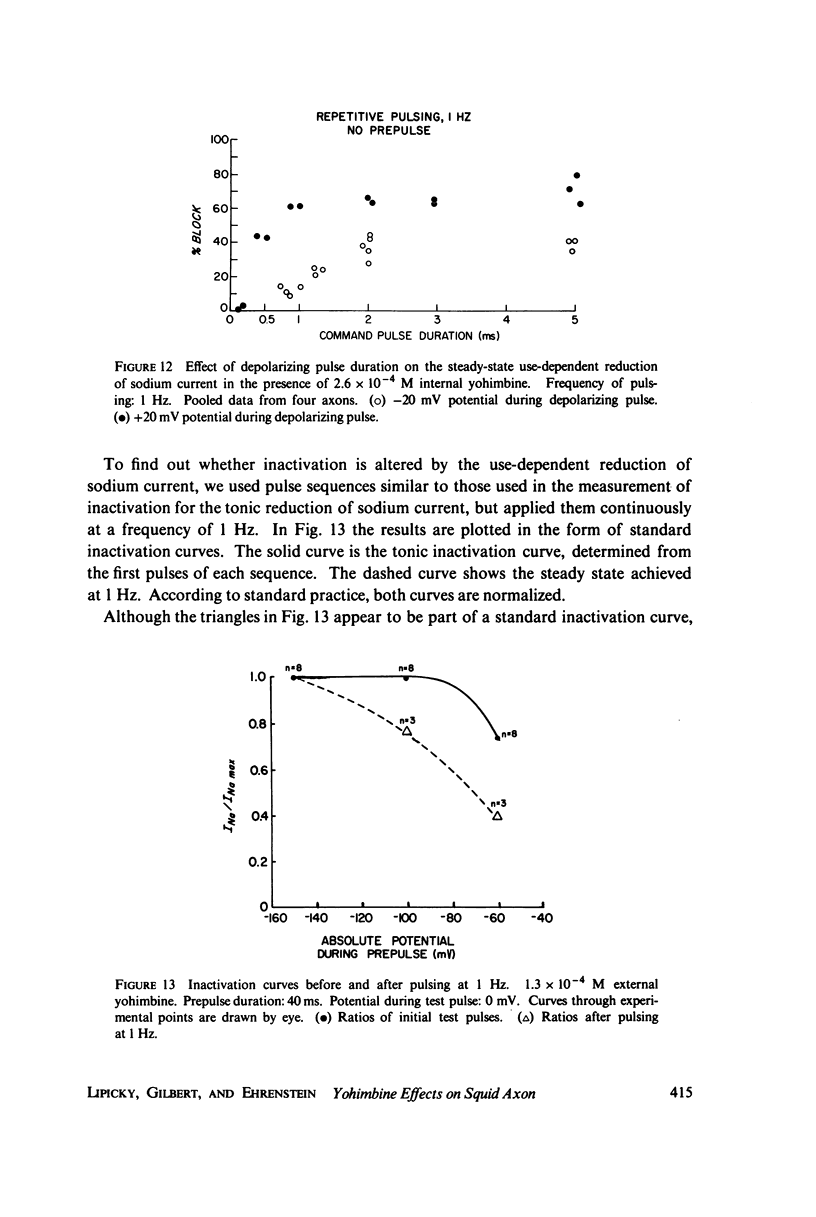
Yohimbine, an indolealkylamine alkaloid, reduces the amplitude of the sodium current in the squid giant axon. For doses that reduce sodium current amplitude by up to 50%, there is no significant change in the kinetics or in any of the voltage-dependent parameters associated with sodium channels. The effective equilibrium constant for yohimbine binding to the sodium channel is 3 x 10(-4) M. Repetitive depolarizing pulses increase the inhibition of squid axon sodium current by yohimbine. This use-dependent inhibition is enhanced by increasing the concentration of yohimbine, by increasing the frequency of pulsing, and by increasing the magnitude or the duration of depolarization. It is reduced by hyperpolarizing prepulses. This behavior can be explained by a model wherein yohimbine binds more readily to open sodium channels than to closed sodium channels and wherein the Hodgkin-Huxley kinetic parameters are modified by the binding of the drug. This type of model may also explain the tonic and use-dependent inhibition previously described by others for local anesthetics.
