Abstract
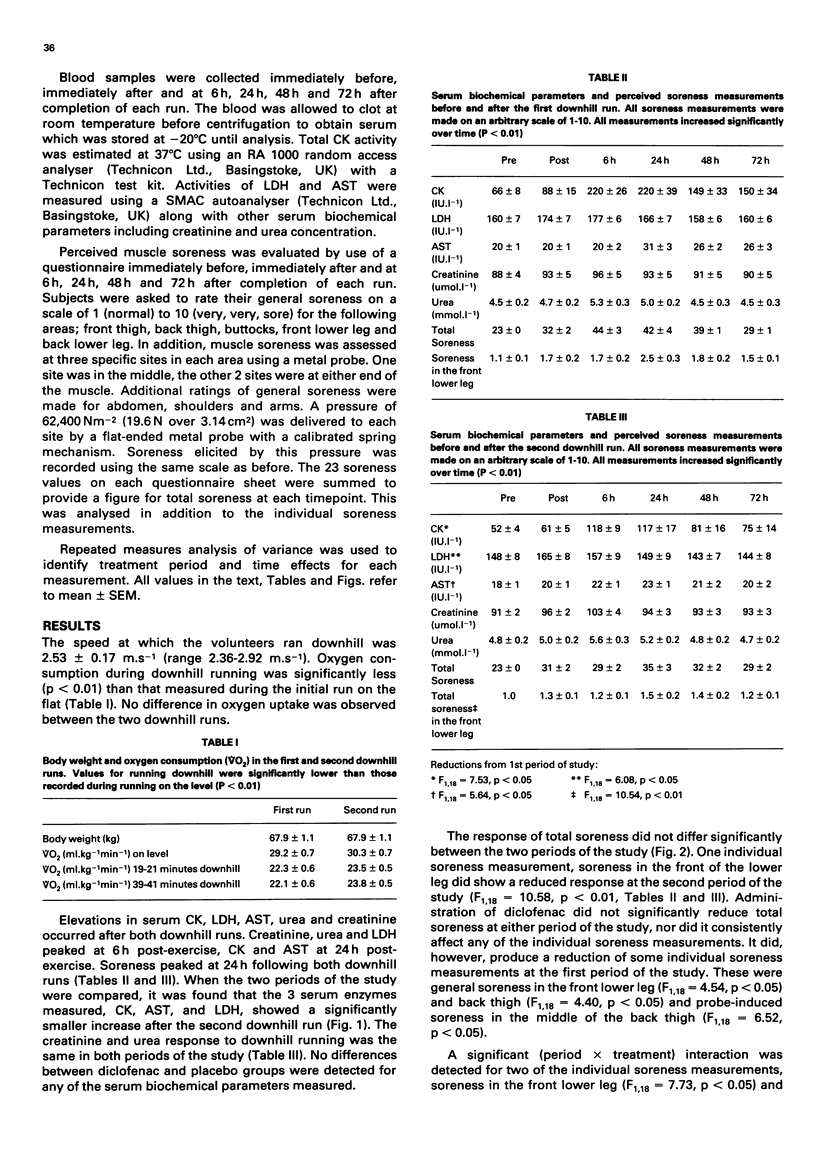
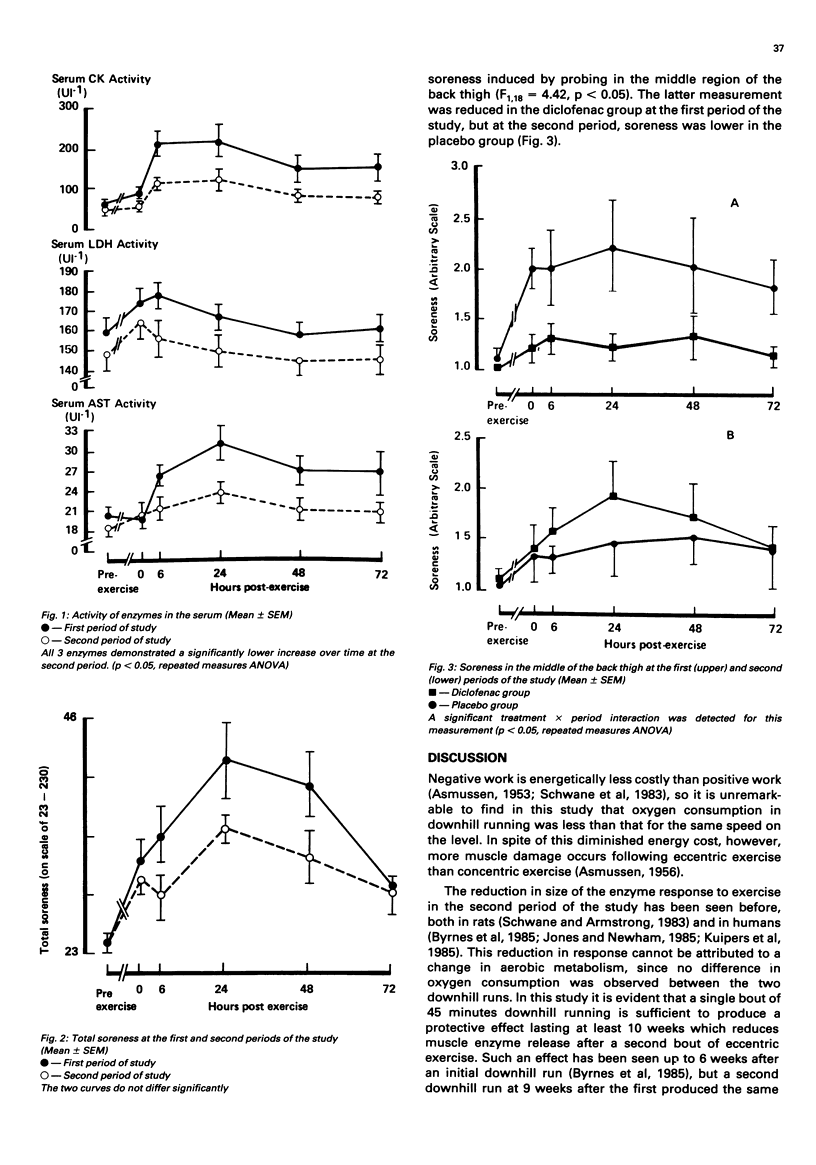
Twenty untrained male volunteers were required to run downhill for 45 minutes on a motor driven treadmill to induce muscle soreness. The volunteers took diclofenac or placebo before and for 72 hours after two runs 10 weeks apart, in a randomised double blind crossover design. Subjective soreness was assessed before and at intervals up to 72 hours after each run; venous blood samples, collected at the same time intervals, were used to estimate serum activities of creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase and aspartate aminotransferase and serum concentrations of creatinine and urea. Subjective soreness and the biochemical parameters increased after both runs, although the serum enzyme response to the second run was reduced. Diclofenac had no influence on the serum biochemical response to downhill running. Although overall soreness was not affected by diclofenac, individual soreness measurements were reduced by diclofenac at the first period of the study. These results suggest that diclofenac does not influence muscle damage, but may slightly reduce the associated soreness.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASMUSSEN E. Observations on experimental muscular soreness. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1956;2(2):109–116. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1956.2.issue-1-4.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASMUSSEN E. Positive and negative muscular work. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953;28(4):364–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes W. C., Clarkson P. M. Delayed onset muscle soreness and training. Clin Sports Med. 1986 Jul;5(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes W. C., Clarkson P. M., White J. S., Hsieh S. S., Frykman P. N., Maughan R. J. Delayed onset muscle soreness following repeated bouts of downhill running. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Sep;59(3):710–715. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.3.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohm G. L., Williams R. T., Kasperek G. J., van Rij A. M. Increased excretion of urea and N tau -methylhistidine by rats and humans after a bout of exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jan;52(1):27–33. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K. N., Bjerre-Knudsen J., Brodthagen U., Jordal R., Paulev P. E. Muscle cell leakage due to long distance training. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1982;48(2):177–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00422979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikida R. S., Staron R. S., Hagerman F. C., Sherman W. M., Costill D. L. Muscle fiber necrosis associated with human marathon runners. J Neurol Sci. 1983 May;59(2):185–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. A., Newham D. J., Round J. M., Tolfree S. E. Experimental human muscle damage: morphological changes in relation to other indices of damage. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:435–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers H., Keizer H. A., Verstappen F. T., Costill D. L. Influence of a prostaglandin-inhibiting drug on muscle soreness after eccentric work. Int J Sports Med. 1985 Dec;6(6):336–339. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Mills K. R., Quigley B. M., Edwards R. H. Pain and fatigue after concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jan;64(1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/cs0640055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refsum H. E., Strömme S. B. Urea and creatinine production and excretion in urine during and after prolonged heavy exercise. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 May;33(3):247–254. doi: 10.1080/00365517409082493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. H., Attwood E. C., Atkin G. E., Villar R. N. A study on the effects of severe repetitive exercise on serum myoglobin, creatine kinase, transaminases and lactate dehydrogenase. Q J Med. 1983 Spring;52(206):268–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Kihlström M. Protective effect of indomethacin against exercise-induced injuries in mouse skeletal muscle fibers. Int J Sports Med. 1987 Feb;8(1):46–49. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwane J. A., Armstrong R. B. Effect of training on skeletal muscle injury from downhill running in rats. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):969–975. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A., Critz J. B. The effect of prednisolone on the serum creatine phosphokinase response to exercise. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jul;128(3):716–720. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


