Abstract
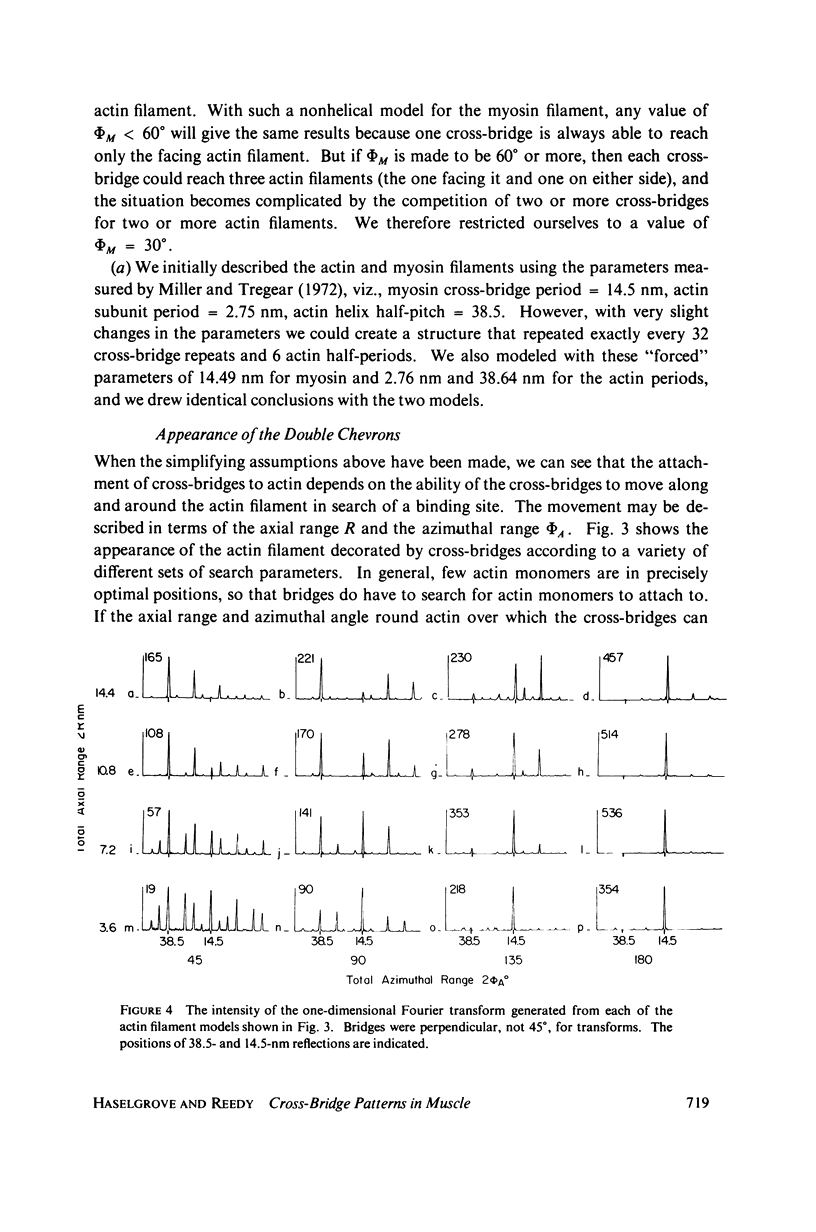
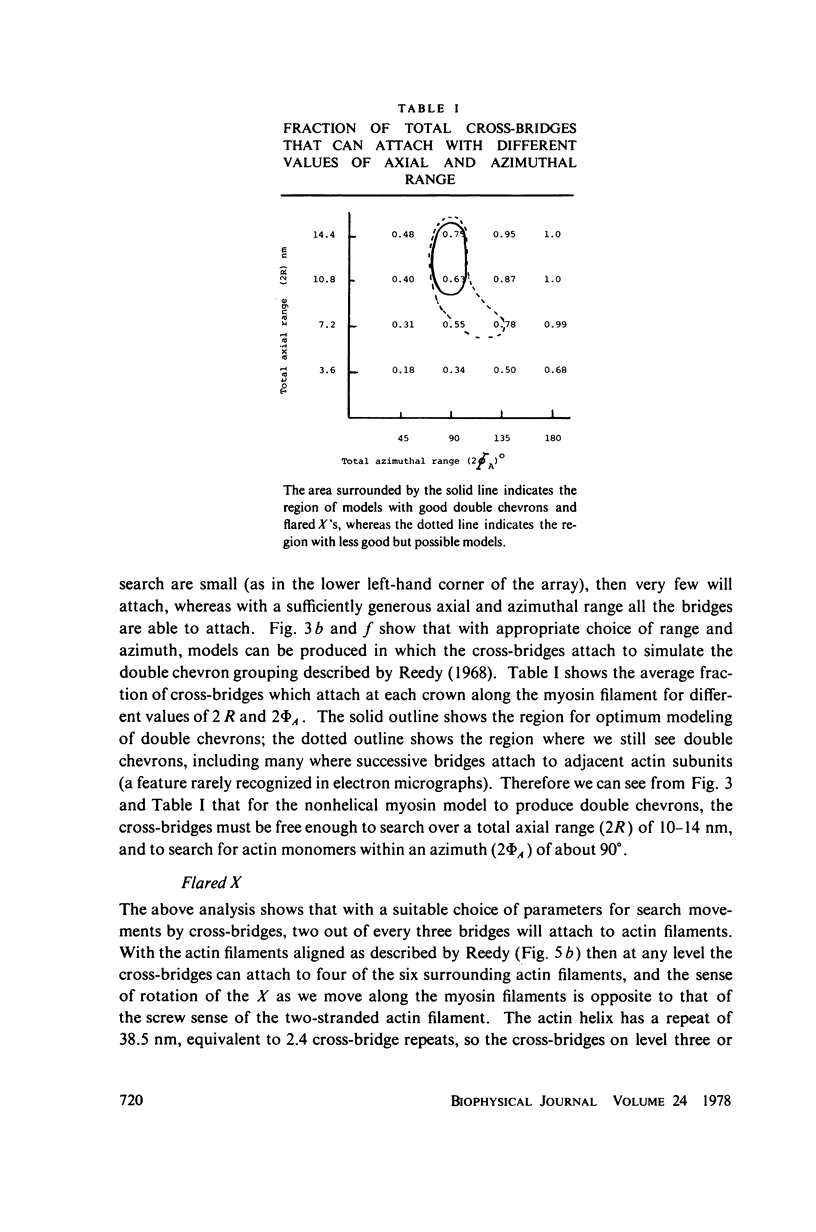
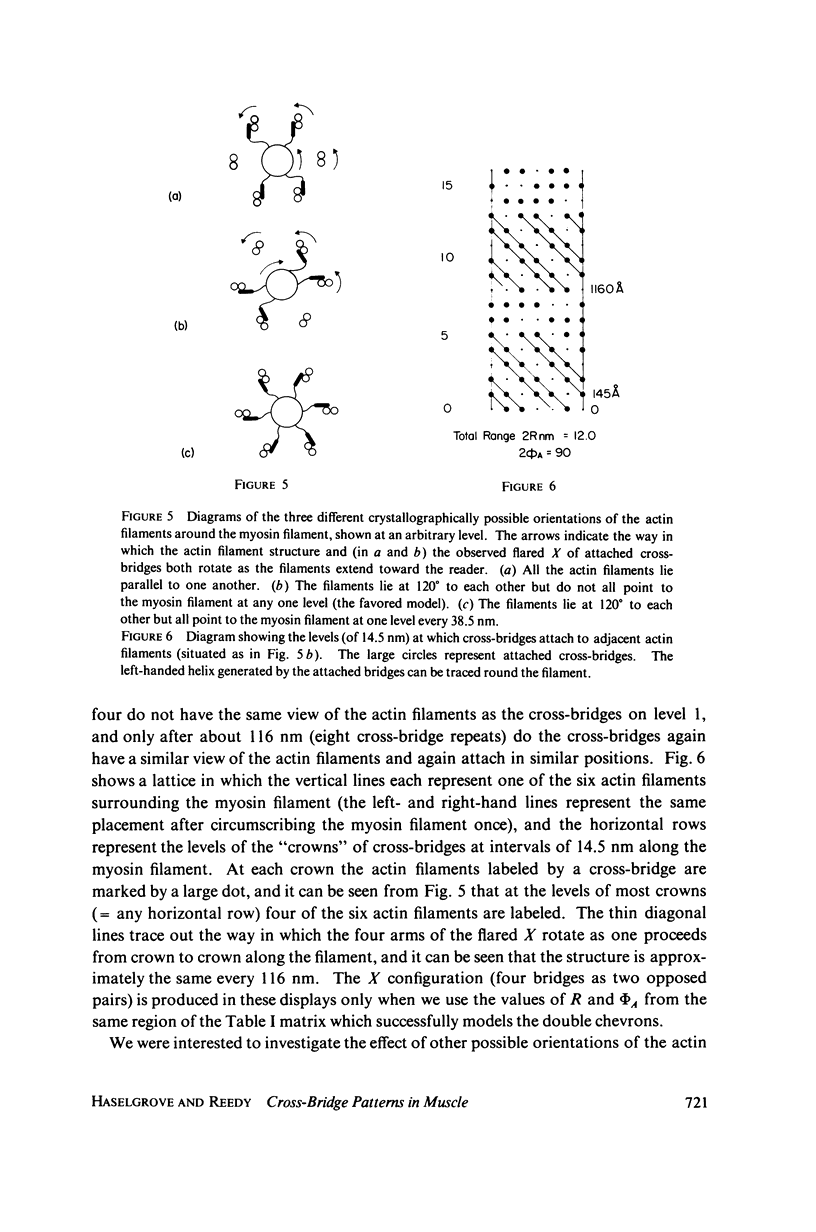
We have undertaken some computer modeling studies of the cross-bridge observed by Reedy in insect flight muscle so that we investigate the geometric parameters that influence the attachment patterns of cross-bridges to actin filaments. We find that the appearance of double chevrons along an actin filament indicates that the cross-bridges are able to reach 10--14 nm axially, and about 90 degrees around the actin filament. Between three and five actin monomers are therefore available along each turn of one strand of actin helix for labeling by cross-bridges from an adjacent myosin filament. Reedy's flared X of four bridges, which appears rotated 60 degrees at successive levels on the thick filament, depends on the orientation of the actin filaments in the whole lattice as well as on the range of movement in each cross-bridge. Fairly accurate chevrons and flared X groupings can be modeled with a six-stranded myosin surface lattice. The 116-nm long repeat appears in our models as "beating" of the 14.5-nm myosin repeat and the 38.5-nm actin period. Fourier transforms of the labeled actin filaments indicate that the cross-bridges attach to each actin filament on average of 14.5 nm apart. The transform is sensitive to changes in the ease with which the cross-bridge can be distorted in different directions.