Full text
PDF

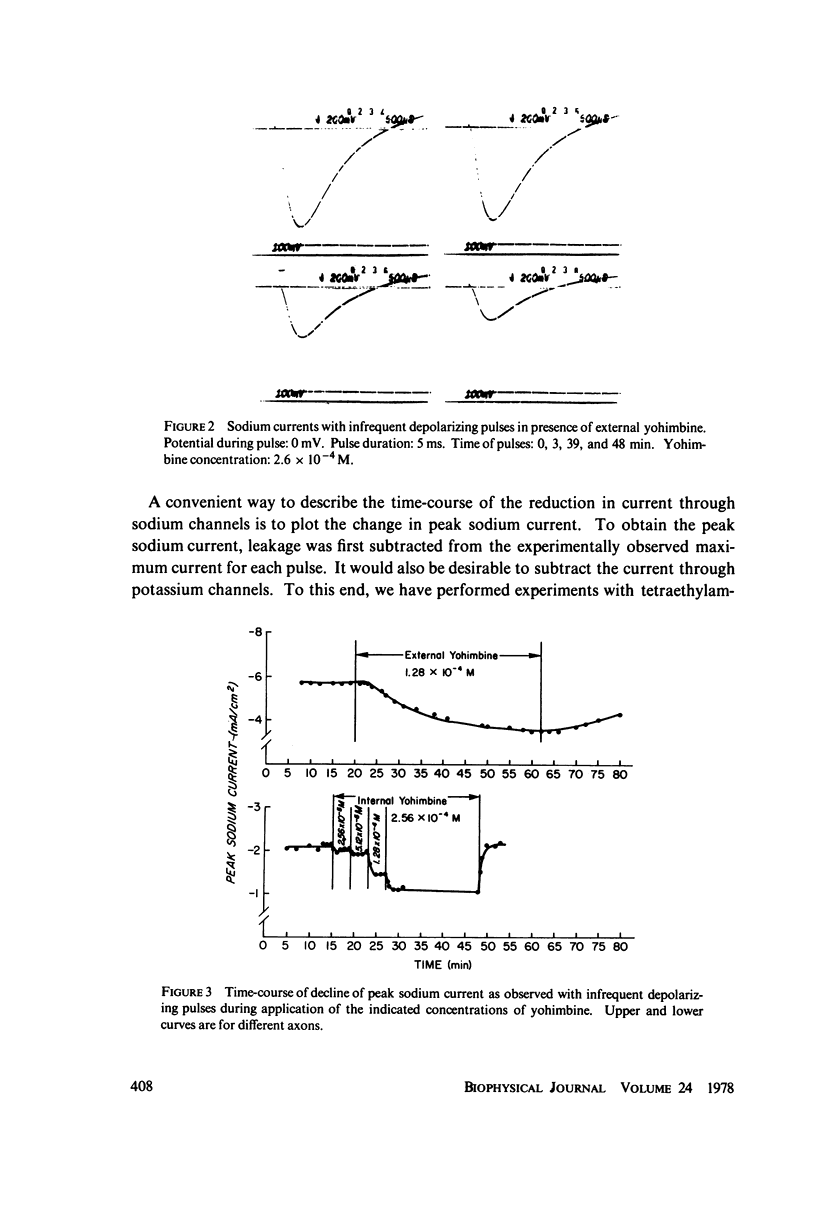

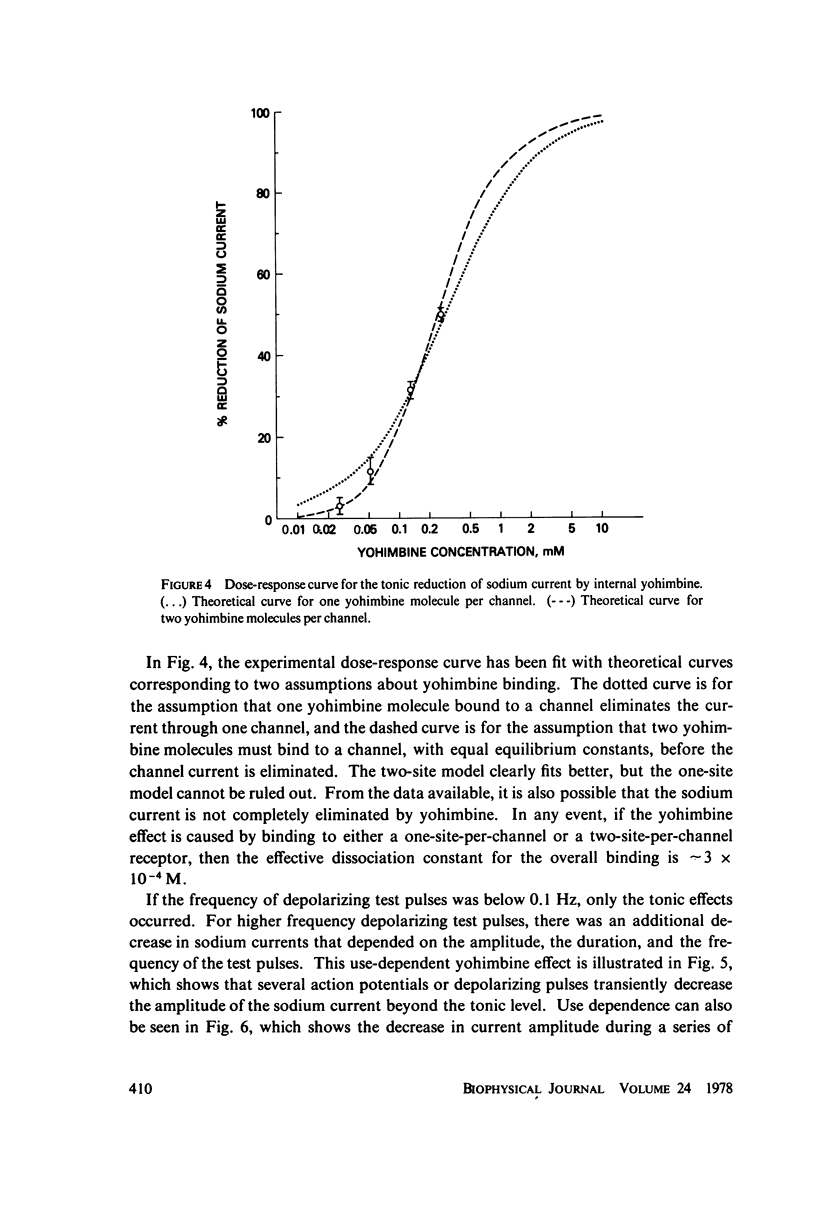
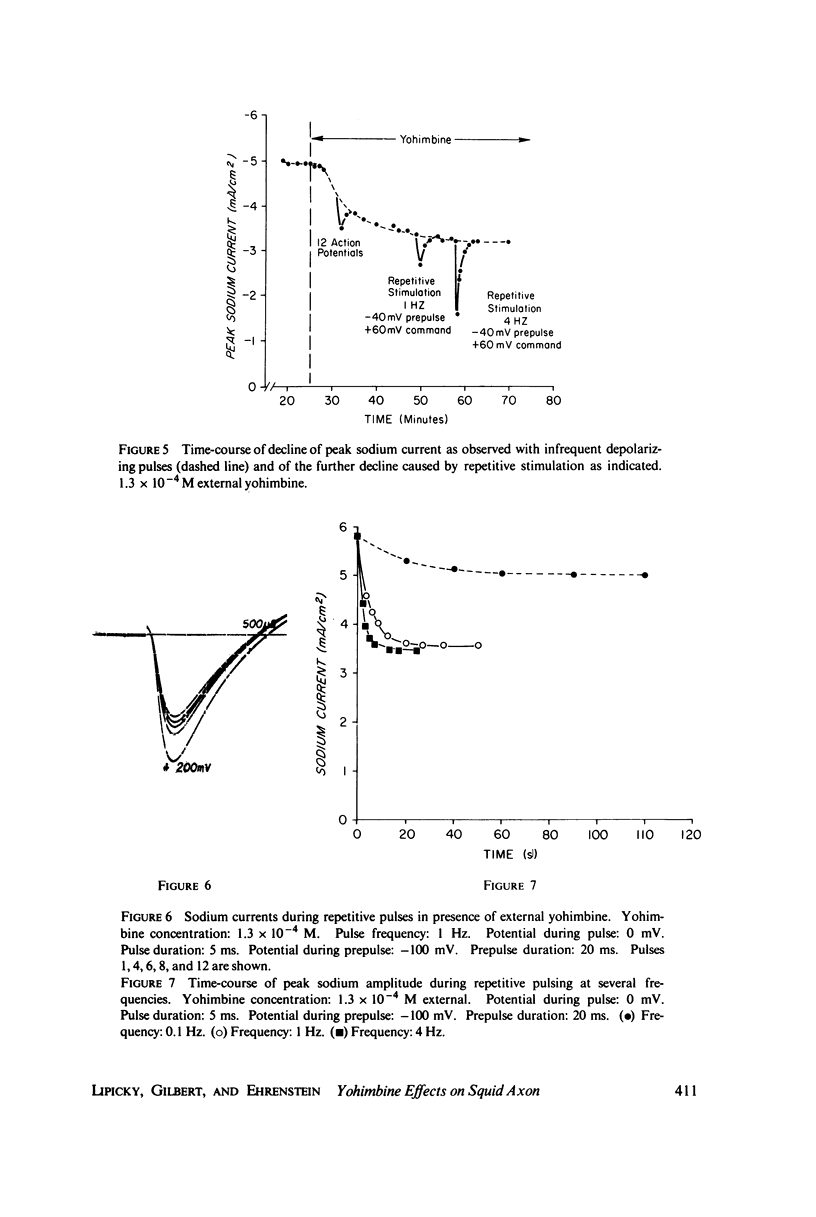





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Daly J. W., Witkop B. Batrachotoxin: chemistry and pharmacology. Science. 1971 Jun 4;172(3987):995–1002. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3987.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Gating currents of the sodium channels: three ways to block them. Science. 1974 Feb 22;183(4126):753–754. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4126.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Negative conductance caused by entry of sodium and cesium ions into the potassium channels of squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):588–608. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., De Weer P. Intracellular pH transients in squid giant axons caused by CO2, NH3, and metabolic inhibitors. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jan;67(1):91–112. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Voltage clamp experiments on internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):788–820. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney K. R. Mechanism of frequency-dependent inhibition of sodium currents in frog myelinated nerve by the lidocaine derivative GEA. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Nov;195(2):225–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOTY R. W., GERARD R. W. Nerve conduction without increased oxygen consumption: action of azide and fluoroacetate. Am J Physiol. 1950 Aug 1;162(2):458–468. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.162.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M. Direct and rapid description of the individual ionic currents of squid axon membrane by ramp potential control. Biophys J. 1970 Sep;10(9):799–817. