Abstract
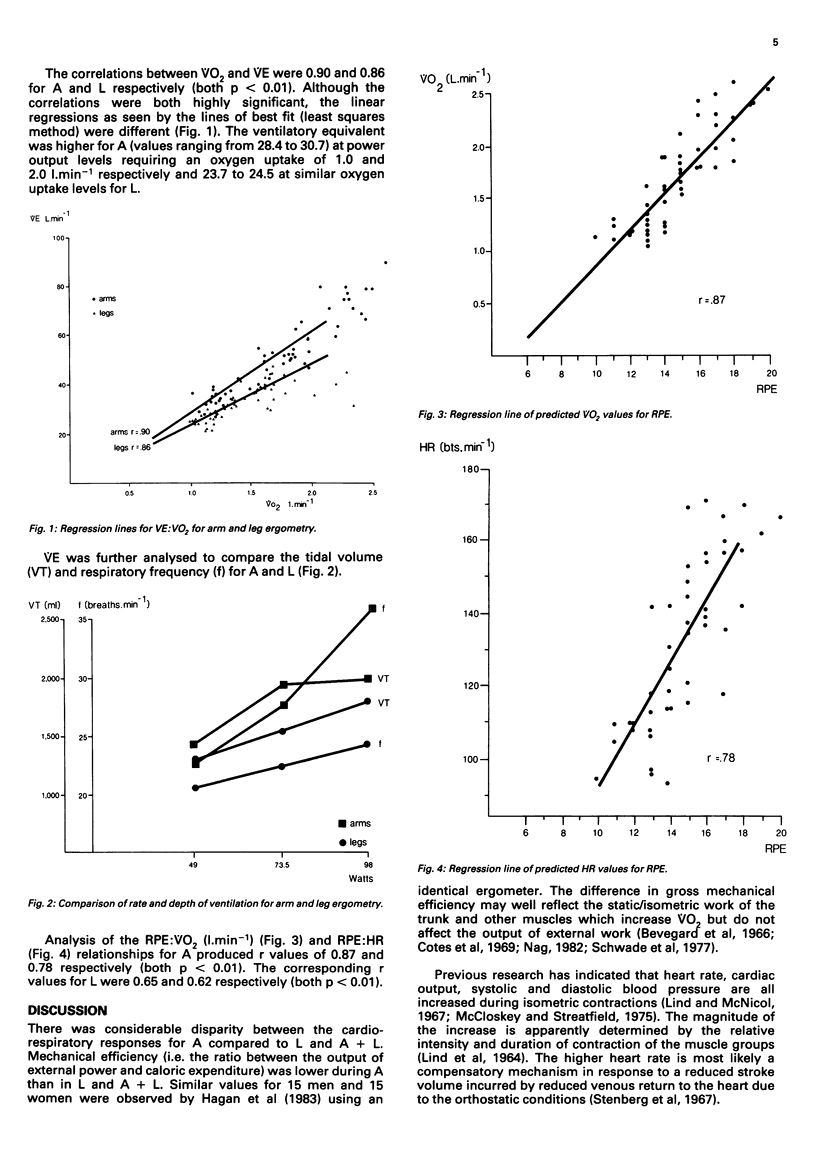
Arm (A), leg (L) and combined arm and leg (A + L) ergometry modes were compared at power outputs of 49, 73.5 and 98 W. Selected cardiorespiratory variables and a rating of perceived exertion (RPE) were measured for 19 males of mean age 25.7 (+/- 5.5) years. Oxygen uptake (VO2), heart rate (HR), minute ventilation and rating of perceived exertion (RPE) were all higher (p less than 0.01) in A compared with L and A + L. Gross mechanical efficiency was significantly lower in A (p less than 0.01) than in L or A + L. No differences were observed in any measurements between L and A + L. the correlations between RPE and cardiorespiratory variables were higher for A (RPE:VO2, r = 0.87, p less than 0.01; RPE:HR, r = 0.78 p less than 0.01) than for L and A + L.
