Abstract
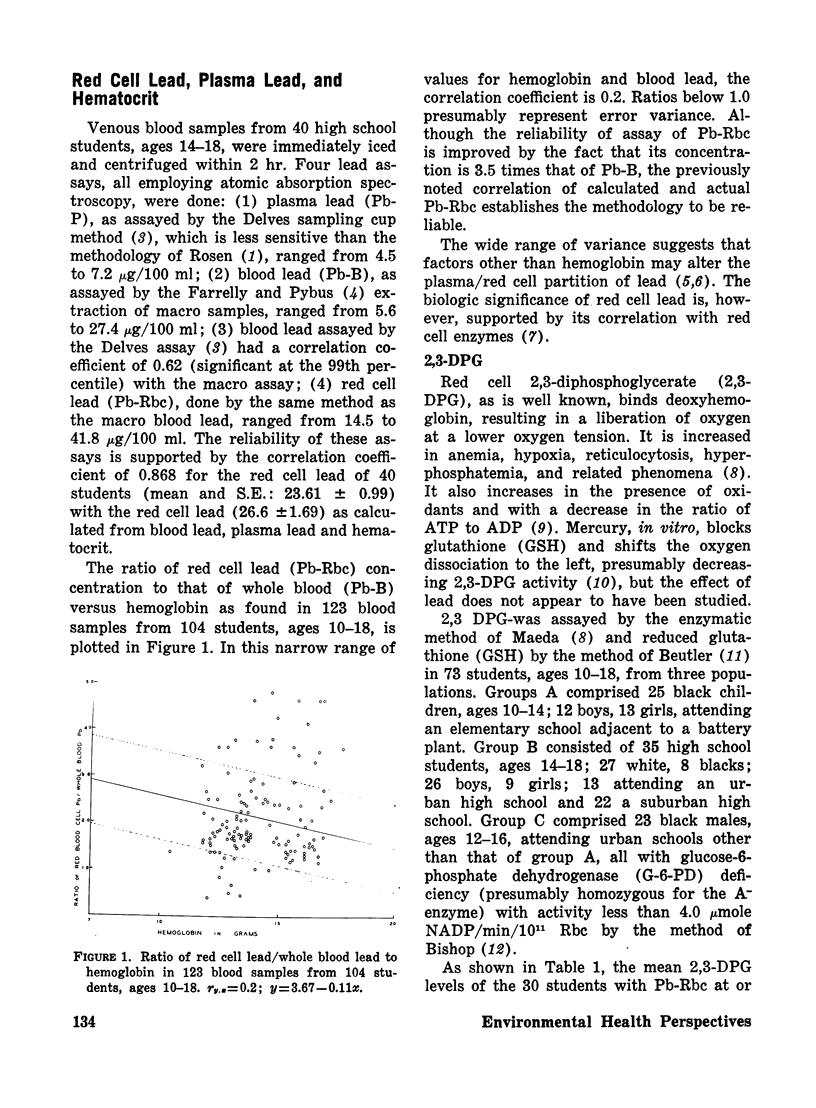
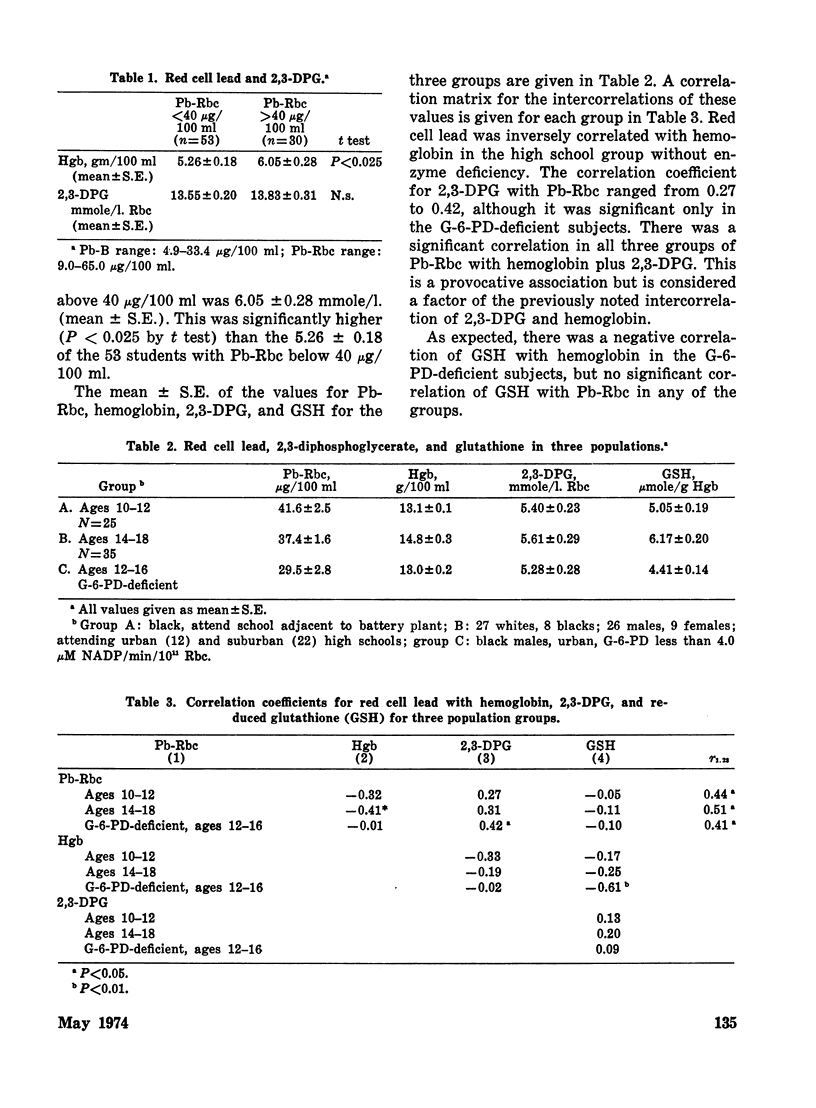
Simultaneous assay of blood lead (Pb-B) and red cell lead (Pb-Rbc) in 123 samples from 104 urban and suburban students, ages 10–18, shows the ratio of concentration (Pb-Rbc)/(Pb-B) to increase as the hematocrit decreases. On direct assay in 40 samples, plasma lead (Pb-P) was fixed in a narrow range. In 28 students with Pb-Rbc >40 μg/100 ml, the mean red cell 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) was 6.05±0.28 (±S.E.), significantly higher (P<.025) than the 5.25±0.18 of 51 students with Pb-Rbc<40 μg/100 ml, although hemoglobin values were comparable (13.83±0.31 versus 13.55±0.20). Analysis of the individual population groups showed this correlation of Pb-Rbc with 2,3-DPG to be primarily related to the intercorrelation of each parameter with hemoglobin.
Rbc membrane Na/K ATPase, as per cent of total membrane ATPase, had a median value of 60% in 48 subjects. Na/K ATPase below 60% was found in 10 (77%) of the 13 students with Pb-Rbc≥40 μg/100 ml, but in only 14 of the 35 with Pb-Rbc<40 μg/100 ml (χ2=5.1, df=1, P<0.05).
Correlation of significant enzyme changes with Pb-Rbc, but not with Pb-B in the normal urban range of Pb-B<35 μg/100 ml suggests Pb-Rbc, increased in anemia, to be a critical factor in the hematotoxicity of lead.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batolska A., Marinova H. Modifications du glutathion chez les travailleurs d'une entreprise métallurgique minière. Arch Mal Prof. 1970 Mar;31(3):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C. Assay of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.1.1.49) and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.1.1.43) in red cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jul;68(1):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delves H. T. A micro-sampling method for the rapid determination of lead in blood by atomic-absorption spectrophotometry. Analyst. 1970 May;95(130):431–438. doi: 10.1039/an9709500431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrelly R. O., Pybus J. Measurement of lead in blood and urine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Clin Chem. 1969 Jul;15(7):566–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan J., Hernberg S., Metsälä P., Vihko V. Enhanced potassium loss in blood cells from men exposed to lead. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Feb;14(2):309–312. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan J., Vihko V., Hernberg S. Deficient red cell membrane /Na++K+/-ATPase in lead poisoning. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Feb;14(2):313–318. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochen J. A., Greener Y. Levels of lead in blood and hematocrit: implications for the evaluation of the newborn and anemic patient. Pediatr Res. 1973 Nov;7(11):937–944. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197311000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Chang H., Benesch R., Benesch R. E. A simple enzymatic method for the determination of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate in small amounts of blood. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jun 3;284(22):1239–1242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197106032842204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire M. S., Angle C. R. Air lead: relation to lead in blood of black school children deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Science. 1972 Aug 11;177(4048):520–522. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4048.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire M. S., Wolf G. L., Angle C. R. Red cell lead and -amino levulinic acid dehydratase. Clin Toxicol. 1973;6(2):183–188. doi: 10.3109/15563657308990516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Passow H. Effects of calcium and lead on potassium permeability of human erythrocyte ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):601–605. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. F., Trinidad E. E. Significance of plasma lead levels in normal and lead-intoxicated children. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 May;7:139–144. doi: 10.1289/ehp.747139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secchi G. C., Alessio L. Ricerche sul meccanismo d'inibizione della Na+-K+-ATPasi eritrocitaria ad opera del piombo. Med Lav. 1969 Nov;60(11):670–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secchi G. C., Ambrosi L., Rezzonico A. Ricerche sulla Na+-K+-ATPasi e sulla acetilcolinesterasi delle membrane eritrocitarie nell'anemia saturnina. Med Lav. 1968 Oct;59(10):593–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINCENT P. C. The effects of heavy metal ions on the human erythrocyte. II. The effects of lead and mercury. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1958 Dec;36(6):589–601. doi: 10.1038/icb.1958.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


