Abstract
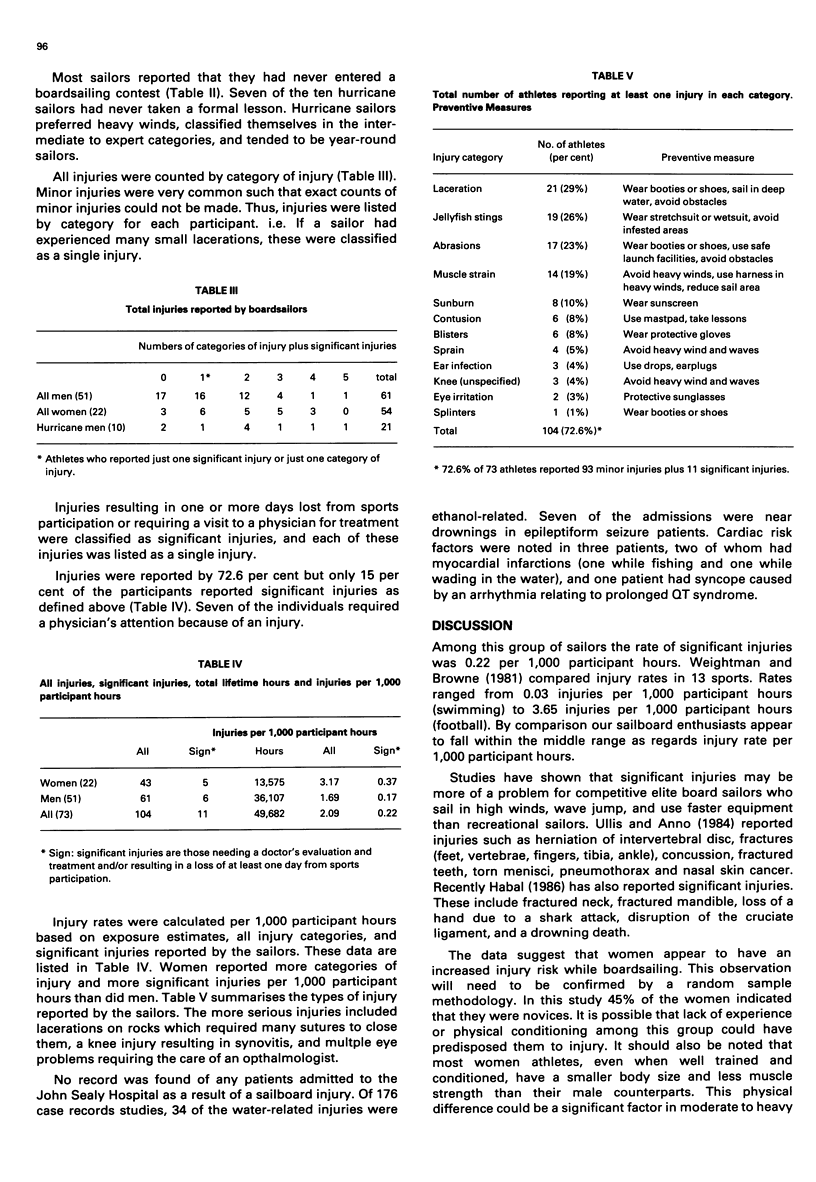
This study was carried out to determine the rate and types of injuries experienced by boardsailors. Results derive from: (a) a review of hospital medical records for water sports injuries, and (b) a questionnaire-interview of 73 athletes windsurfing on waters in the Galveston area during a hurricane and in moderate and light wind conditions. Windsurfers reported 0.22 injuries per 1,000 participant hours. Seventy-six per cent of athletes reported injuries while boardsailing, but only 15 per cent reported significant injuries. The most common reported injuries included lacerations, jellyfish stings, abrasions, muscle strain, sunburn, contusions, and blisters. A small number of athletes reported ligament sprain, ear infection, knee injury, eye injury, and splinters. The large majority of injuries reported are preventable by wearing protective gear, applying sunscreen, avoiding overpowering winds, and selecting safe sailing areas. Four per cent of water-sport injuries requiring hospitalisation resulted when epileptic water-sports participants had a seizure in or near the water.
