Abstract
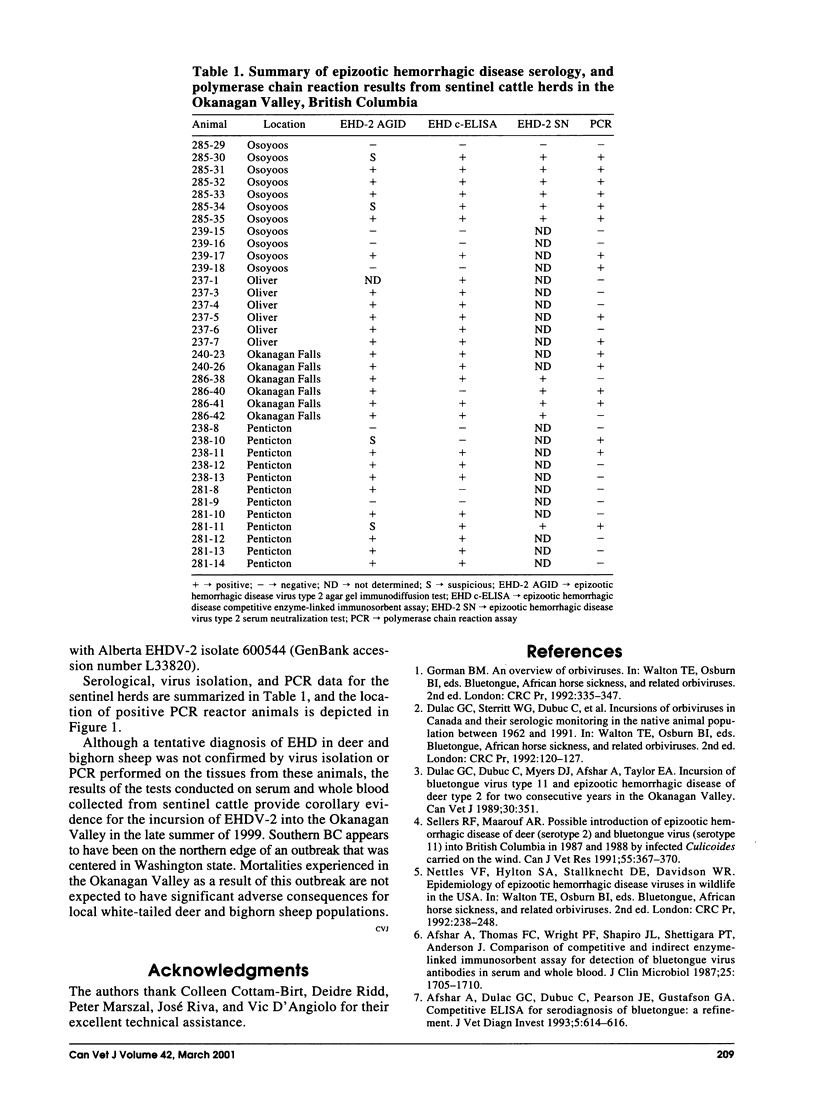
In September 1999, unusually high mortality rates in white-tailed deer and California bighorn sheep occurred in the southern Okanagan Valley. Necropsy and histopathologic findings were compatible with epizootic hemorrhagic disease (EHD); the presence of virus was not demonstrated. Subsequent serologic and polymerase chain reaction assays on sentinel cattle suggested an EHD virus incursion.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afshar A., Dulac G. C., Dubuc C., Pearson J. E., Gustafson G. A. Competitive ELISA for serodiagnosis of bluetongue: a refinement. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1993 Oct;5(4):614–616. doi: 10.1177/104063879300500419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afshar A., Thomas F. C., Wright P. F., Shapiro J. L., Shettigara P. T., Anderson J. Comparison of competitive and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of bluetongue virus antibodies in serum and whole blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1705–1710. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1705-1710.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gc D., C D., Dj M., A A., Ea T., D W., W S. British Columbia. Incursion of bluetongue virus type 11 and epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer type 2 for two consecutive years in the Okanagan Valley. Can Vet J. 1989 Apr;30(4):351–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers R. F., Maarouf A. R. Possible introduction of epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer virus (serotype 2) and bluetongue virus (serotype 11) into British Columbia in 1987 and 1988 by infected Culicoides carried on the wind. Can J Vet Res. 1991 Oct;55(4):367–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



