Abstract
The Raman spectra of aqueous solutions of myosin and mixtures of myosin in solutions of the salts CaCl2, MgCl2, and LiBr have been taken. The spectrum of the solvent background has been subtracted by means of a computer, leaving only the Raman peaks of the protein. From an analysis of the Raman bands in the regions at 900, 940, 1,240-1,300, and 1,650-1,670 cm-1, it seems likely that CaCl2 effects an α-to β-transition in myosin, probably owing to the interaction of the Ca2+ ion, LiBr appears to denature the protein leading to increased random coil structure, and MgCl2 appears to have an effect intermediate between the two other salts. These results are reported for concentrations as low as 10-5 M of CaCl2 and MgCl2.
This investigation indicates the usefulness of the Raman light-scattering technique for the study of protein conformational changes.
Full text
PDF


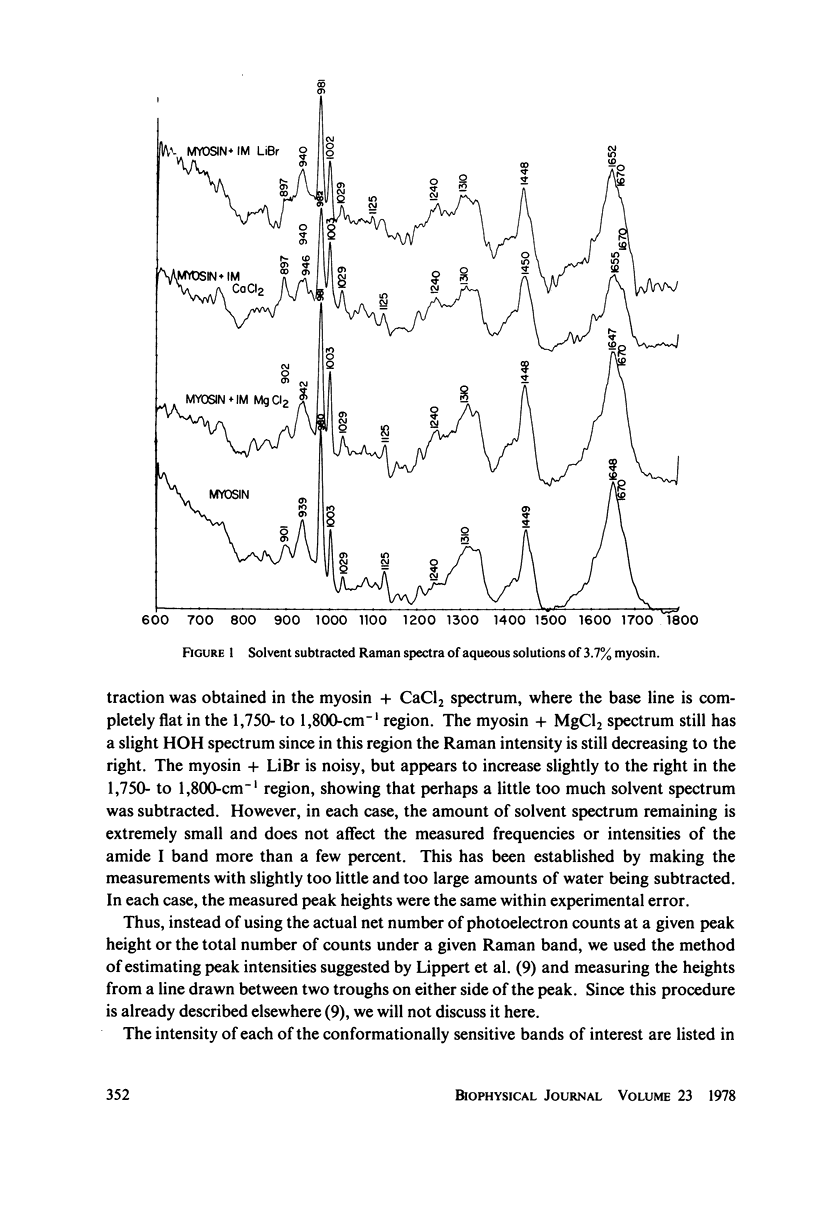
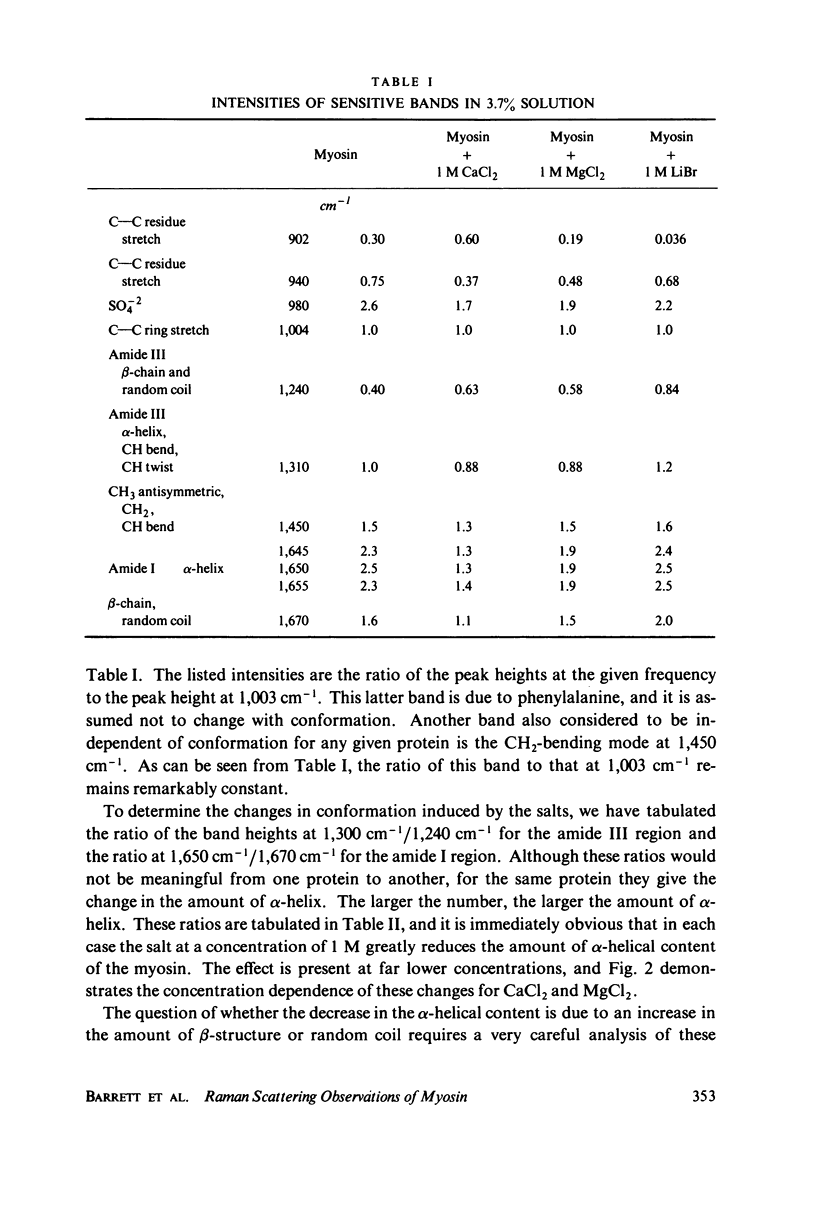
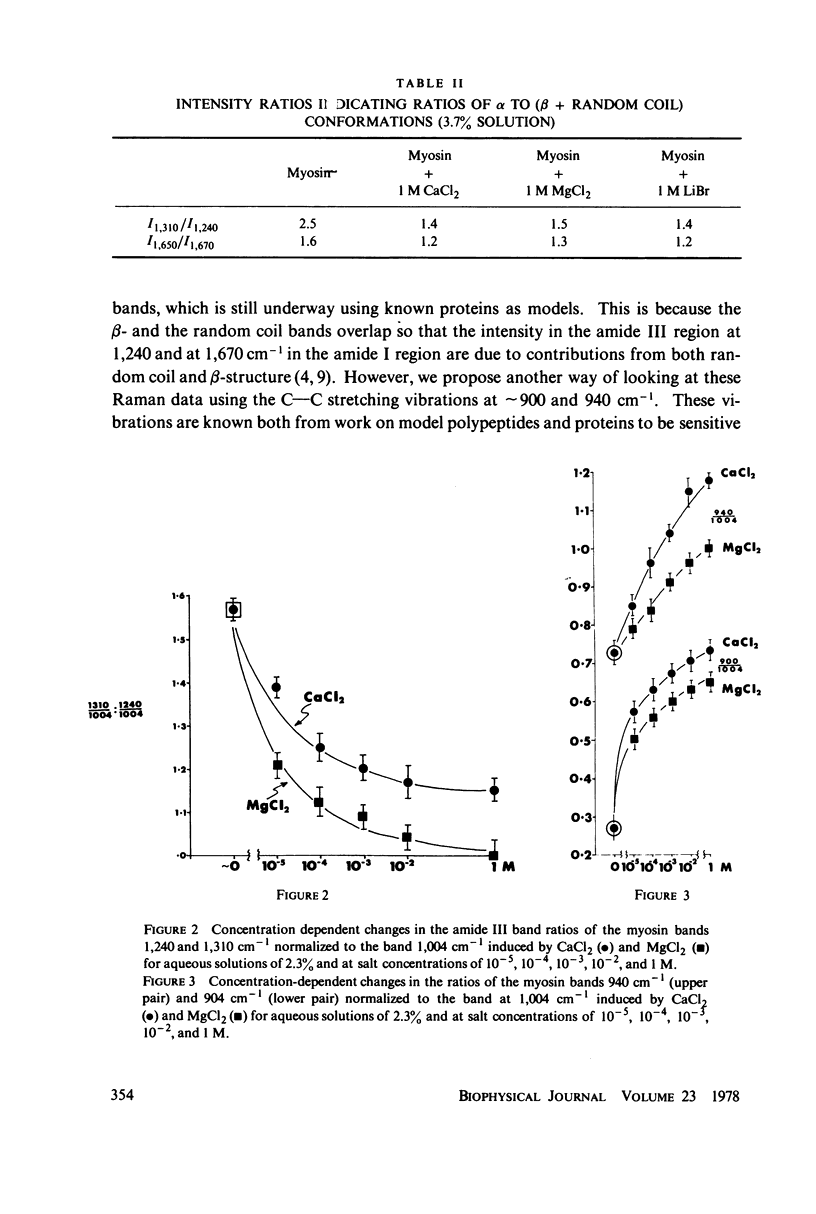




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa N., Robson R. M., Goll D. E. An improved method for the preparation of alpha-actinin from rabbit striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):284–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Isenberg I. On the analysis of circular dichroic spectra of proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):629–634. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremel R. D., Weber A. Calcium binding to rabbit skeletal myosin under physiological conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 17;376(2):366–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány K., Bárány M. Phosphorylation of the 18,000-dalton light chain of myosin during a single tetanus of frog muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4752–4754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew E. B., Asher I. M., Stanley H. E. Laser raman spectroscopy--new probe of myosin substructure. Science. 1975 May 30;188(4191):933–936. doi: 10.1126/science.1138362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. C., Lord R. C. Laser Raman spectroscopic studies of the thermal unfolding of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1889–1897. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. C., Lord R. C., Mendelsohn R. Laser-excited Raman spectroscopy of biomolecules. V. Conformational changes associated with the chemical denaturation of lysozyme. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 May 15;96(10):3038–3042. doi: 10.1021/ja00817a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. C., Lord R. C., Mendelsohn R. Laser-excited raman spectroscopy of biomolecules. IV. Thermal denaturation of aqueous lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 6;328(2):252–260. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Martinez H. M. Determination of the secondary structures of proteins by circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4120–4131. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. C., Cooke R. Effects of alkali ions on myosin conformation. Biopolymers. 1971;10(3):523–529. doi: 10.1002/bip.360100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson N., Solaro R. J., Perry S. V. Changes in phosphorylation of P light chain of myosin in perfused rabbit heart. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):801–802. doi: 10.1038/264801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Phosphorylated proteins as physiological effectors. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):146–152. doi: 10.1126/science.22932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond K. S., Goll D. E. Purification of insect myosin and alpha-actinin. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1510189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. C., Lowey S. An immunological approach to the role of the low molecular weight subunits in myosin. II. Interaction of myosin and its subfragments with antibodies to the light chains. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4609–4620. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick-Jones J., Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulation in molluscan muscles. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick-Jones J., Szentkiralyi E. M., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulatory light chains in myosins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 15;104(4):747–775. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuck J. F., Jr, East E. J., Yu N. T. Prevalence of alpha-helical form in avian lens proteins. Exp Eye Res. 1976 Jul;23(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulation of muscular contraction. Distribution of actin control and myosin control in the animal kingdom. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippert J. L., Tyminski D., Desmeules P. J. Determination of the secondary structure of proteins by laser Raman spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Oct 27;98(22):7075–7080. doi: 10.1021/ja00438a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Fluorimetric studies on the influence of metal ions and chelators on the interaction between myosin and ATP. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jul 1;33(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt W., Yang J. T. THE OPTICAL ROTATORY DISPERSION OF SIMPLE POLYPEPTIDES. I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):596–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto K., Harrington W. F. Evidence for structural changes in vertebrate thick filaments induced by calcium. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 25;88(3):693–709. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter P. C., Koenig J. L. The solution conformation of poly(L-lysine). A Raman and infrared spectroscopic study. Biopolymers. 1976 Feb;15(2):229–240. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peticolas W. L. Application of Raman spectroscopy to biological macromolecules. Biochimie. 1975;57(4):417–428. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G. Calcium regulation of muscle contraction. Biophys J. 1975 Jul;15(7):707–723. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85849-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONOMURA Y., SEKIYA K., IMAMURA K. The optical rotatory dispersion of myosin A. I. Effect of inorganic salt. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3110–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu N. T. Raman spectroscopy: a conformational probe in biochemistry. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1977;4(3):229–280. doi: 10.3109/10409237709102559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu T. J., Lippert J. L., Peticolas W. L. Laser Raman studies of conformational variations of poly-L-lysine. Biopolymers. 1973;12(9):2161–2175. doi: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


