Abstract
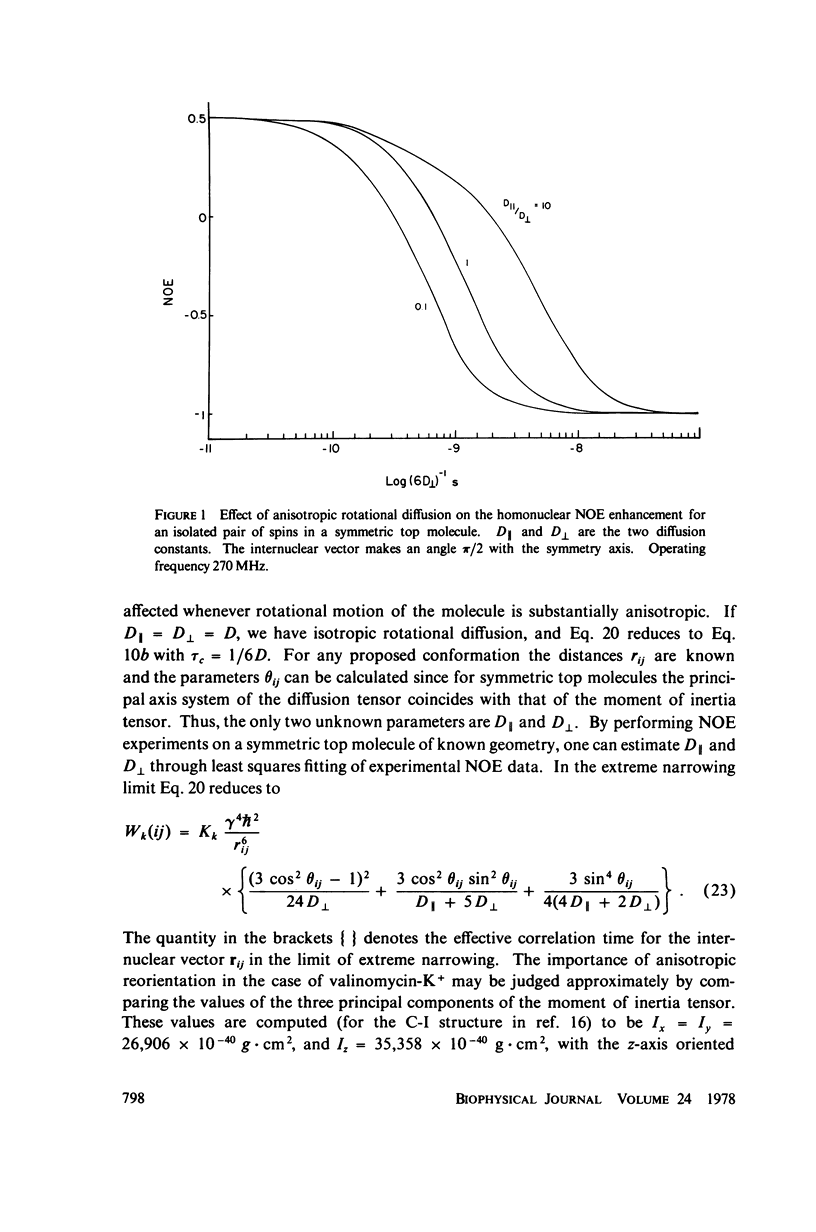
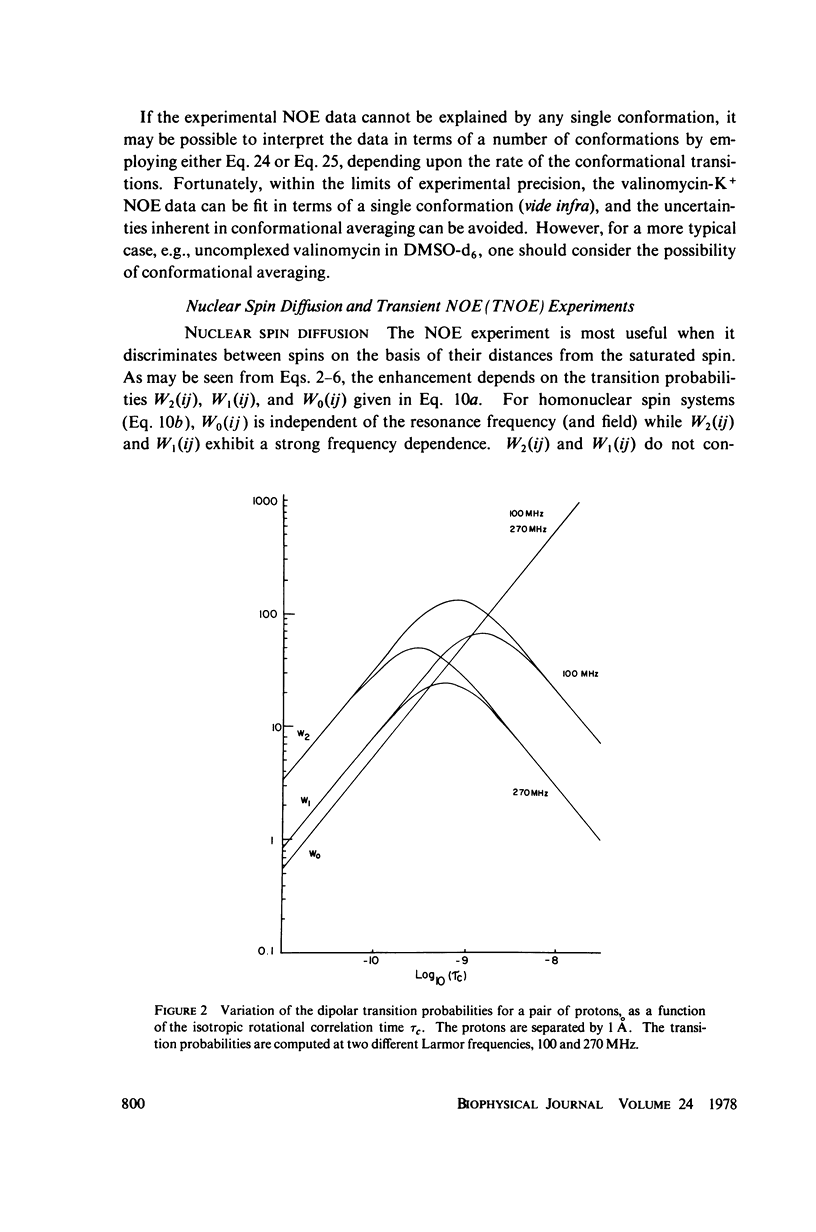
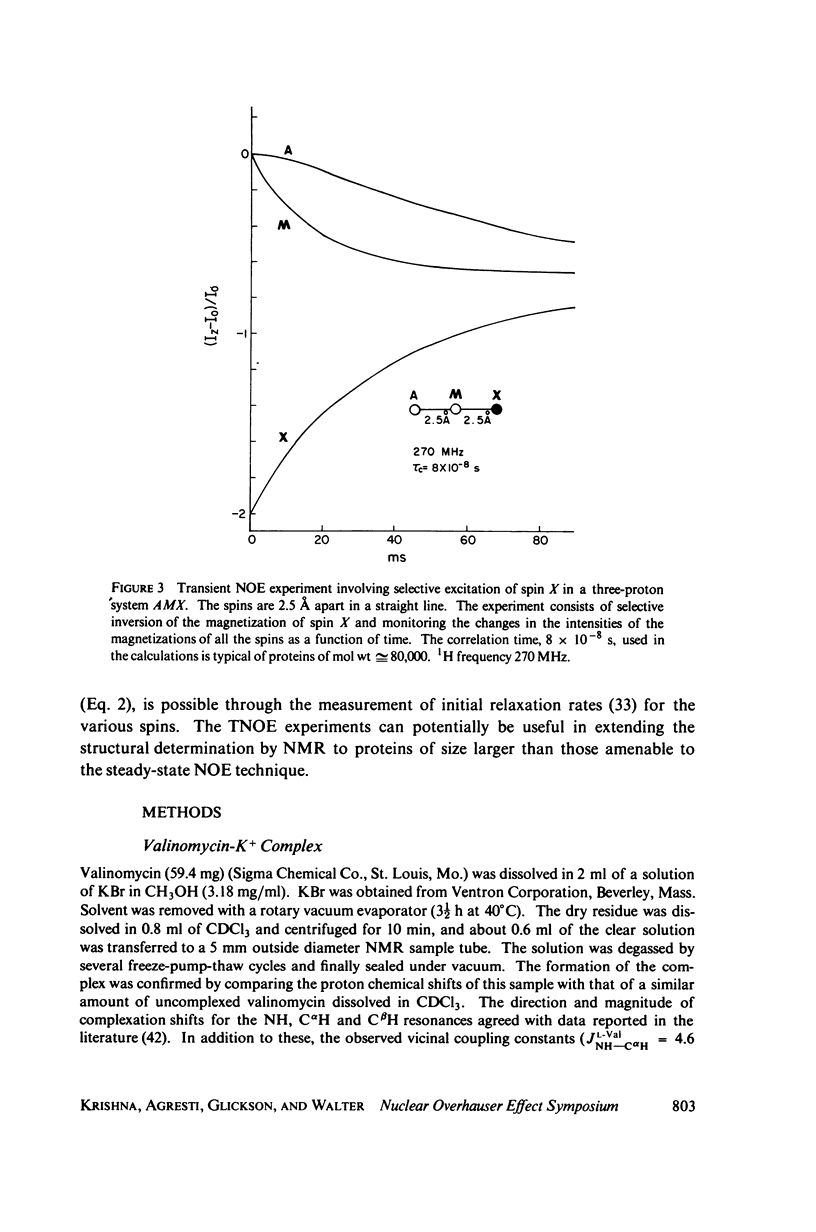
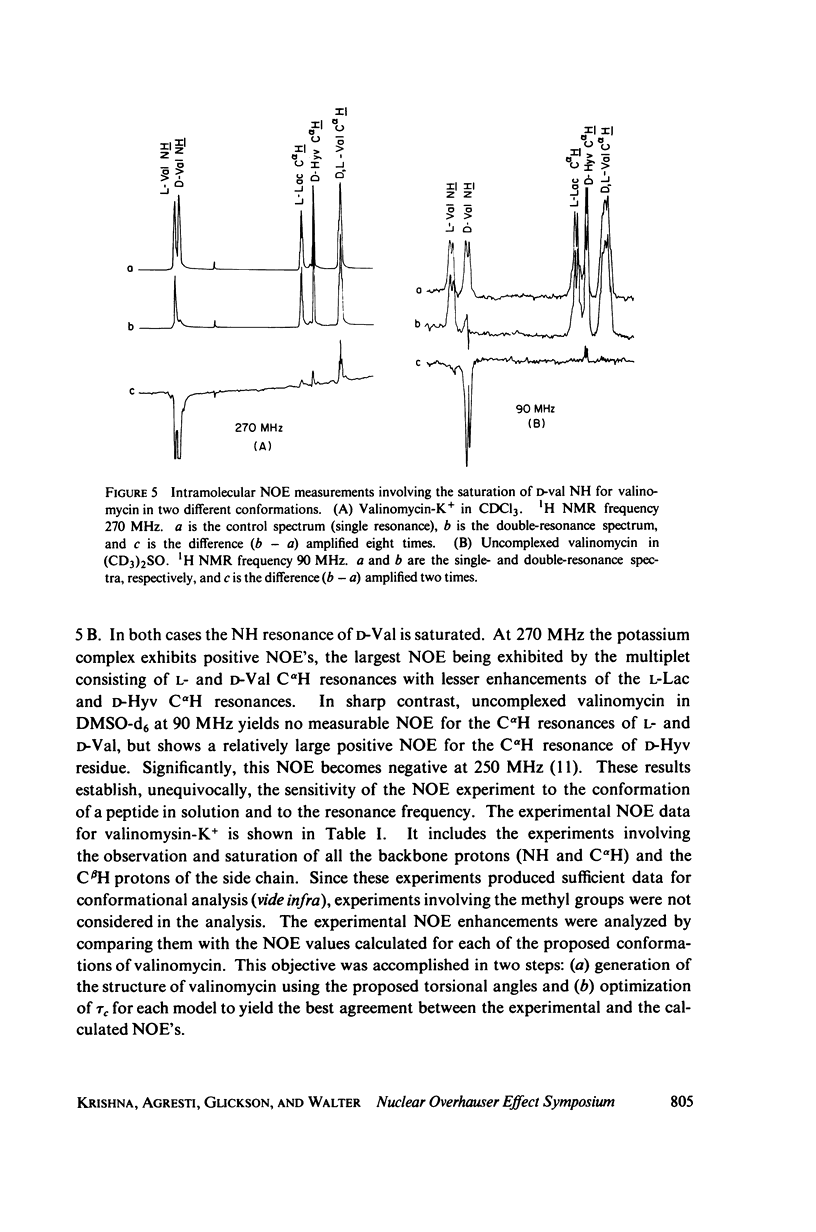
This study demonstrates how the intramolecular nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) experiment can be employed quantitatively to select from a set of possible conformations for a peptide or a protein the particular conformation (or a group of conformations) most consistent with the data. This procedure is demonstrated on a model depsipeptide system--valinomycin K+ in CDCl3--for which the solution conformation has been inferred by other methods. The NOE enhancements are very sensitive to the conformations assumed by this antibiotic. It is shown that the set of conformations, collectively labeled as A2 (including the X-ray crystallographic structure) gives a very good description of the NOE enhancements. The structure proposed by Bystrov et al. (1977. Eur. J. Biochem. 78:63) for the uncomplexed valinomycin in nonpolar solvents is also consistent with the experimental data on the potassium complex. Using statistical hypothesis testing involving the Hamilton R-factor ratio criterion, all the other models have been rejected as inconsistent with the experimental data. A general formalism is presented for describing the NOE effects in isotropically reorienting molecules. The formalism is not restricted to the extreme narrowing limit of the rotational correlation times and hence applies to both small and large molecules. Some of the factors that can influence the NOE measurements, viz. anisotropic rotational diffusion, conformational averaging, and nuclear spin diffusion, have been considered in this study.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agresti D. G., Lenkinski R. E., Glickson J. D. Lanthanide induced NMR perturbations of HEW lysozyme: evidence for nonaxial symmetry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91558-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Tieffenberg M., Tosteson D. C. The effect of valinomycin on the ionic permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Dec;50(11):2527–2545. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.11.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asher I. M., Rothschild K. J., Anastassakis E., Stanley H. E. Raman spectroscopy of uncomplexed valinomycin. I. The solid state. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Mar 30;99(7):2024–2032. doi: 10.1021/ja00449a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asher I. M., Rothschild K. J., Stanley H. E. Raman spectroscopic study of the valinomycin--KSCN complex. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):205–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaram P., Bothner-By A. A., Breslow E. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the interaction of peptides and hormones with bovine neurophysin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4695–4704. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystrov V. F., Gavrilov Y. D., Ivanov V. T., Ovchinnikov Y. A. Refinement of the solution conformation of valinomycin with the acid coupling constants from the 13C-nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectra. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):63–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickson J. D., Gordon S. L., Pitner P., Agresti D. G., Walter R. Intramolecular 1H nuclear Overhauser effect study of the solution conformation of valinomycin in dimethyl sulfoxide. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5721–5729. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. H., Kowalsky A., Pressman B. C. Application of nuclear magnetic resonance to the conformational changes in valinomycin during complexation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karle I. L. Conformation of valinomycin in a triclinic crystal form. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jul 23;97(15):4379–4386. doi: 10.1021/ja00848a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaled M. A., Urry D. W. Nuclear Overhauser enhancement demonstration of the type II beta-turn in repeat peptides of tropoelastin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):485–491. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach S. J., Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. Use of proton nuclear Overhauser effects for the determination of the conformations of amino acid residues in oligopeptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Development of K+-Na+ discrimination in experimental bimolecular lipid membranes by macrocyclic antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 21;26(4):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90559-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neupert-Laves K., Dobler M. The crystal structure of a K+ complex of valinomycin. Helv Chim Acta. 1975 Mar 12;58(2):432–442. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19750580212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Tonelli A. E. Solvent-dependent conformations of valinomycin in solution. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):486–496. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton M., Steinrauf L. K., Dawkins P. The molecular structure and some transport properties of valinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):512–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitner T. P., Walter R., Glickson J. D. Mechanism of the intramolecular 1H nuclear Overhauser effect in peptides and depsipeptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):746–751. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90655-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Induced active transport of ions in mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1076–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Ionophorous antibiotics as models for biological transport. Fed Proc. 1968 Nov-Dec;27(6):1283–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae I. D., Stimson E. R., Scheraga H. A. Nuclear Overhauser effects and the conformation of gramicidin S. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):225–229. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80186-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer R. E., Davis J. P., Noggle J. H., Hart P. A. Conformational analysis of nucleosides in solution by quantitative application of the nuclear Overhauser effect. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Apr 19;94(8):2561–2572. doi: 10.1021/ja00763a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Duax W. L., Langs D. A., DeTitta G. T., Edmonds J. W., Rohrer D. C., Weeks C. M. The crystal and molecular structure of the triclinic and monoclinic forms of valinomycin, C54H90N6O18. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Dec 10;97(25):7242–7247. doi: 10.1021/ja00858a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. D., Weingarten H. I., Schlesinger M. J. Fluorotyrosine alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli: preparation, properties, and fluorine-19 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):469–473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson D. C., Cook P., Andreoli T., Tieffenberg M. The effect of valinomycin on potassium and sodium permeability of HK and LK sheep red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Dec;50(11):2513–2525. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.11.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Khaled M. A., Rapaka R. S., Okamoto K. Nuclear Overhauser enhancement evidence for inverse temperature dependence of hydrophobic side chain proximity in the polytetrapeptide of tropoelastin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):700–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Kumar N. G. Affirmation of critical proton magnetic resonance data on the solution conformation of the valinomycin-potassium ion complex. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1829–1831. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



