Abstract
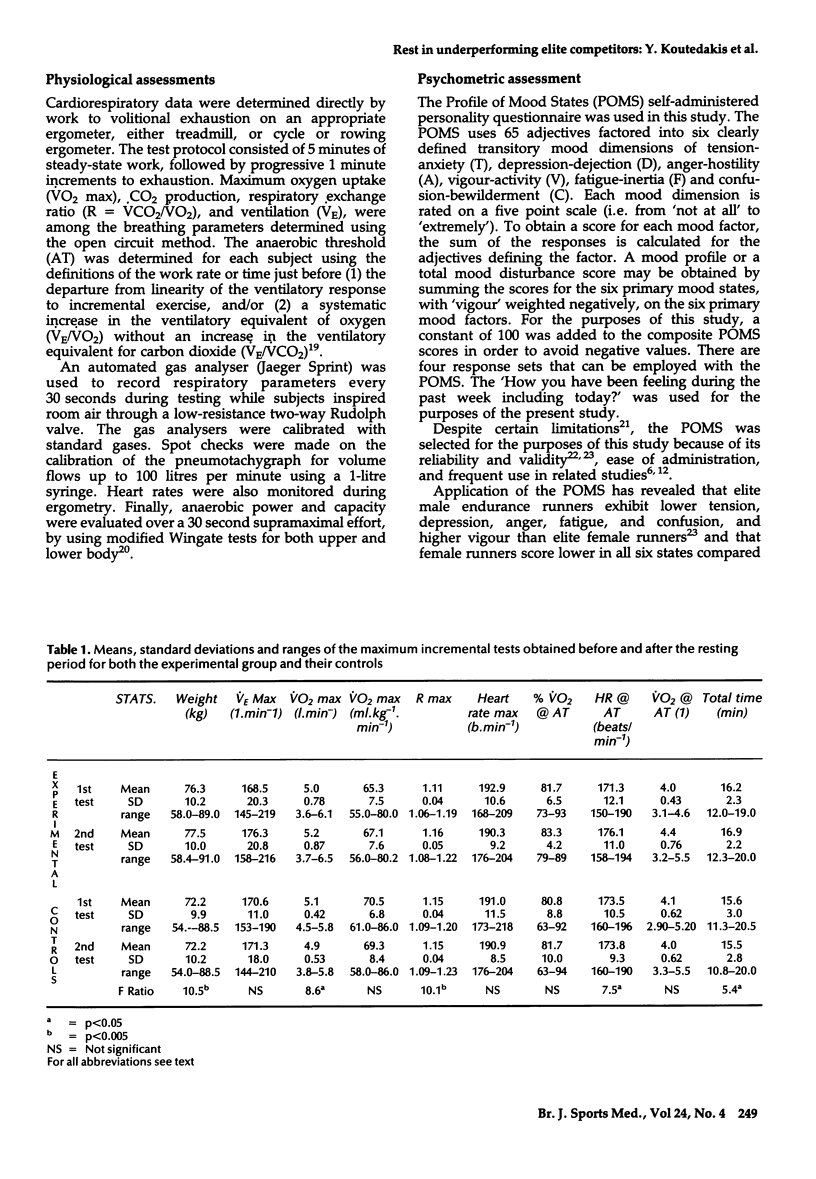
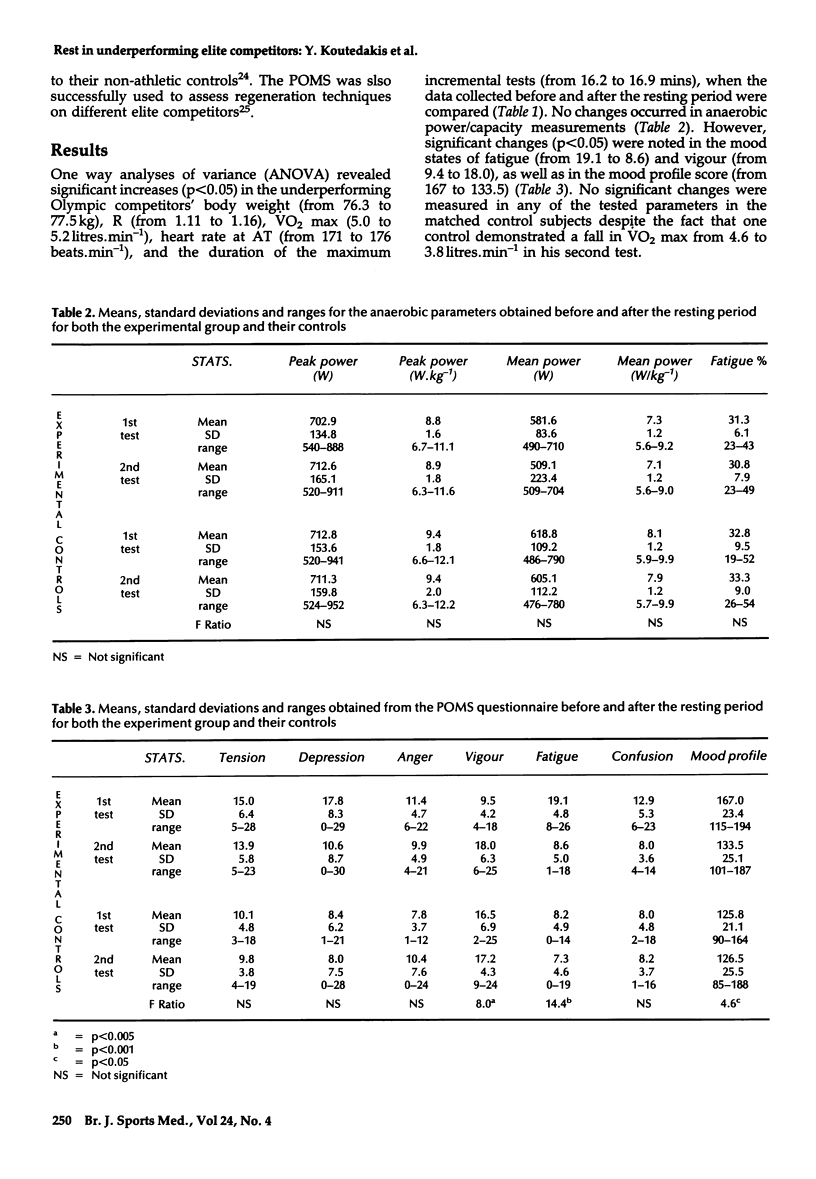
This study examines the effects of 3-5 weeks of physical rest on selected physical, physiological and psychological parameters obtained from 12 Olympic but latterly underperforming competitors and their matched control subjects. Cardiorespiratory data were directly determined from their work to volitional exhaustion on either a treadmill, cycle, or rowing ergometer. Anaerobic power and capacity were evaluated through modified Wingate tests. For psychometric assessments, the Profile of Mood States (POMS) was used. For the Olympic competitors, one-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) revealed significant increases (p less than 0.05) in body weight, maximum respiratory exchange ratio, maximum oxygen consumption, and heart rate at the anaerobic threshold, following the rest period. There was also a significant reduction in fatigue and mood profile score, and a significant increase in vigour. No significant changes were found in the matched control subjects. The present data show that resting for 3-5 weeks assists underperforming elite competitors to improve their aerobic performance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker G. H. Psychological factors and immunity. J Psychosom Res. 1987;31(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(87)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costill D. L., Flynn M. G., Kirwan J. P., Houmard J. A., Mitchell J. B., Thomas R., Park S. H. Effects of repeated days of intensified training on muscle glycogen and swimming performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988 Jun;20(3):249–254. doi: 10.1249/00005768-198806000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David A. S., Wessely S., Pelosi A. J. Postviral fatigue syndrome: time for a new approach. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Mar 5;296(6623):696–699. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6623.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. A., Bassett J., Hughes P., Gass G. C. Anaerobic threshold and lactate turnpoint. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1983;50(3):383–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00423244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier S. E., Nagy S. Mood state changes of women as a function of regular aerobic exercise. Percept Mot Skills. 1989 Feb;68(1):283–287. doi: 10.2466/pms.1989.68.