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86336-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M. Low-impedance capillary electrode for wide-band recording of membrane potential in large axons. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1973 Sep;20(5):380–382. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1973.324235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN M. E., SHAW F. H. The effect of yohimbine and other drugs on the isolated frog skin potential. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Dec;33(6):671–676. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. Evidence that tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin act at a metal cation binding site in the sodium channels of nerve membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3936–3940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):497–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Ehrenstein G., Catterall W. A. Interaction between batrachotoxin and yohimbine. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):219–231. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85444-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang W. J., Lambert G. A., Rush M. L. The role of the central nervous system in the cardiovascular responses to yohimbine. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1975 Sep;217(1):57–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKERSON M. The pharmacology of adrenergic blockade. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1949 Apr;95(Pt 2)(4):27–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Anderson N. C., Moore J. W. Comparison of tetrodotoxin and procaine in internally perfused squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1413–1428. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papeschi R., Sourkes T. L., Youdim M. B. The effect of yohimbine on brain serotonin metabolism, motor behavior and body temperature of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971;15(3):318–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. D., Sloboda W. Afrodex vs. placebo in the treatment of male impotence: statistical analysis of two double-blind crossover studies. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1974 Jan;16(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Electrical phenomena in nerve. III. Frog sciatic nerve. J Cell Physiol. 1951 Aug;38(1):17–40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030380103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW F. H., HOLMAN M., MACKENZIE J. G. The action of yohimbine on nerve and muscle of amphibia. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Aug;33(4):497–505. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON S. E. The effect of yohimbine on sodium and potassium movements in resting nerve and muscle. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Apr;33(2):179–187. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourkes T. L., Missala K., Madras B. K. Effect of yohimbine on tryptophan metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Feb;165(2):289–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strichartz G. R. The inhibition of sodium currents in myelinated nerve by quaternary derivatives of lidocaine. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jul;62(1):37–57. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strichartz G. Molecular mechanisms of nerve block by local anesthetics. Anesthesiology. 1976 Oct;45(4):421–441. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197610000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKII, WATANABE A., TAKENAKA T. Resting and action potential of intracellularly perfused squid giant axon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1177–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