Full text
PDF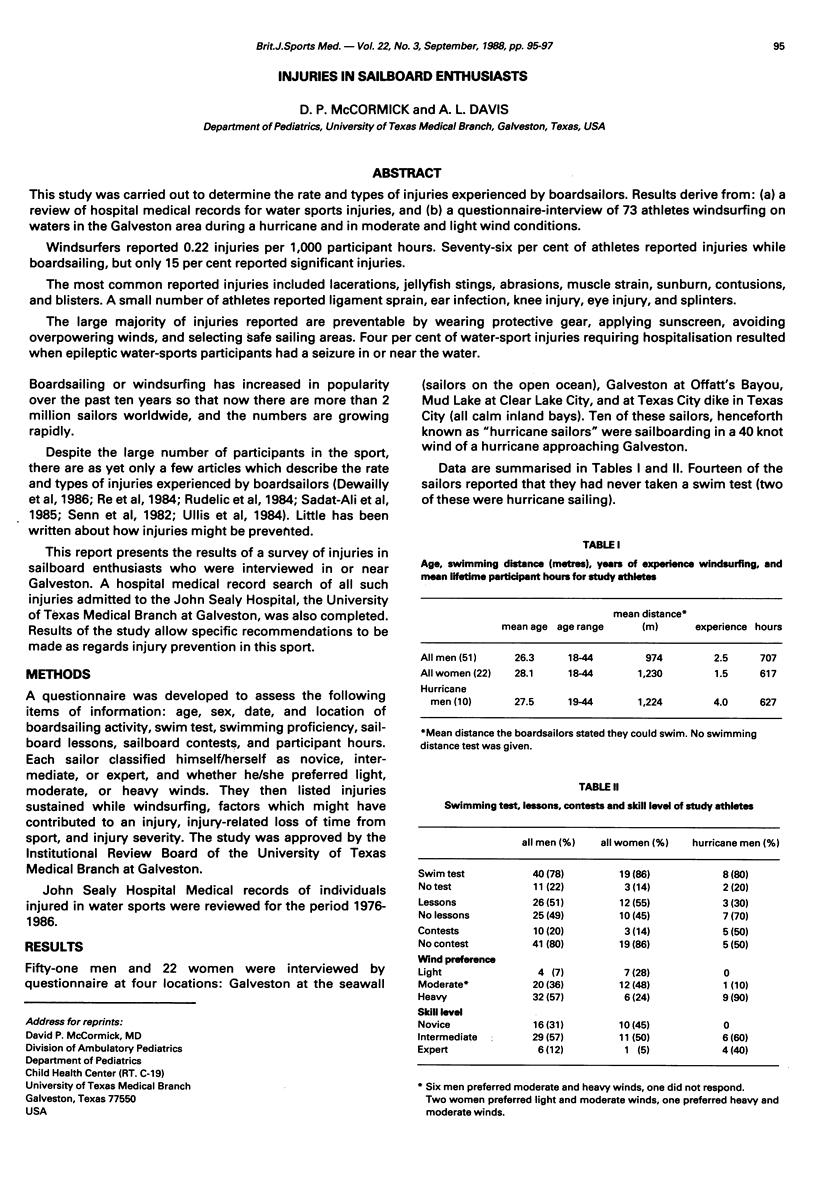

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cairns F. J., Koelmeyer T. D., Smeeton W. M. Deaths from drowning. N Z Med J. 1984 Feb 8;97(749):65–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHaven K. E., Lintner D. M. Athletic injuries: comparison by age, sport, and gender. Am J Sports Med. 1986 May-Jun;14(3):218–224. doi: 10.1177/036354658601400307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewailly E., Poirier C., Meyer F. M. Health hazards associated with windsurfing on polluted water. Am J Public Health. 1986 Jun;76(6):690–691. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.6.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habal M. B. Athletic injuries caused by the new sport of windsurfing and a proposed set of preventive measures. J Fla Med Assoc. 1986 Aug;73(8):609–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J. P., Rothner A. D., Lueders H. Submersion accidents in children with epilepsy. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Sep;136(9):777–780. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970450019004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re G., Borgogna E., Fogliano F., Scotto G. Patologia e traumatologia dento-maxillo-facciale nella pratica del nuoto subacqueo e del wind-surf. Minerva Stomatol. 1984 Mar-Apr;33(2):375–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudelić I., Rudelić E. Jedrenje na dasci i turisticka medicina. Lijec Vjesn. 1984 Nov-Dec;106(11-12):463–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadat-Ali M., Al-Awami S. M. Wind-surfing injury to axillary artery. Br J Sports Med. 1985 Sep;19(3):165–166. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.19.3.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senn E., Bandhauer K. Urethraverletzung beim Windsurfen. Schweiz Z Sportmed. 1982 Mar;30(1):18–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


