Abstract
High-intensity eccentric contractions induce performance decrements and delayed onset muscle soreness. The purpose of this investigation was to study the magnitude and time course of such decrements and their interrelationships in 26 young women of mean(s.d.) age 21.4(3.3) years. Subjects performed 70 maximal eccentric contractions of the elbow flexors on a pulley system, specially designed for the study. The non-exercised arm acted as the control. Measures of soreness, tenderness, swelling (SW), relaxed elbow joint angle (RANG) and isometric strength (STR) were taken before exercise, immediately after exercise (AE), analysis of variance and at 24-h intervals for 11 days. There were significant (P < 0.01, analysis of variance) changes in all factors. Peak effects were observed between 24 and 96 h AE. With the exception of STR, which remained lower (P < 0.01), all variables returned to baseline levels by day 11. A non-significant correlation between pain and STR indicated that pain was not a major factor in strength loss. Also, although no pain was evident, RANG was decreased immediately AE. There was no relationship between SW, RANG and pain. The prolonged nature of these symptoms indicates that repair to damaged soft tissue is a slow process. Strength loss is considered particularly important as it continues when protective pain and tenderness have disappeared. This has implications for the therapeutic management of patients with myopathologies and those receiving eccentric exercise for rehabilitation.
Full text
PDF
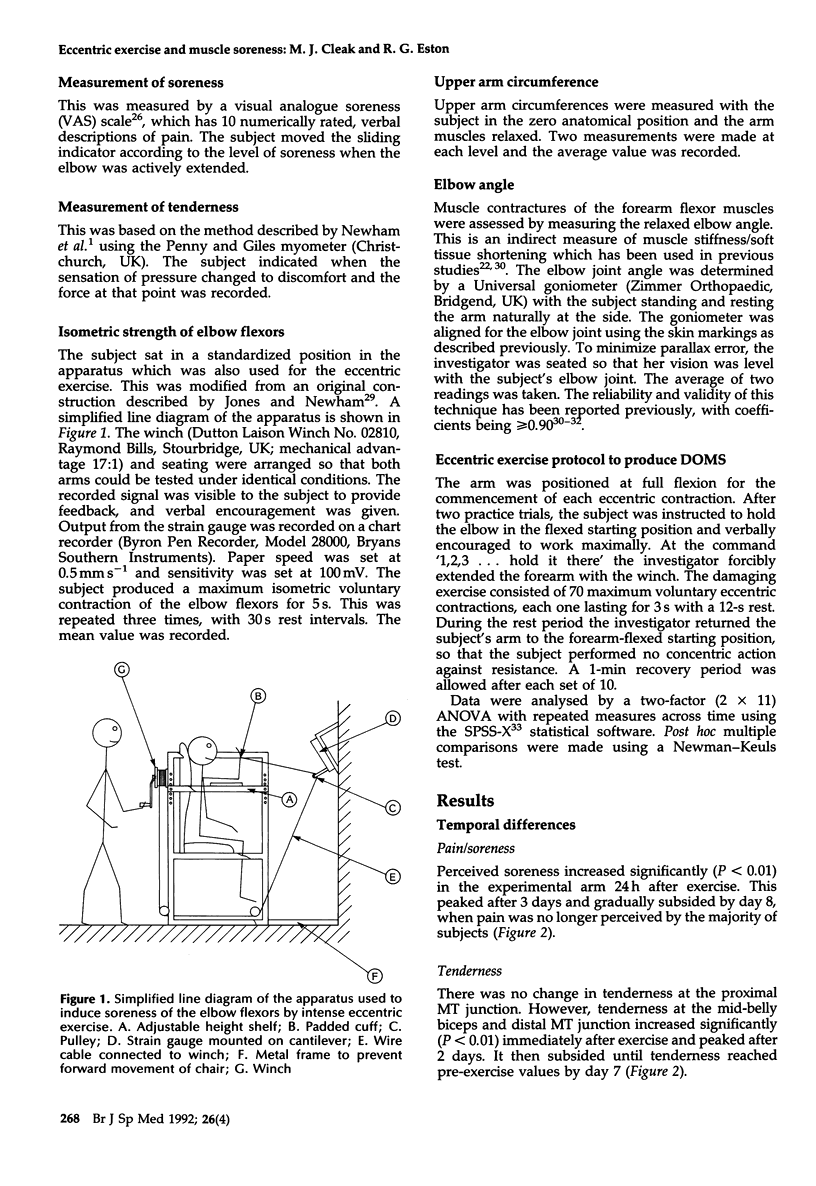
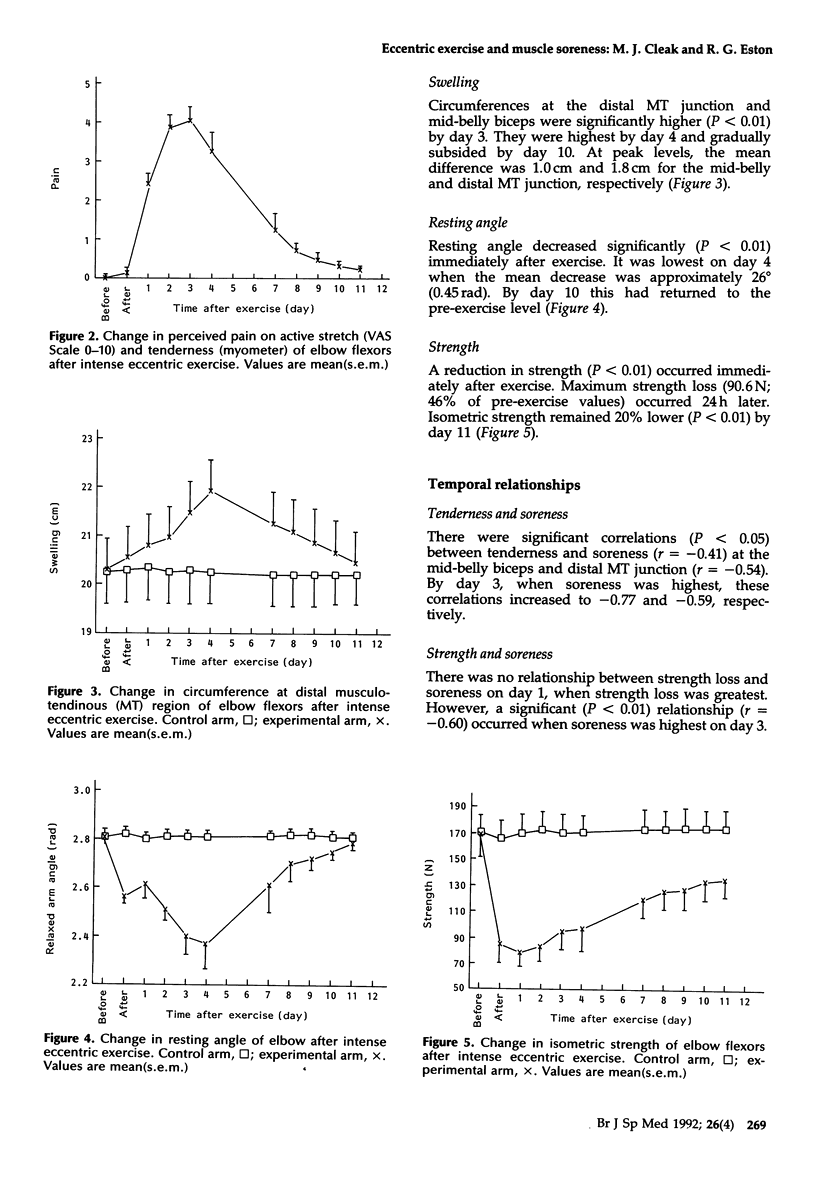



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASMUSSEN E. Observations on experimental muscular soreness. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1956;2(2):109–116. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1956.2.issue-1-4.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham W. M. Factors in delayed muscle soreness. Med Sci Sports. 1977 Spring;9(1):11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. B. Mechanisms of exercise-induced delayed onset muscular soreness: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1984 Dec;16(6):529–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobbert M. F., Hollander A. P., Huijing P. A. Factors in delayed onset muscular soreness of man. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1986 Feb;18(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody I. A. Muscle contracture induced by exercise. A syndrome attributable to decreased relaxing factor. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 24;281(4):187–192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907242810403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes W. C., Clarkson P. M. Delayed onset muscle soreness and training. Clin Sports Med. 1986 Jul;5(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey K. L. Neural mechanisms of pain: an overview. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1982;74:13–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1982.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson P. M., Tremblay I. Exercise-induced muscle damage, repair, and adaptation in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jul;65(1):1–6. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleak M. J., Eston R. G. Delayed onset muscle soreness: mechanisms and management. J Sports Sci. 1992 Aug;10(4):325–341. doi: 10.1080/02640419208729932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody F. W., Moore R. B., Richardson H. C. Patterns of activity evoked in cerebellar interpositus nuclear neurones by natural somatosensory stimuli in awake cats. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:1–20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. T., White M. J. Muscle weakness following eccentric work in man. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Dec;392(2):168–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00581267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. T., White M. J. Muscle weakness following eccentric work in man. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Dec;392(2):168–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00581267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbeling C. B., Clarkson P. M. Exercise-induced muscle damage and adaptation. Sports Med. 1989 Apr;7(4):207–234. doi: 10.2165/00007256-198907040-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish D. R., Wingate L. Sources of goniometric error at the elbow. Phys Ther. 1985 Nov;65(11):1666–1670. doi: 10.1093/ptj/65.11.1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Seger J., Ekblom B. Sublethal muscle fibre injuries after high-tension anaerobic exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1988;57(3):360–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00635996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Sfakianos P. N., Hargens A. R. Muscle soreness and intramuscular fluid pressure: comparison between eccentric and concentric load. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Dec;61(6):2175–2179. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.6.2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Sjöström M., Ekblom B. A morphological study of delayed muscle soreness. Experientia. 1981 May 15;37(5):506–507. doi: 10.1007/BF01986165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Sjöström M., Ekblom B. Myofibrillar damage following intense eccentric exercise in man. Int J Sports Med. 1983 Aug;4(3):170–176. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1026030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdosik R. L., Bohannon R. W. Clinical measurement of range of motion. Review of goniometry emphasizing reliability and validity. Phys Ther. 1987 Dec;67(12):1867–1872. doi: 10.1093/ptj/67.12.1867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell J. N., Chila A. G., Ford G., David D., Gates T. An electromyographic study of elbow motion during postexercise muscle soreness. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 May;58(5):1713–1718. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.5.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. A., Newham D. J., Clarkson P. M. Skeletal muscle stiffness and pain following eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Pain. 1987 Aug;30(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)91079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuttgen H. G. Human performance in high-intensity exercise with concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Int J Sports Med. 1986 Jun;7 (Suppl 1):6–9. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komi P. V., Buskirk E. R. Effect of eccentric and concentric muscle conditioning on tension and electrical activity of human muscle. Ergonomics. 1972 Jul;15(4):417–434. doi: 10.1080/00140137208924444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Jones D. A., Clarkson P. M. Repeated high-force eccentric exercise: effects on muscle pain and damage. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1381–1386. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Jones D. A., Clarkson P. M. Repeated high-force eccentric exercise: effects on muscle pain and damage. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1381–1386. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Jones D. A., Edwards R. H. Large delayed plasma creatine kinase changes after stepping exercise. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Jun;6(5):380–385. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Jones D. A., Ghosh G., Aurora P. Muscle fatigue and pain after eccentric contractions at long and short length. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 May;74(5):553–557. doi: 10.1042/cs0740553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Jones D. A., Tolfree S. E., Edwards R. H. Skeletal muscle damage: a study of isotope uptake, enzyme efflux and pain after stepping. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1986;55(1):106–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00422903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., McPhail G., Mills K. R., Edwards R. H. Ultrastructural changes after concentric and eccentric contractions of human muscle. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Sep;61(1):109–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Mills K. R., Quigley B. M., Edwards R. H. Pain and fatigue after concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jan;64(1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/cs0640055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J. The consequences of eccentric contractions and their relationship to delayed onset muscle pain. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1988;57(3):353–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00635995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosaka K., Clarkson P. M., McGuiggin M. E., Byrne J. M. Time course of muscle adaptation after high force eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1991;63(1):70–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00760804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly K. P., Warhol M. J., Fielding R. A., Frontera W. R., Meredith C. N., Evans W. J. Eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage impairs muscle glycogen repletion. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jul;63(1):252–256. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.1.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers K. L., Berger R. A. Motor-unit involvement and tension during maximum, voluntary concentric, eccentric, and isometric contractions of the elbow flexors. Med Sci Sports. 1974 Winter;6(4):253–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talag T. S. Residual muscular soreness as influenced by concentric, eccentric, and static contractions. Res Q. 1973 Dec;44(4):458–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiidus P. M., Ianuzzo C. D. Effects of intensity and duration of muscular exercise on delayed soreness and serum enzyme activities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1983;15(6):461–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yackzan L., Adams C., Francis K. T. The effects of ice massage on delayed muscle soreness. Am J Sports Med. 1984 Mar-Apr;12(2):159–165. doi: 10.1177/036354658401200214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



