Abstract
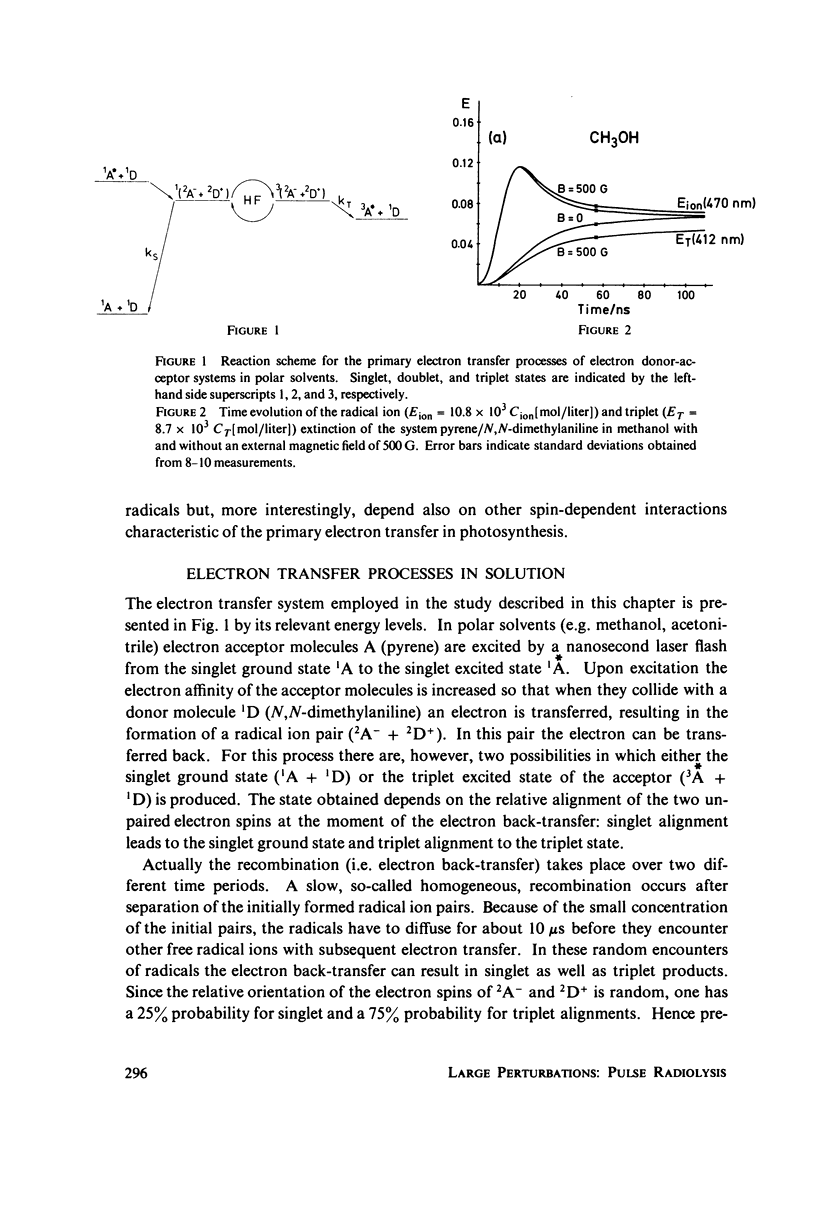
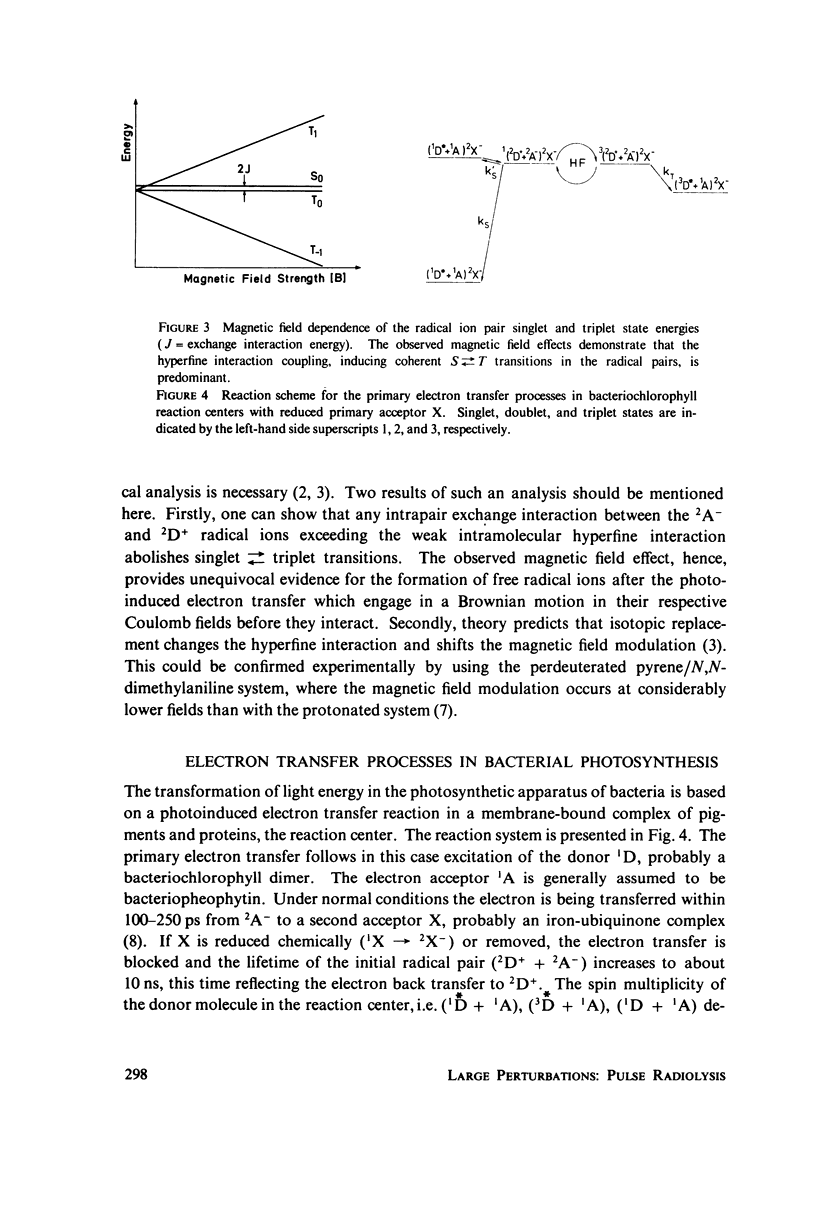
Photoinduced electron transfer generates radical pairs which recombine with 10(-9)10(-8)s by electron back-transfer to either singlet or triplet products. The product distribution determined by the spin motion of the unpaired electrons in the radical pairs is affected by external magnetic fields. The analysis of the magnetic field effect furnishes new information about electron transfer processes. Light-induced electron transfer in polar solvents and in the bacterial photosynthetic reaction center are discussed as examples.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blankenship R. E., Schaafsma T. J., Parson W. W. Magnetic field effects on radical pair intermediates in bacterial photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 10;461(2):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogdell R. J., Monger T. G., Parson W. W. Carotenoid triplet states in reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 11;408(3):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff A. J., Rademaker H., van Grondelle R., Duysens L. N. On the magnetic field dependence of the yield of the triplet state in reaction centers of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 9;460(3):547–554. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parson W. W., Cogdell R. J. The primary photochemical reaction to bacterial photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 31;416(1):105–149. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(75)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sono M., Smith P. D., McCray J. A., Asakura T. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of the reactions of heme-substituted horse heart myoglobins with oxygen and carbon monoxide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1418–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