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barden J. A., Mason P. Muscle crossbridge stroke and activity revealed by optical diffraction. Science. 1978 Mar 17;199(4334):1212–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.415364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEPUE R. H., Jr, RICE R. V. F-ACTIN IS A RIGHT-HANDED HELIX. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:302–303. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L. Theoretical formalism for the sliding filament model of contraction of striated muscle. Part II. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;29(2):105–159. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Rodger C. D., Tregear R. T. Changes in muscle crossbridges when beta, gamma-imido-ATP binds to myosin. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 14;104(1):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S., Weber A. The dissociation constant of the actin-heavy meromyosin subfragment-1 complex. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3868–3873. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Tregear R. T. Structure of insect fibrillar flight muscle in the presence and absence of ATP. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):85–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Elliott A. Can a myosin molecule bind to two actin filaments? Nature. 1978 Jan 26;271(5643):325–329. doi: 10.1038/271325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. K. Ultrastructure of insect flight muscle. I. Screw sense and structural grouping in the rigor cross-bridge lattice. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):155–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome E. M., Hirabayashi T., Perry S. V. X-ray diffraction of muscle labelled with antibody to troponin-C. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):154–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio244154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire J. M. General model of myosin filament structure. II. Myosin filaments and cross-bridge interactions in vertebrate striated and insect flight muscles. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear R. T., Squire J. M. Myosin content and filament structure in smooth and striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90336-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