Full text
PDF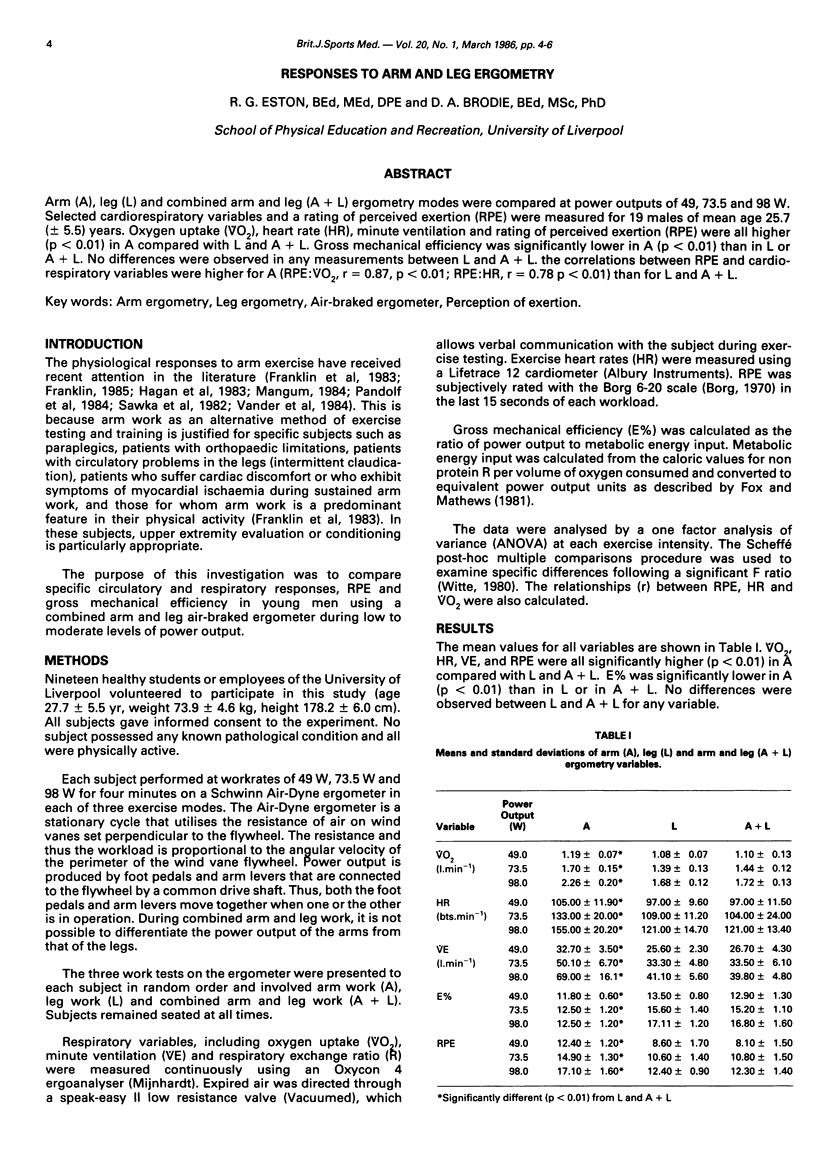

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevegård S., Freyschuss U., Strandell T. Circulatory adaptation to arm and leg exercise in supine and sitting position. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):37–46. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg G. Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1970;2(2):92–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carton R. L., Rhodes E. C. A critical review of the literature on ratings scales for perceived exertion. Sports Med. 1985 May-Jun;2(3):198–222. doi: 10.2165/00007256-198502030-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Allsopp D., Sardi F. Human cardiopulmonary responses to exercise: comparisons between progressive and steady state exercise, between arm and leg exercise, and between subjects differing in body weight. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1969 Apr;54(2):211–222. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1969.sp002019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. T., Few J., Foster K. G., Sargeant A. J. Plasma catecholamine concentration during dynamic exercise involving different muscle groups. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1974 Mar 28;32(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00423215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin B. A. Exercise testing, training and arm ergometry. Sports Med. 1985 Mar-Apr;2(2):100–119. doi: 10.2165/00007256-198502020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIND A. R., TAYLOR S. H., HUMPHREYS P. W., KENNELLY B. M., DONALD K. W. THE CIRCULATIORY EFFECTS OF SUSTAINED VOLUNTARY MUSCLE CONTRACTION. Clin Sci. 1964 Oct;27:229–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind A. R., McNicol G. W. Circulatory responses to sustained hand-grip contractions performed during other exercise, both rhythmic and static. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):595–607. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Streatfeild K. A. Muscular reflex stimuli to the cardiovascular system during isometric contractions of muscle groups of different mass. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):431–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag P. K. Influence of posture and speed of arm and leg work on physiological responses. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 1982 Dec;22(4):426–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolf K. B., Billings D. S., Drolet L. L., Pimental N. A., Sawka M. N. Differential ratings of perceived exertion and various physiological responses during prolonged upper and lower body exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1984;53(1):5–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00964681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawka M. N., Miles D. S., Petrofsky J. S., Wilde S. W., Glaser R. M. Ventilation and acid-base equilibrium for upper body and lower body exercise. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1982 Apr;53(4):354–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwade J., Blomqvist C. G., Shapiro W. A comparison of the response to arm and leg work in patients with ischemic heart disease. Am Heart J. 1977 Aug;94(2):203–208. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(77)80281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg J., Astrand P. O., Ekblom B., Royce J., Saltin B. Hemodynamic response to work with different muscle groups, sitting and supine. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jan;22(1):61–70. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


