Abstract
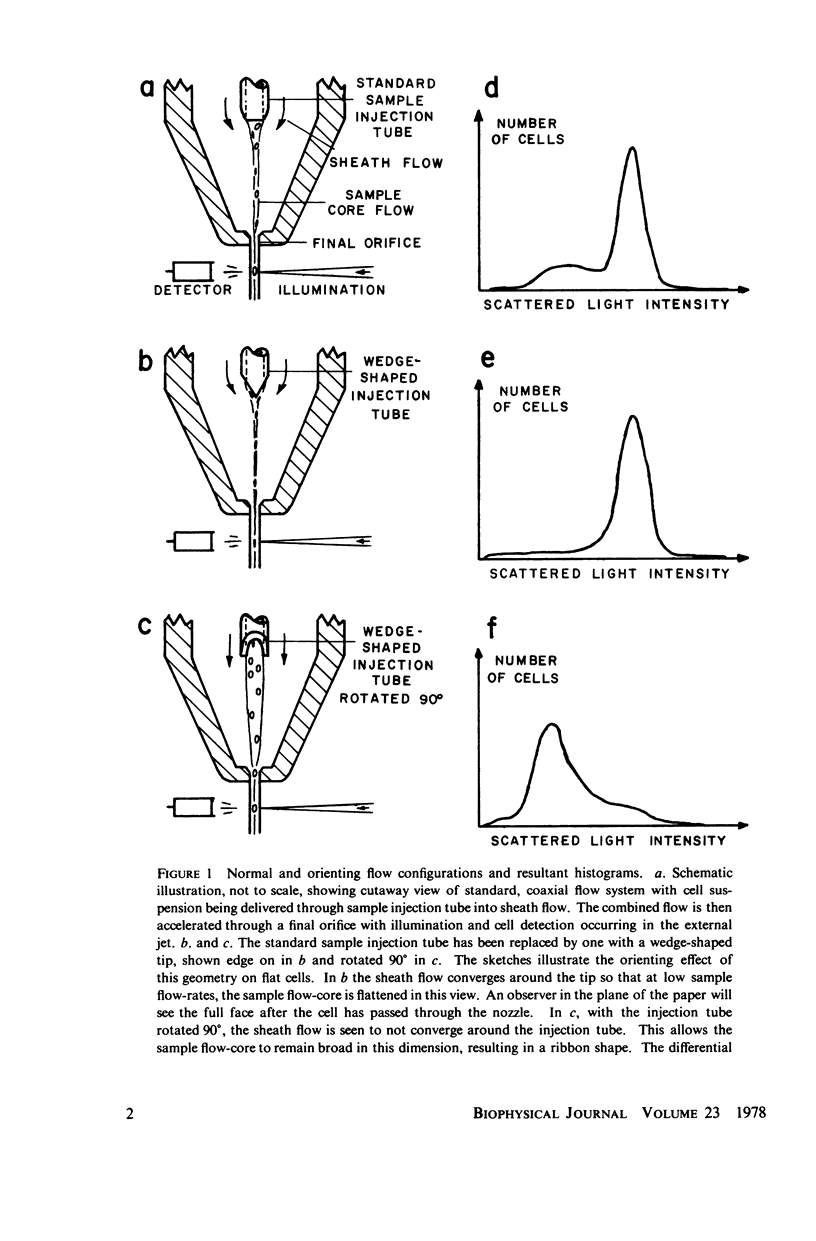
Flattened cells, such as red blood cells, epithelial cells, and sperm of many species, cause problems for fluorescence-activated cell analysis and sorting machines because the flow systems of such devices are unable to control the orientation of these cells as they flow past the detectors. For this reason, the fluorescence or scattered light measurements for identical cells may vary greatly. A flow geometry is here described that orients flat cells in a coaxial flow system so that each cell presents the same aspect to the observation device. A wedge-shaped exit on the sample injection tube in a coaxial flow system is sufficient to produce the desired orientation effect when used with low sample flow rates. Data is presented showing the effect of orientation of fixed chicken erythrocytes on histograms of small forward-angle light-scattering measurements.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fulwyler M. J. Hydrodynamic orientation of cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):781–783. doi: 10.1177/25.7.330728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. A., Wheeless L. L., Jr Application of Fraunhofer diffraction theory to feature-specific detector design. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):857–863. doi: 10.1177/25.7.330735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Sci Am. 1976 Mar;234(3):108–117. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0376-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulett H. R., Bonner W. A., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Development and application of a rapid cell sorter. Clin Chem. 1973 Aug;19(8):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachel V., Kordwig E., Glossner E. Uniform lateral orientation, caused by flow forces, of flat particles in flow-through systems. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):774–780. doi: 10.1177/25.7.330727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D. B., Wheeless L. L., Jr Experimental findings on gynecologic cell orientation and dynamics for three flow nozzle geometries. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):870–874. doi: 10.1177/25.7.330737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken M. R., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. Identification of cell asymmetry and orientation by light scattering. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):790–795. doi: 10.1177/25.7.330730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dilla M. A., Gledhill B. L., Lake S., Dean P. N., Gray J. W., Kachel V., Barlogie B., Göhde W. Measurement of mammalian sperm deoxyribonucleic acid by flow cytometry. Problems and approaches. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):763–773. doi: 10.1177/25.7.70455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