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirwan J. P., Costill D. L., Flynn M. G., Mitchell J. B., Fink W. J., Neufer P. D., Houmard J. A. Physiological responses to successive days of intense training in competitive swimmers. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988 Jun;20(3):255–259. doi: 10.1249/00005768-198806000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutedakis Y., Sharp N. C. A modified Wingate test for measuring anaerobic work of the upper body in junior rowers. Br J Sports Med. 1986 Dec;20(4):153–156. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.20.4.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastro J. V., French R., Hall M. M. Test-retest reliability of the Profile of Mood States using visually impaired athletes. Percept Mot Skills. 1987 Oct;65(2):593–594. doi: 10.2466/pms.1987.65.2.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. P., Brown D. R., Raglin J. S., O'Connor P. J., Ellickson K. A. Psychological monitoring of overtraining and staleness. Br J Sports Med. 1987 Sep;21(3):107–114. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.21.3.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. P., Costill D. L., Flynn M. G., Raglin J. S., O'Connor P. J. Mood disturbance following increased training in swimmers. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988 Aug;20(4):408–414. doi: 10.1249/00005768-198808000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. P., O'Connor P. J., Sparling P. B., Pate R. R. Psychological characterization of the elite female distance runner. Int J Sports Med. 1987 Nov;8 (Suppl 2):124–131. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noakes T. D. Effect of exercise on serum enzyme activities in humans. Sports Med. 1987 Jul-Aug;4(4):245–267. doi: 10.2165/00007256-198704040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock M. L., Foster C., Knapp D., Rod J. L., Schmidt D. H. Effect of age and training on aerobic capacity and body composition of master athletes. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Feb;62(2):725–731. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.2.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes M. J., Cooper R. G., Edwards R. H. Normal muscle strength and fatigability in patients with effort syndromes. BMJ. 1988 Oct 22;297(6655):1014–1017. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6655.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


